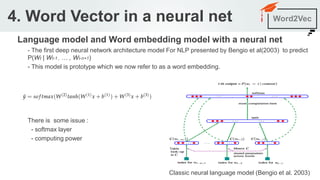
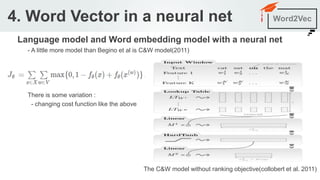
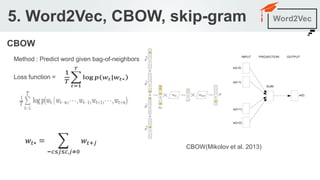
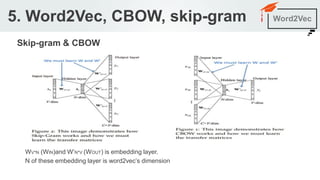
The document outlines a seminar agenda on word embeddings, focusing on Word2Vec and its comparison with models like GloVe. It details the architecture of neural networks for language modeling, including the continuous bag-of-words (CBOW) and skip-gram methods, as well as techniques for representing words through co-occurrence probabilities. Additionally, it references several resources for further learning in natural language processing.




![One-hot representation
Dim = |V| (v is the size of vocabulary)
- motel
- hotel
If you search for [Seattle motel] key word, we want the search engine to match web page containing
“Seattle hotel”
Similarity(motal, hotel) = 0
motel
hotel = 0
If we do inner product with the above vectors, we can not find out similarity between words
2. Word2Vec Word2Vec
T](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/word2vec-171109061918-181014084333/85/Word2Vec-5-320.jpg)
![Co-occurrence matrix
Let’s see window based co-occurrence matrix
- Example Corpus :
- I like deep learning.
- I like NLP.
- I enjoy flying.
Total vocabulary size(|V|) = 8
Vector(“I”) = [0, 2, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
Vector(“like”) = [2, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0 , 0] …
2. Word2Vec Word2Vec](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/word2vec-171109061918-181014084333/85/Word2Vec-6-320.jpg)










![Word Analogies with Word2Vec
[king] – [man] + [woman] ≈ [queen]
5. Word2Vec, CBOW, skip-gram Word2Vec](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/word2vec-171109061918-181014084333/85/Word2Vec-21-320.jpg)
![Word Analogies with Word2Vec
[king] – [man] + [woman] ≈ [queen]
5. Word2Vec, CBOW, skip-gram Word2Vec](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/word2vec-171109061918-181014084333/85/Word2Vec-22-320.jpg)