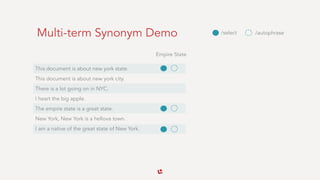
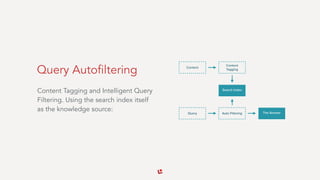
The document discusses the complexities of semantic search and the languages used in search applications, emphasizing the importance of understanding language at the semantic level to improve search quality. It outlines key requirements for effective search systems, including performance, accuracy, precision, and user experience, and presents various techniques like autophrasing and query autofiltering to enhance search results. Additionally, it highlights challenges with handling unstructured text and the role of machine learning and classification technologies in improving search outcomes.