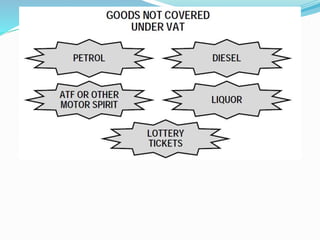
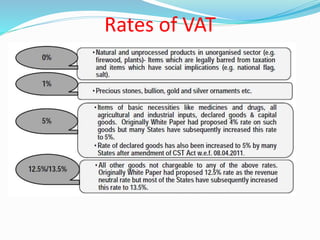
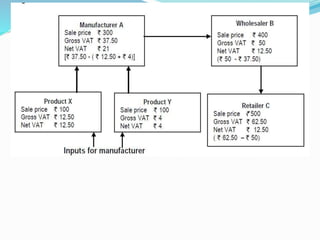
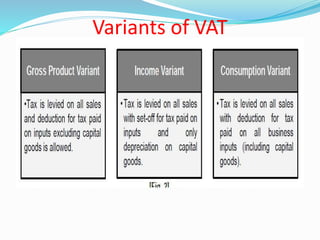
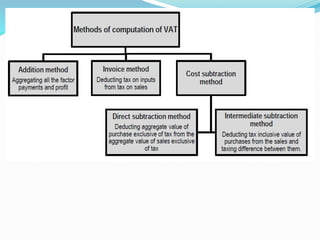
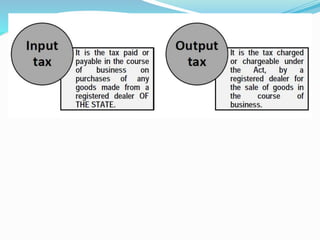
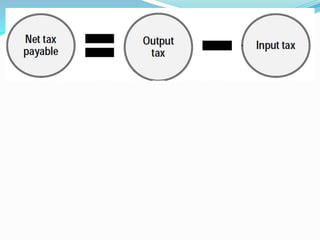
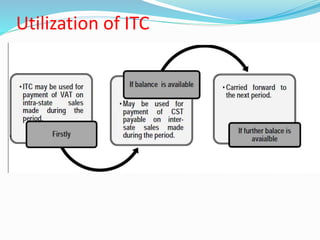
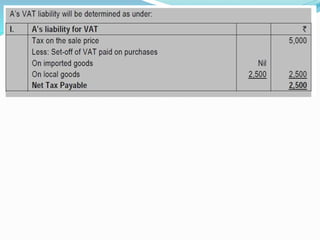
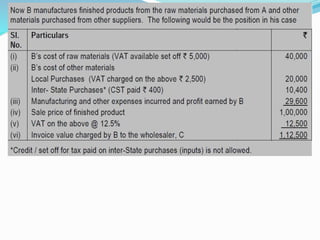
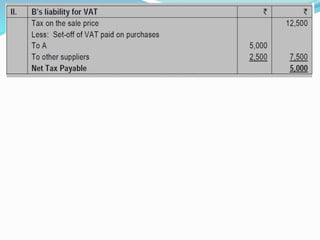
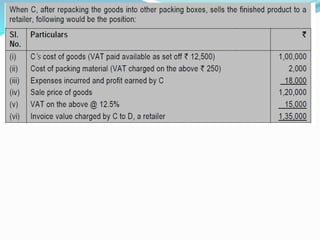
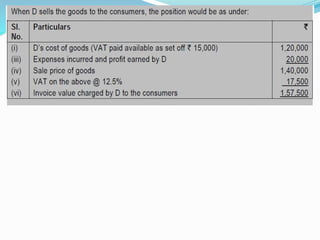
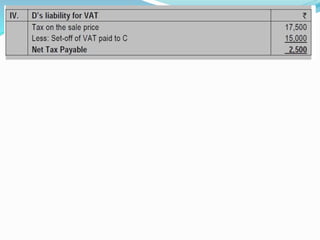
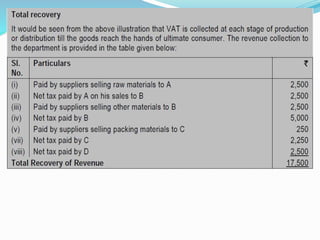
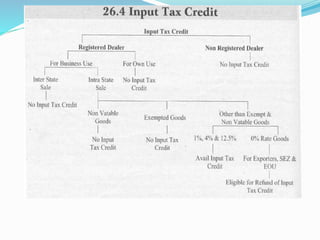
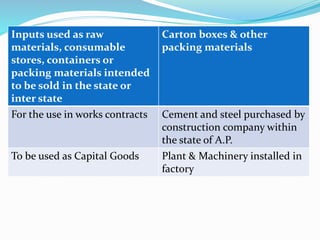
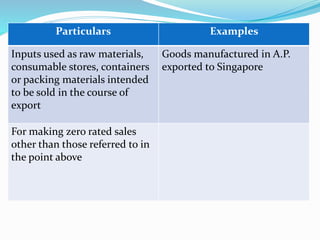
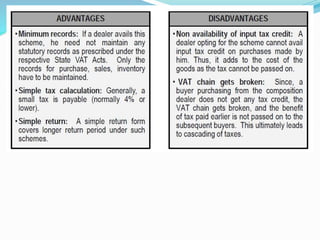
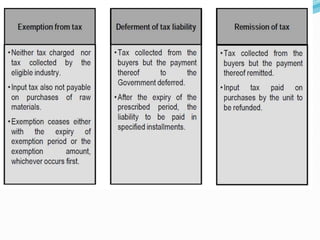
Value Added Tax (VAT) is a multi-stage tax levied on value addition at each stage of sale. It provides input tax credit which eliminates cascading of taxes and double taxation. VAT aims to prevent trade distortions, ensure equitable tax distribution, and promote transparency through self-assessment. It is calculated using the invoice method, subtraction method, or addition method depending on the variant of VAT. Registered dealers are eligible for input tax credit subject to certain conditions.