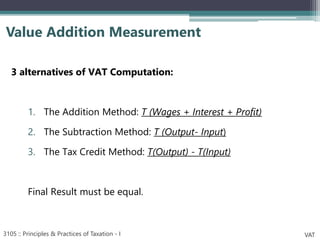
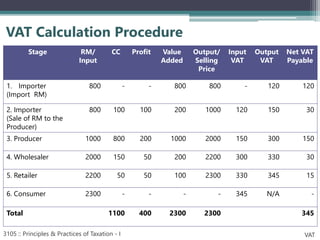
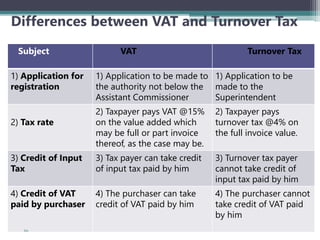
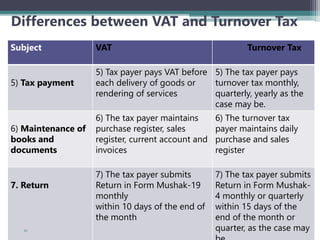
VAT is an indirect tax applied at each stage of production and distribution of goods and services, with taxpayers able to claim a credit for VAT paid on inputs. It is ultimately borne by the final consumer. Key characteristics of VAT include that it is charged on value addition at each stage, has various rates including zero-rating, and exemptions. VAT aims to broaden the tax base and mobilize more revenue, while eliminating cascading effects of taxes. The document outlines definitions, persons liable, determination of value, payment and adjustment of advance tax, and time of payment under Bangladesh's VAT law.










![Some features of VAT
Tax Base for VAT:
Import Stage
Customs Assessable Value + Customs duty +
Supplementary Duty
Domestic/Local Stage:
a) Goods (manufacturing): [Production cost + Profit
and Commission (if any) + Supplementary duty (if any)]
b) Services: [total receipts excluding VAT but
including supplementary duty (if any)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vatpart1-170806080015/85/Value-added-tax-12-320.jpg)