This document provides information about value-added tax (VAT) in India, including:
1) VAT was introduced in India in 2005 to replace sales taxes and eliminate double taxation. It is now implemented across all Indian states except three.
2) VAT is charged on the value added at each stage of production and distribution. It aims to reduce the cascading effect of taxes.
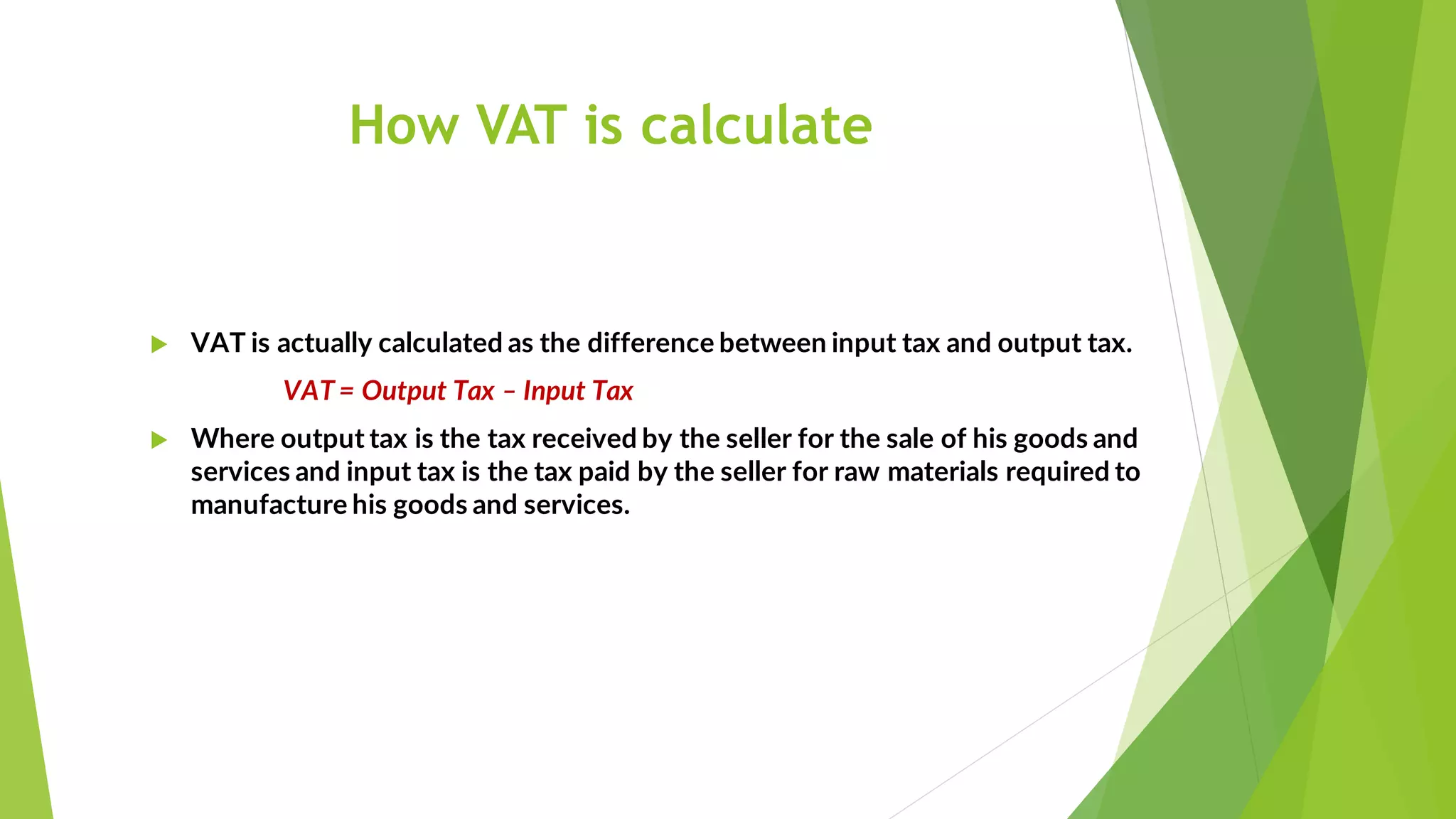
3) VAT is calculated as the difference between output tax (tax collected on sales) and input tax (tax paid on purchases). Maintaining purchase and sales invoices is important for accurate VAT calculation.