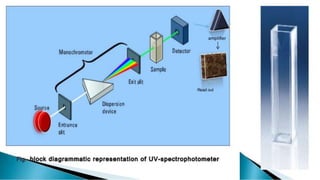
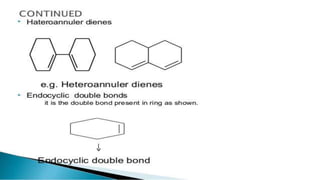
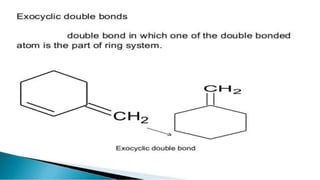
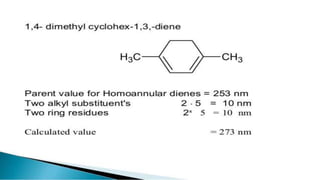
Uv absorption spectra arise from electronic transitions in molecules where electrons move from lower to higher energy levels. The amount of energy absorbed is proportional to the concentration of the solution based on Beer-Lambert's law. Uv-visible spectroscopy can be used to determine structural information about organic compounds, identify additional impurities, and perform quantitative analysis of compounds that absorb uv radiation.