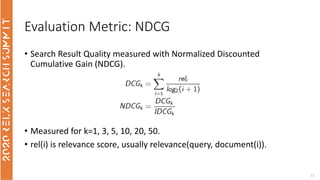
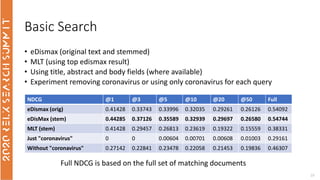
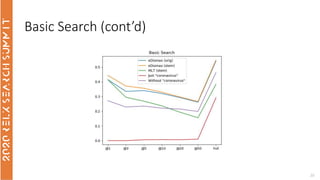
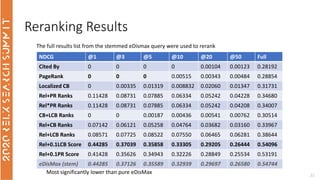
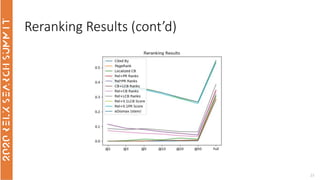
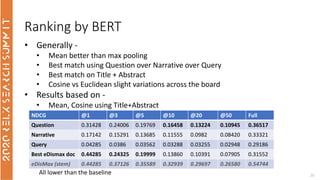
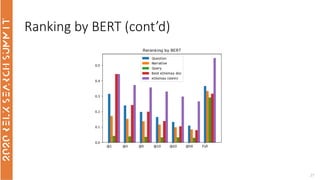
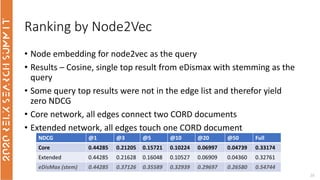
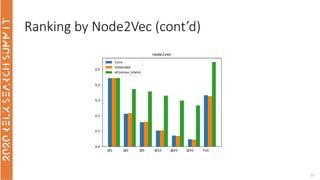
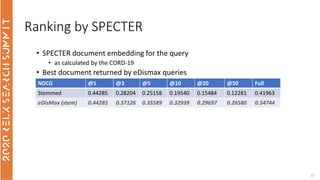
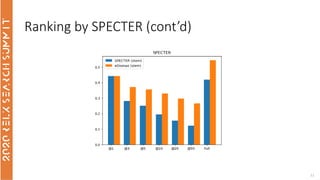
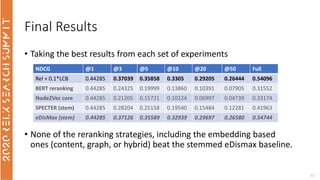
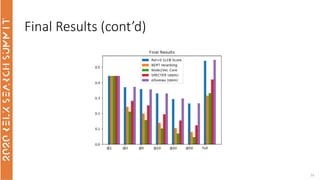
The document discusses the use of term-based, vector-based, and graph-based search methods for information retrieval, comparing their effectiveness through experiments and results. It evaluates various reranking strategies using metrics such as normalized discounted cumulative gain (ndcg) to assess different approaches on the scopus dataset. The findings indicate that while edismax serves as a reliable baseline, more advanced techniques including embedding methods did not outperform this baseline, suggesting areas for future research.