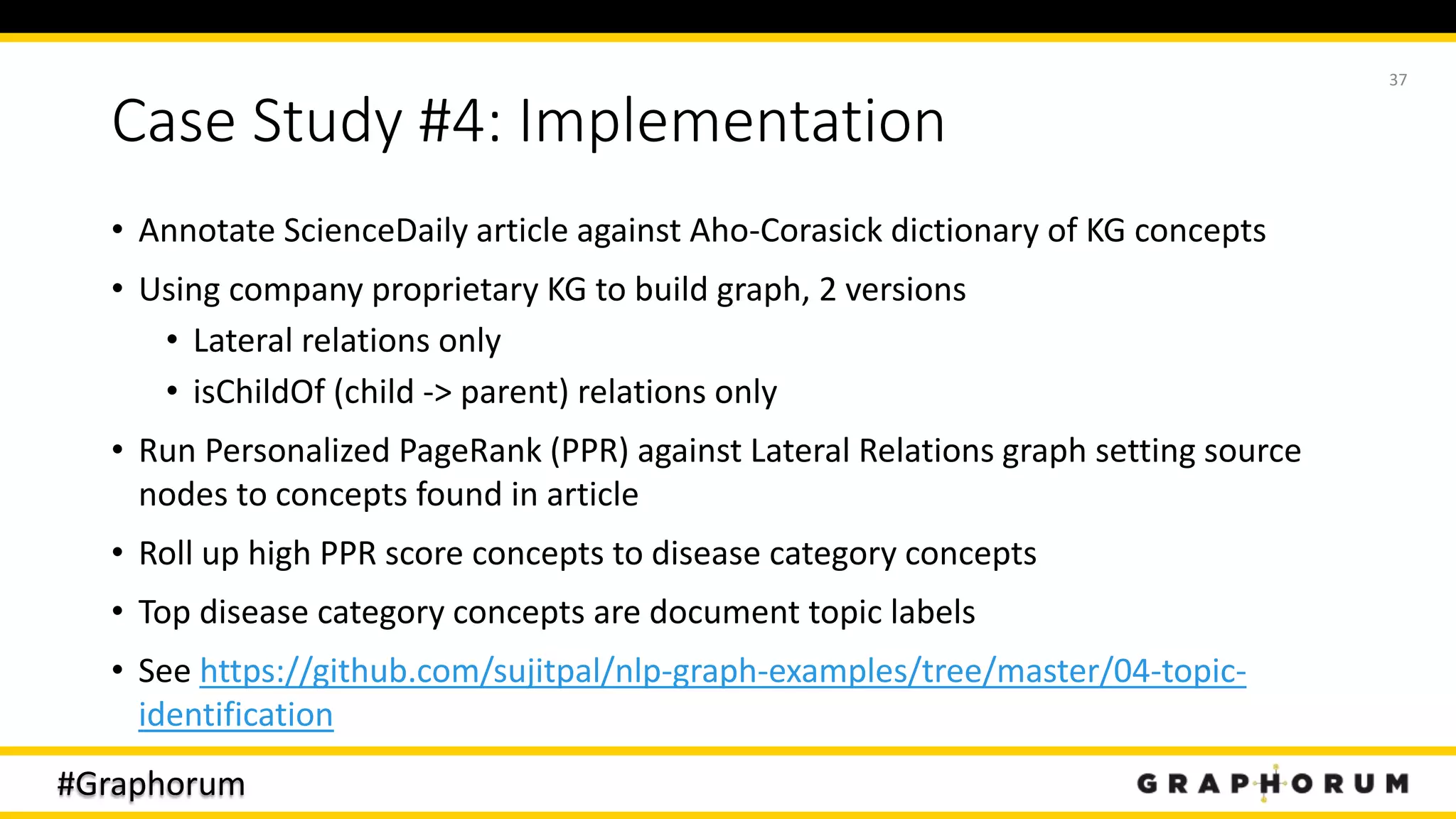
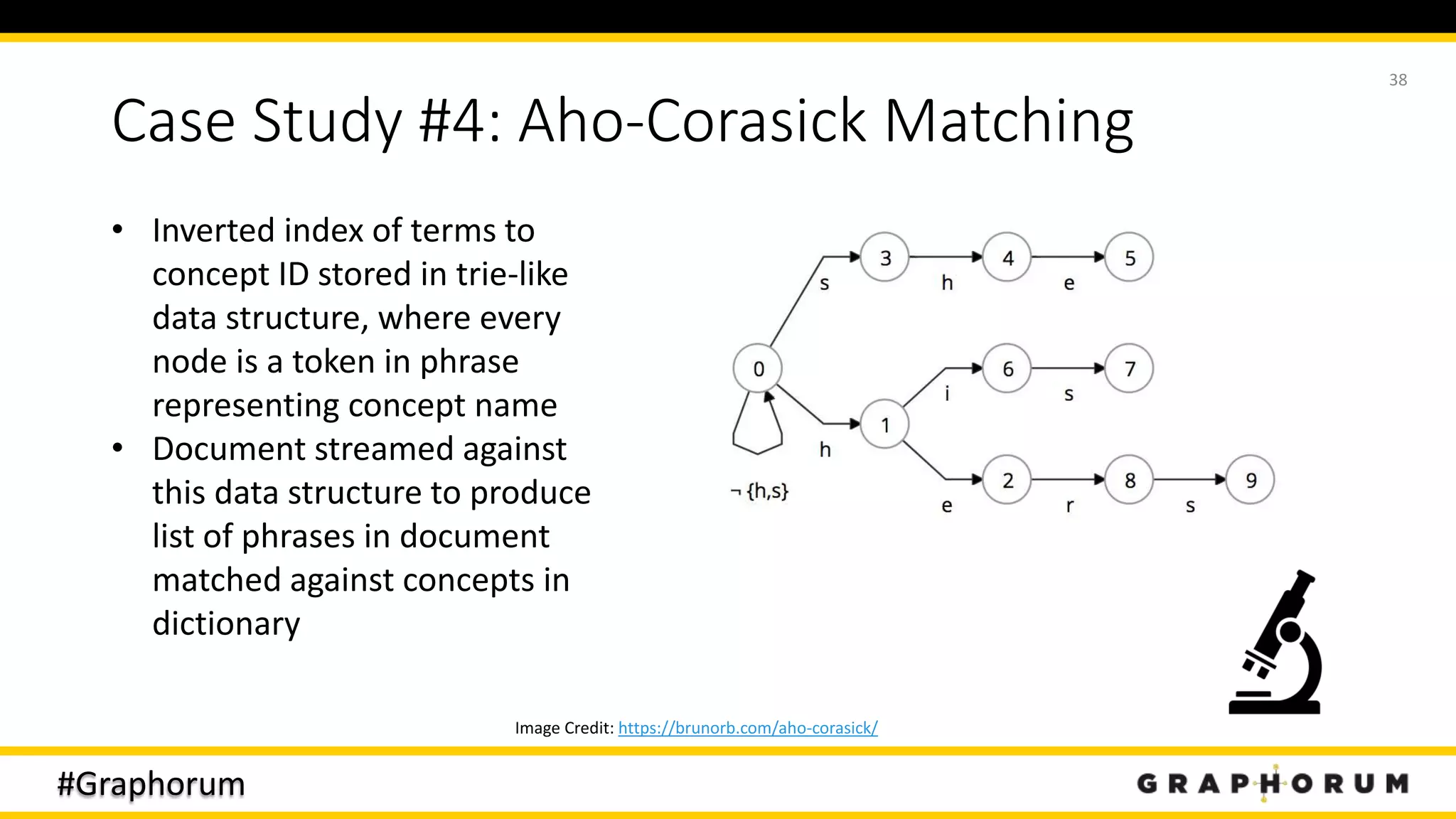
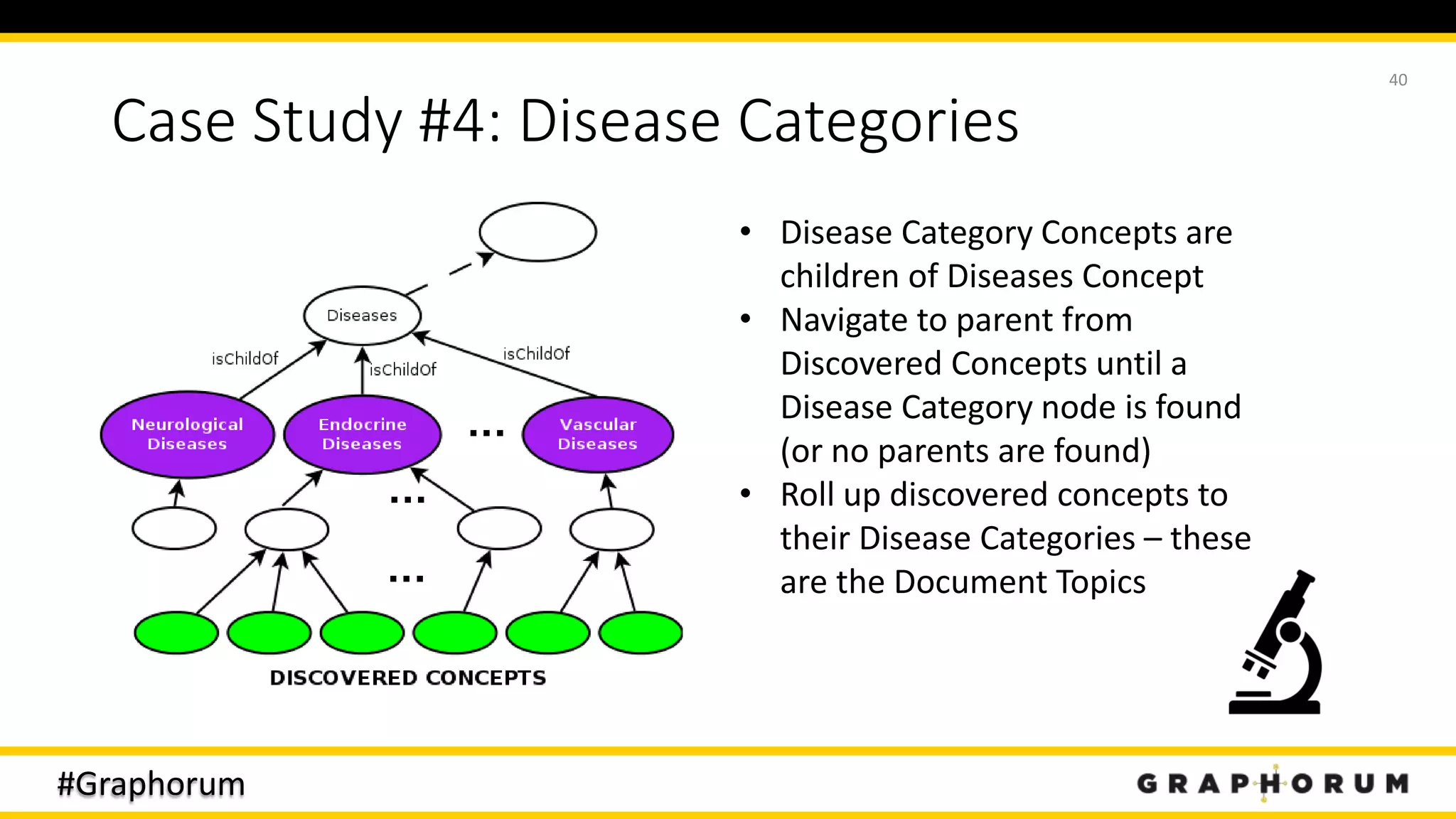
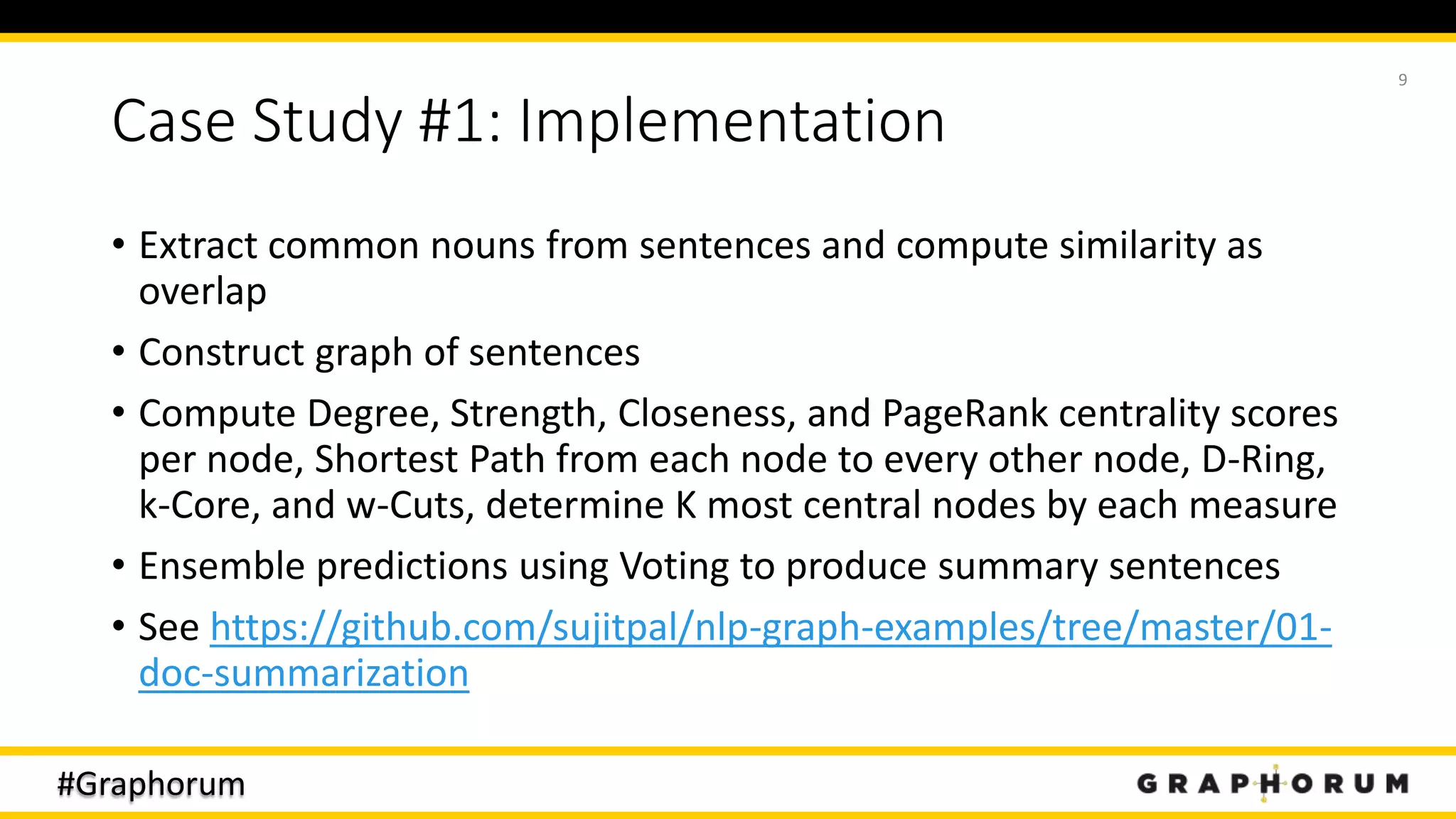
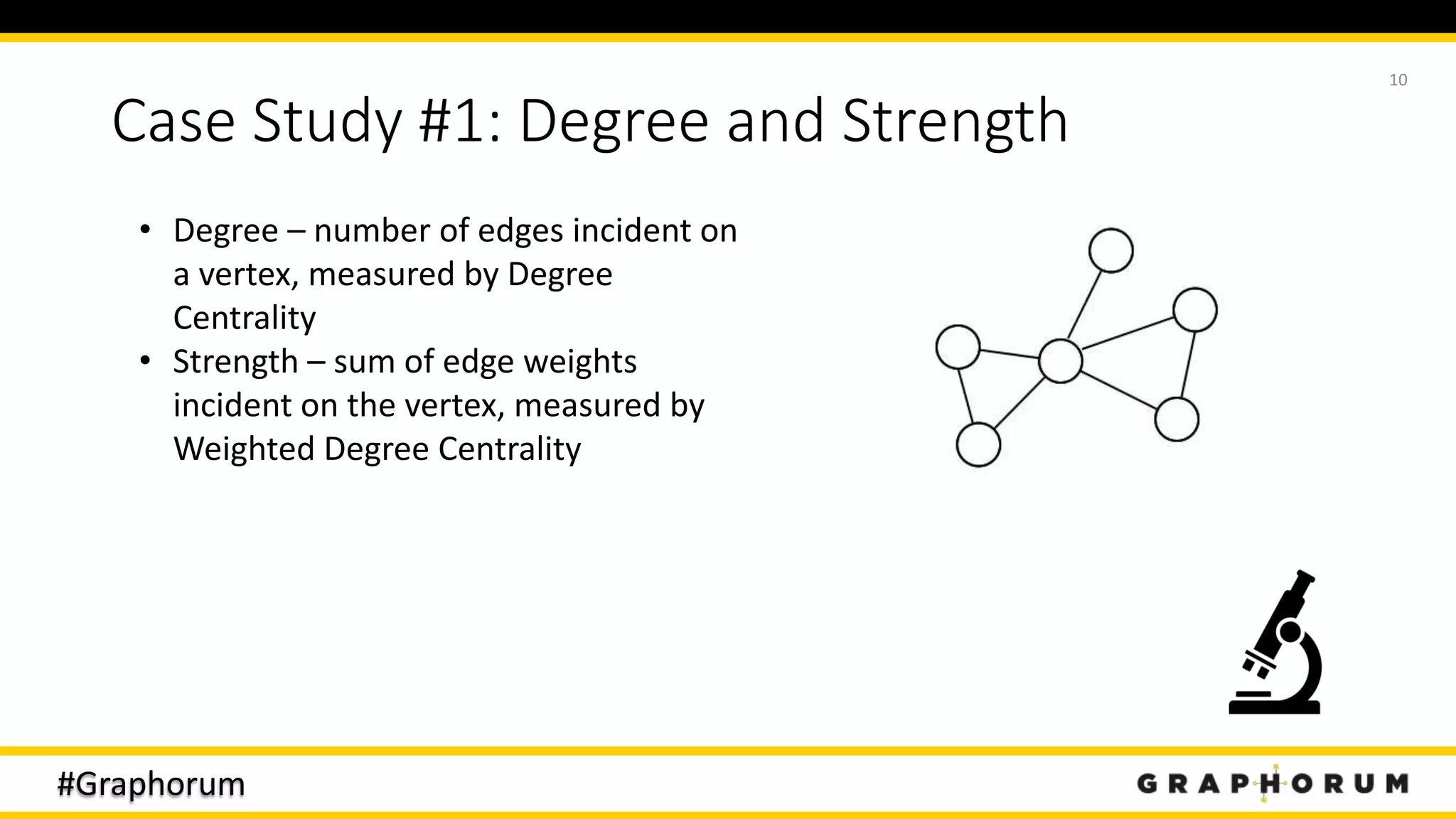
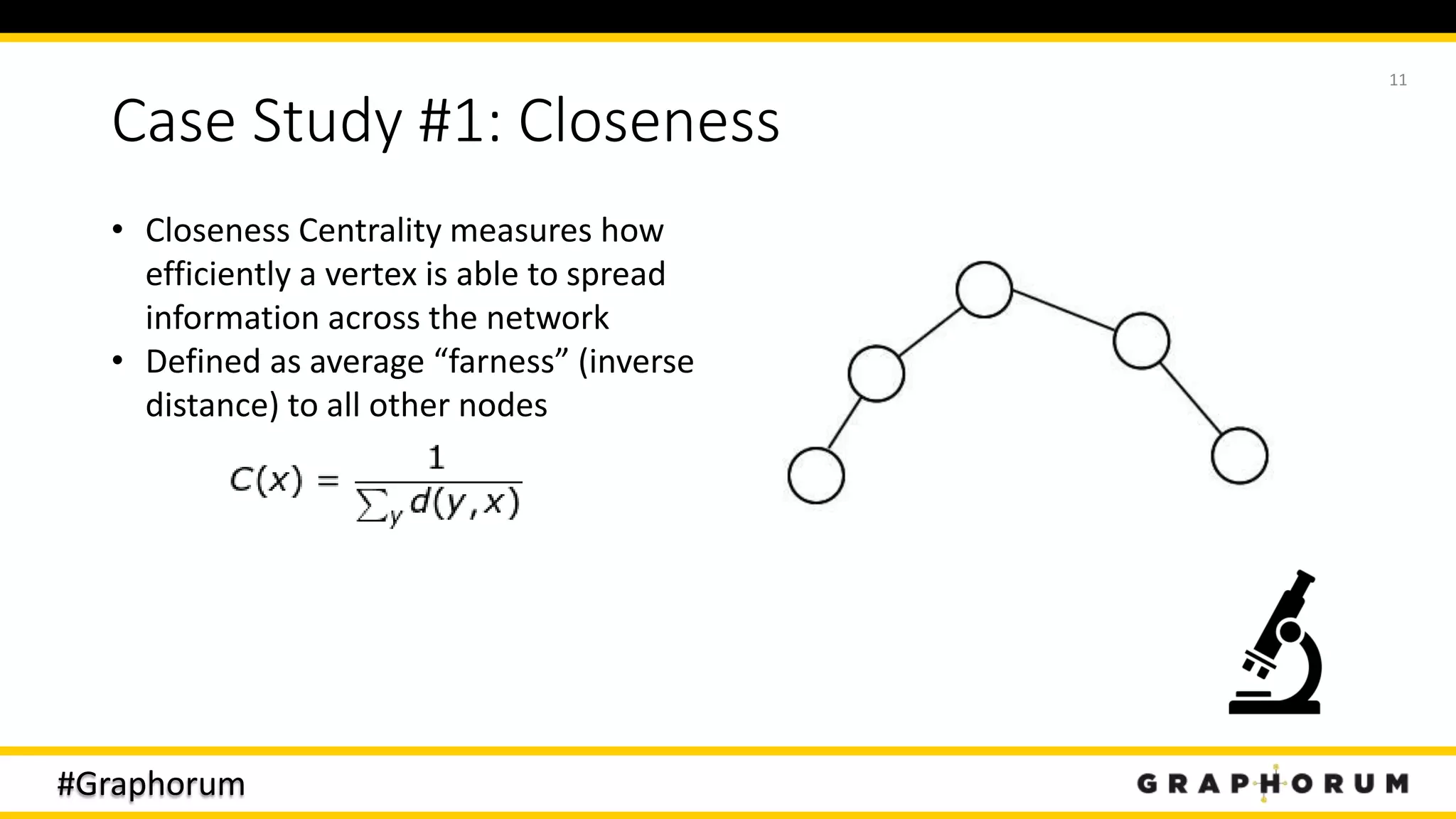
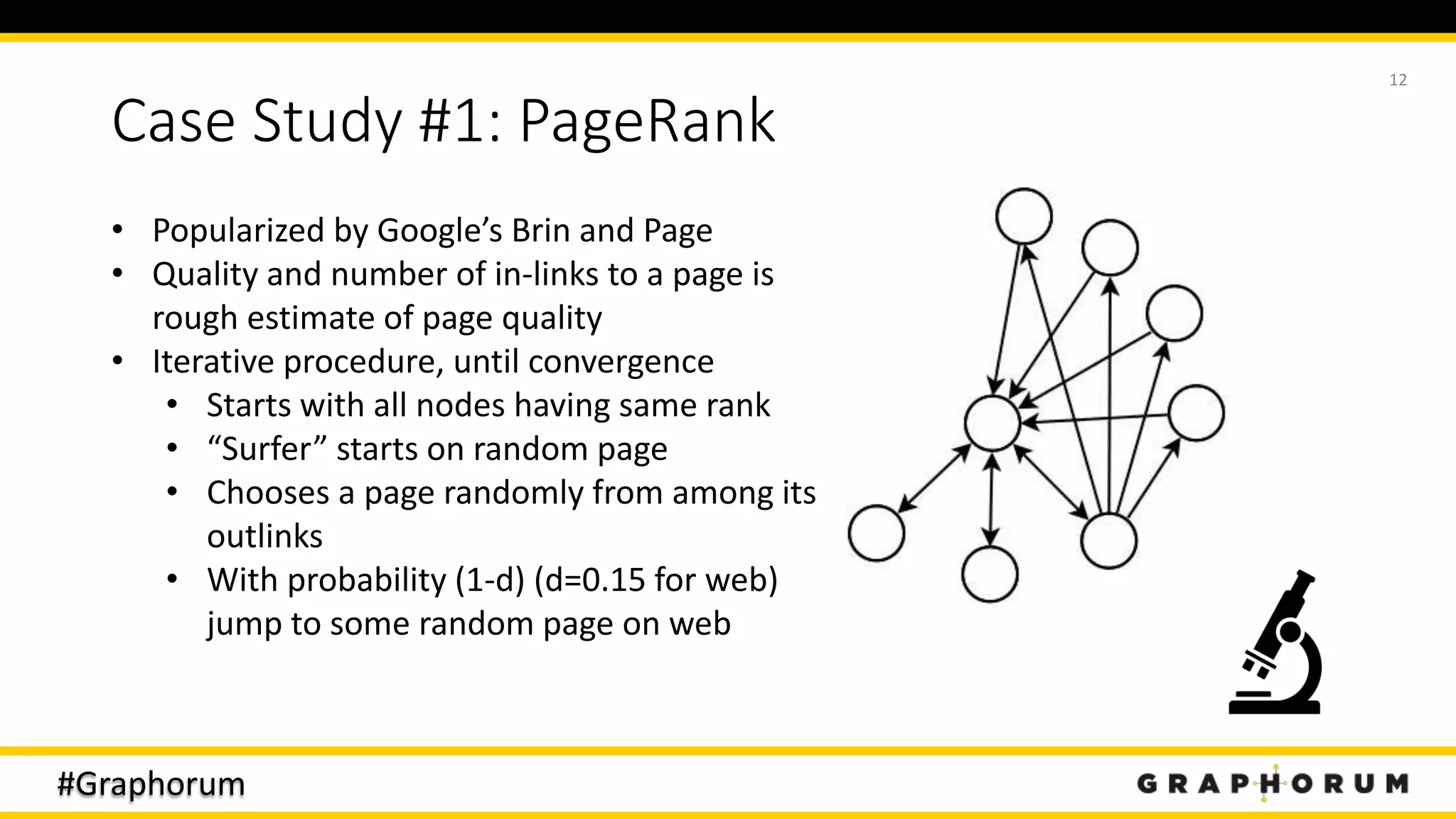
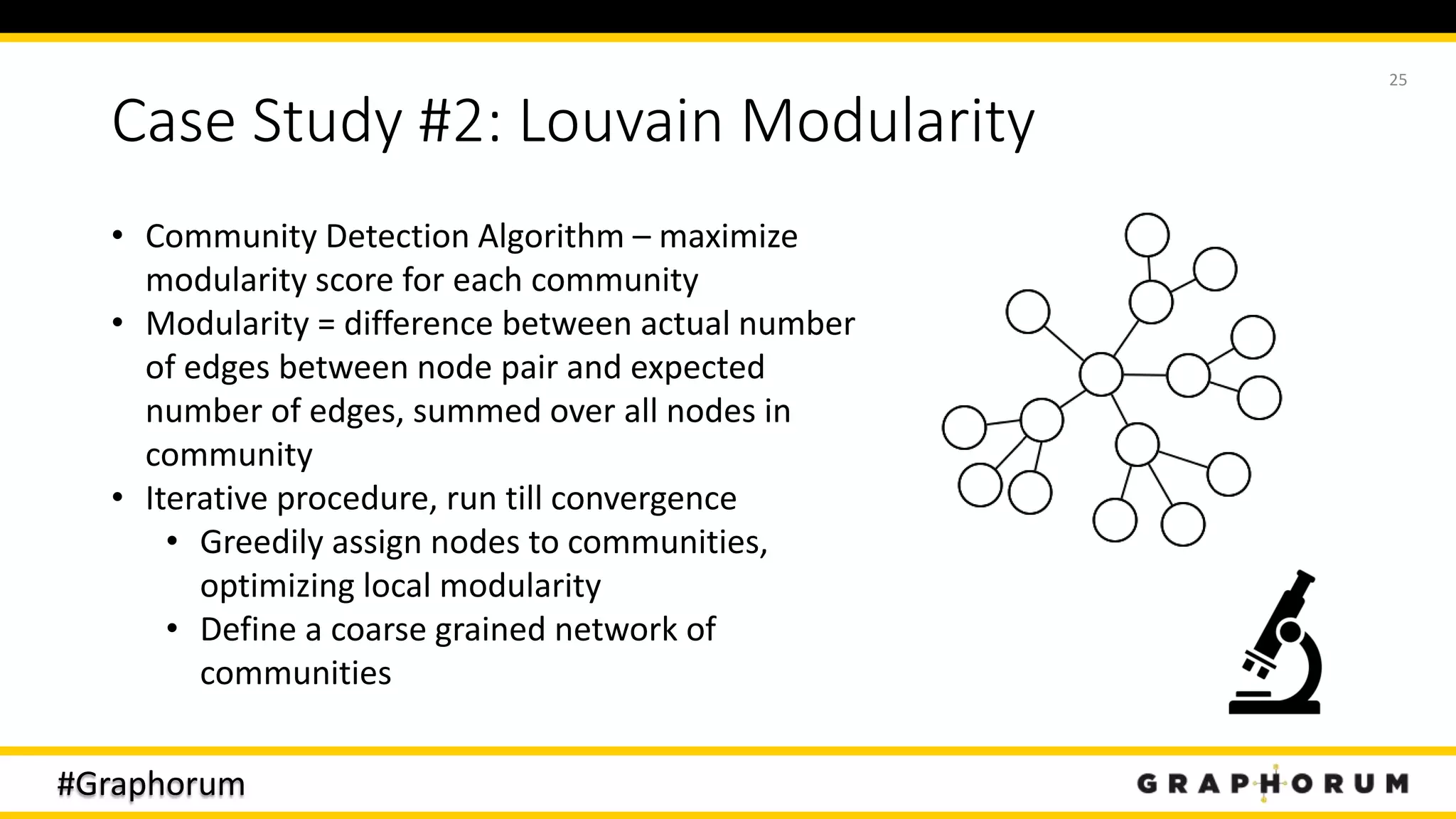
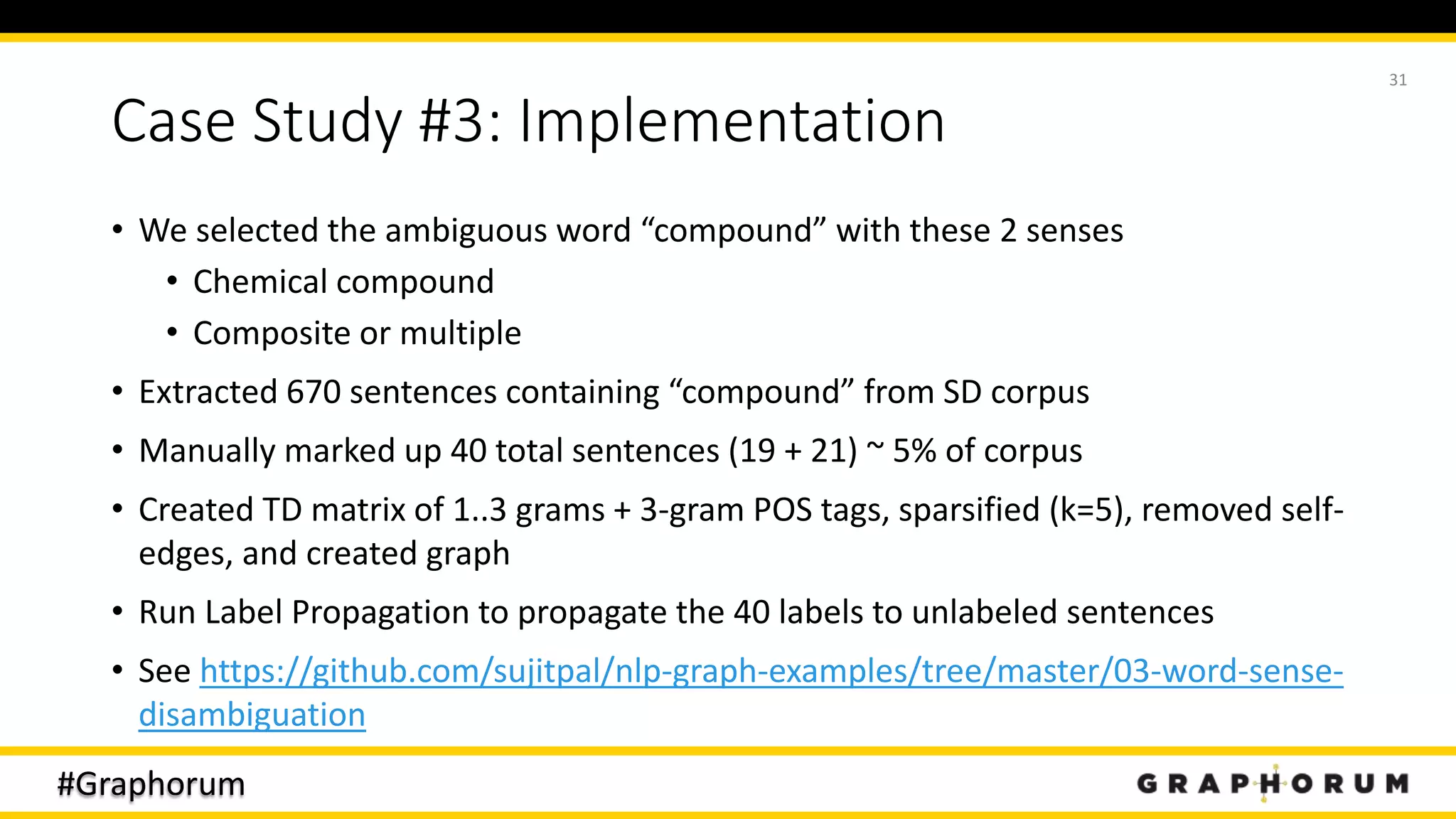
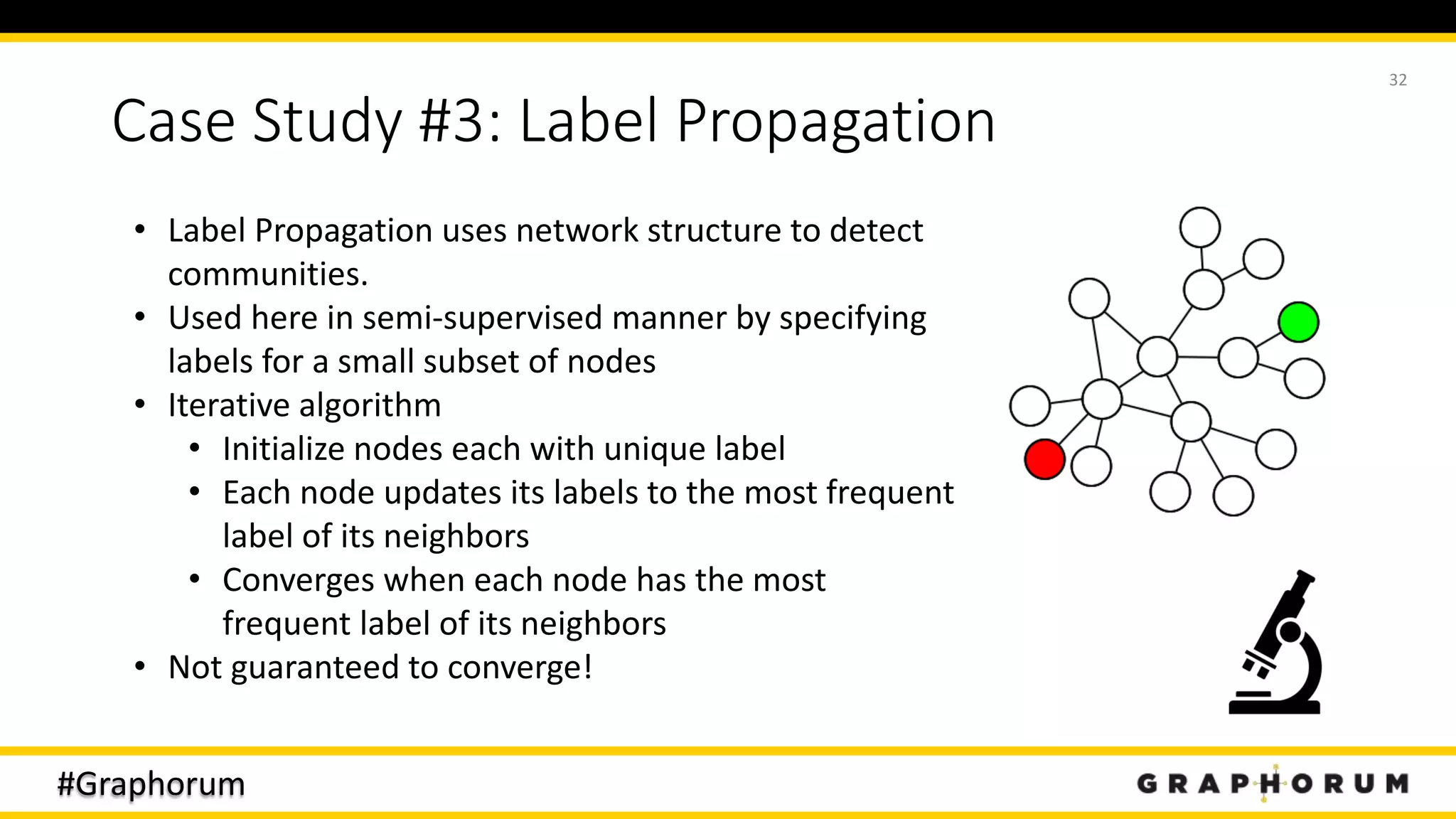
The document discusses the application of graph techniques in natural language processing (NLP) to improve tasks such as summarization, clustering, and word sense disambiguation. It presents multiple case studies demonstrating how graphs can represent text data and leverage intrinsic and extrinsic structures for enhanced performance in various NLP tasks. The author highlights challenges, strategies, and results from using graphs alongside traditional methods, emphasizing the integration of content features and graph structures in NLP.













![#Graphorum
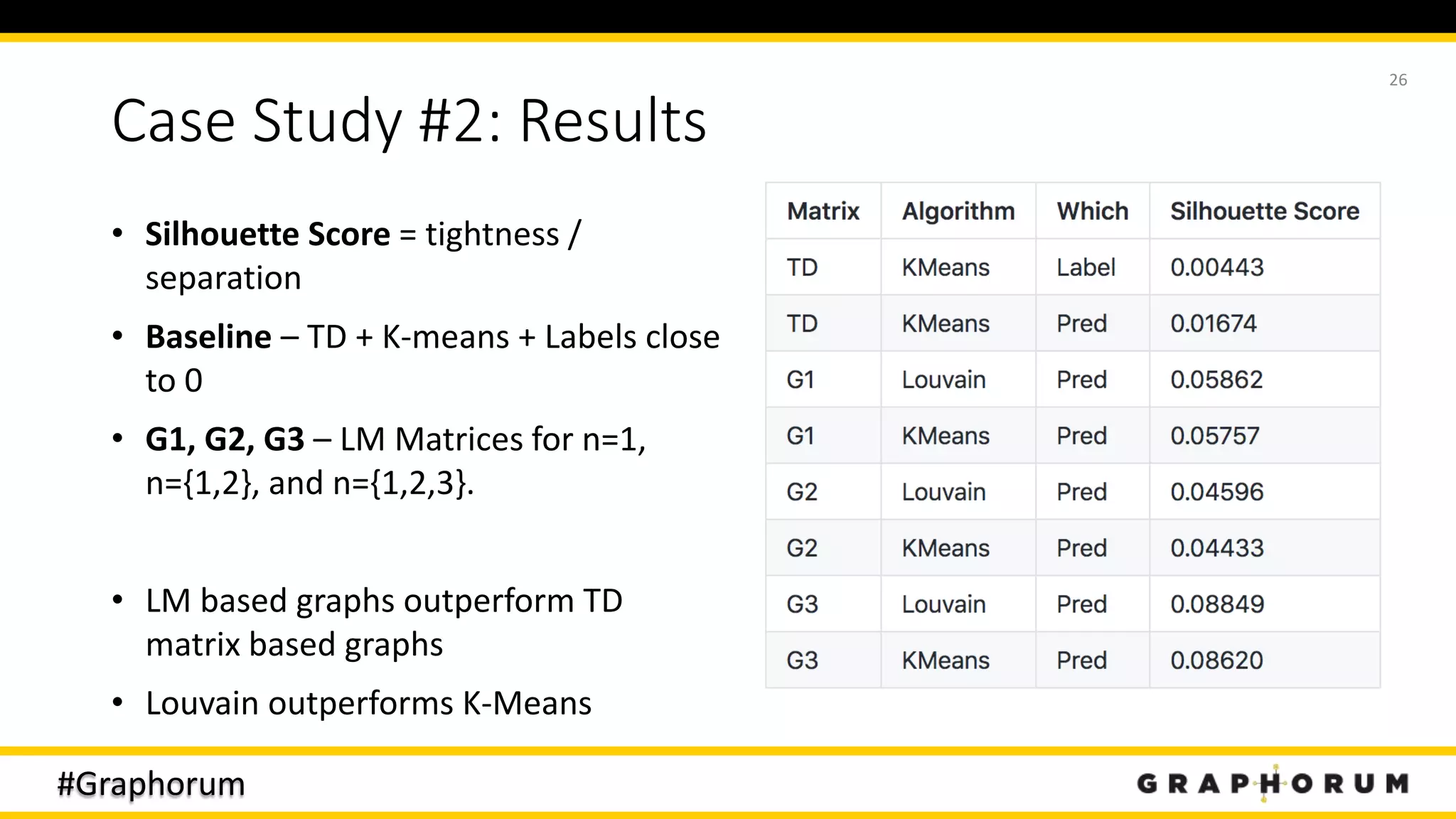
Case Study #3: Results
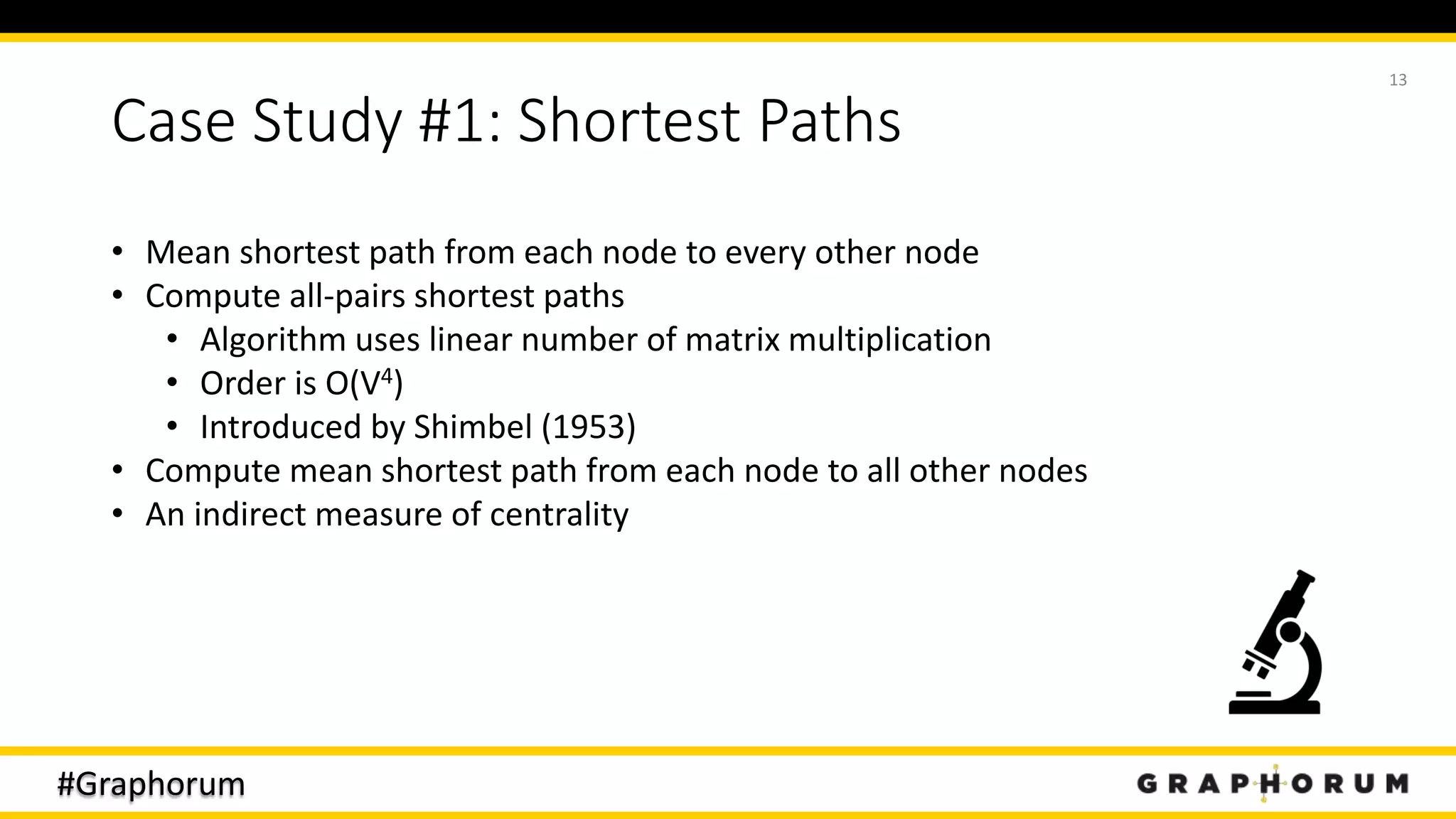
• Of 623 unlabeled sentences, Label Propagation predicts 319 sentences use the
first sense (chemical compound), 7 use the second sense (composite), and misses
298
• Misses are mostly chemical compounds (sense 1)
• Examples:
• Sense #1: ORTEP view of the compound [CuL8(ClO4)2] with the numbering
scheme adopted.
• Sense #2: Sensitive to compound fluorescence.
• Results can probably be improved – tried increasing initial labels, and by starting
with denser networks (so LP does not terminate as quickly)
33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphorum2019-sujitpal-191017113929/75/Graph-Techniques-for-Natural-Language-Processing-33-2048.jpg)