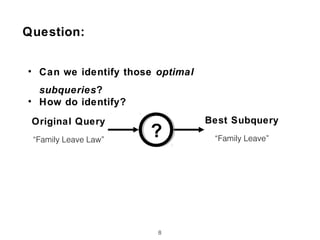
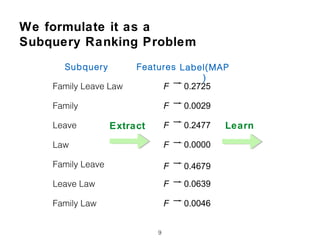
The document discusses research into whether short queries can be shortened further through identifying optimal subqueries.
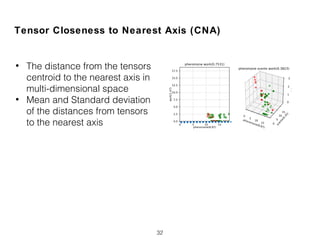
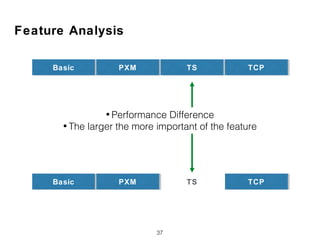
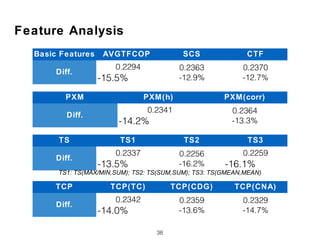
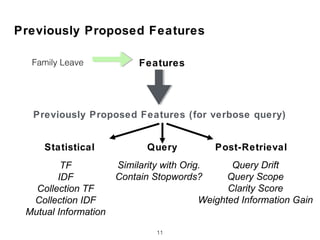
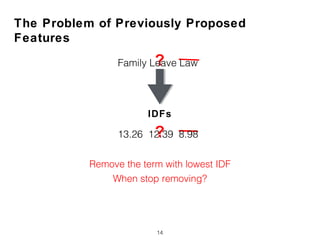
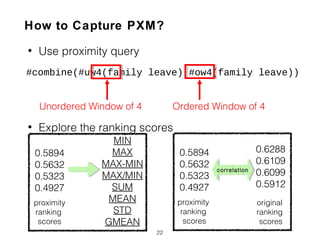
New features are proposed to evaluate subqueries, focusing on term relationships rather than statistical features used for long queries. These include term proximity, term score distribution, and compactness of term score tensors.
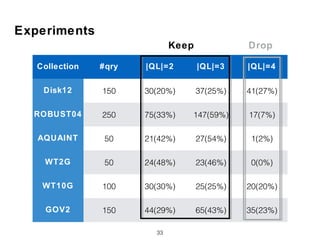
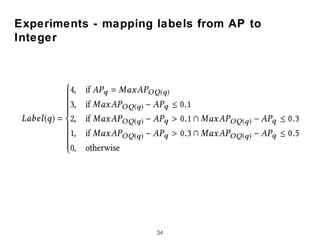
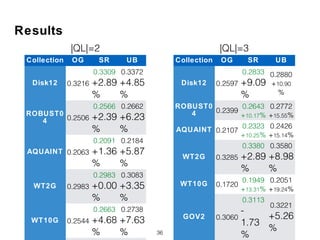
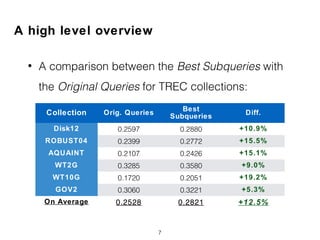
Experiments on TREC collections found the new features improved subquery selection over baselines, with term proximity and score distribution features most important. Analysis indicates the new approach can effectively shorten short queries.












![Term Proximity based Features (PXM)
• Term Dependency Model [Metzler05]
18
Family Leave Law](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ictir2017-180313173014/85/Can-Short-Queries-be-Even-Shorter-18-320.jpg)
![Term Proximity based Features (PXM)
• Term Dependency Model [Metzler05]
19
Family Leave Law
• Already know it is a law code
• Occur together
• In that order](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ictir2017-180313173014/85/Can-Short-Queries-be-Even-Shorter-19-320.jpg)
![Term Proximity based Features (PXM)
• Term Dependency Model [Metzler05]
20
• Already know it is a law code
• Occur together
• In that order
How to capture the feature?
Family Leave Law](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ictir2017-180313173014/85/Can-Short-Queries-be-Even-Shorter-20-320.jpg)

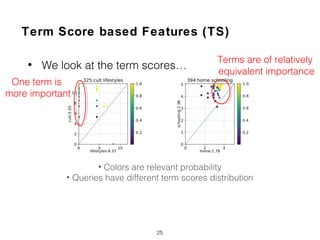
![Term Score based Features (TS)
• TF-IDF Constraint [Fang2011]
23
SVM Tutorial SVM Tutorial
99 1 50 50
Counter Intuitive](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ictir2017-180313173014/85/Can-Short-Queries-be-Even-Shorter-23-320.jpg)
![• TF-IDF Constraint [Fang2011]
24
• We instead look at the term scores…
SVM Tutorial SVM Tutorial
99 1 50 50
Counter Intuitive
Term Score based Features (TS)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ictir2017-180313173014/85/Can-Short-Queries-be-Even-Shorter-24-320.jpg)
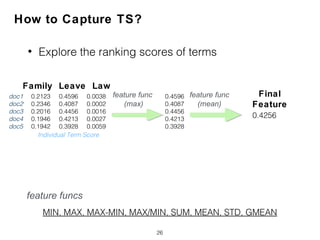
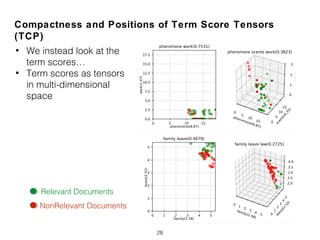
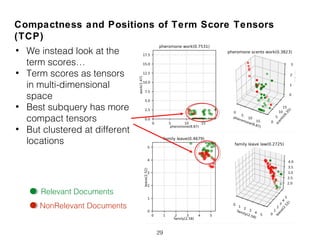
![Compactness and Positions of Term Score Tensors
(TCP)
• Normalized Query Commitment (NQC) [Shtok2012]
27
0.5894
0.5632
0.5323
0.4927
document ranking scores
0.6678
0.5632
0.4896
Quote:
“Higher deviation value was
correlated with potentially lower
query drift, and thus indicating the
better effectiveness"
Larger
Gap
Larger
Gap](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ictir2017-180313173014/85/Can-Short-Queries-be-Even-Shorter-27-320.jpg)