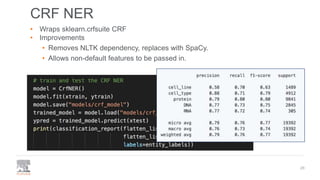
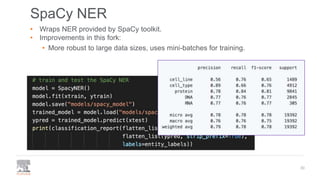
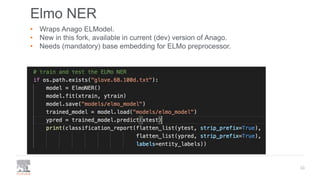
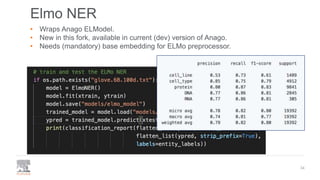
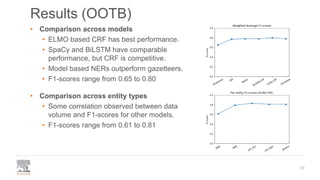
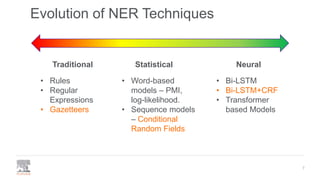
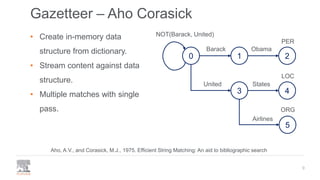
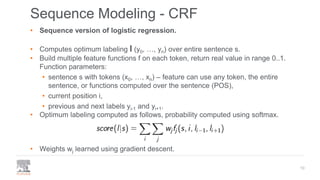
The document discusses the efficient building of Named Entity Recognition (NER) models using the NERDS framework, which provides easy access to various third-party NER models while boosting data science productivity. It covers the evolution of NER techniques, including statistical and neural models, as well as NERDS architecture and usage. Future work involves enhancing the API to align more closely with scikit-learn standards and expanding the model support.







![Neural Model – Transformer based
• BERT = Bidirectional Encoder Representation for Transformers.
• Source of embeddings similar to ELMo in standard BiLSTM + CRF models, OR
• Fine-tune LM backed NERs such as HuggingFace’s BertForTokenClassification.
15
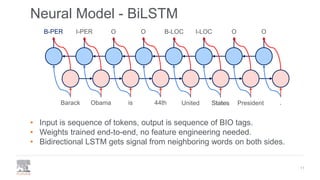
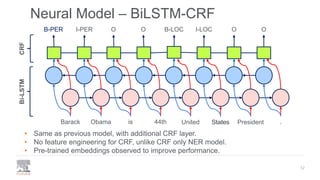
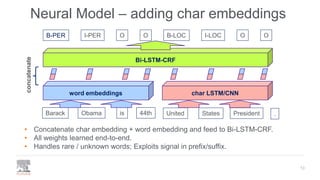
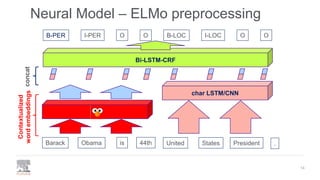
.Barack Obama is 44th United PresidentStates[CLS]
B-PER I-PER O O B-LOC I-LOC O O](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pydatalanerds-191205153221/85/Building-Named-Entity-Recognition-Models-Efficiently-using-NERDS-15-320.jpg)



![Unification through I/O Format
19
pyAhoCorasick CRFSuite SpaCy NER Anago BiLSTM
AnnotatedDocument (
doc: Document(“Barack Obama is 44th United States President .”),
annotations: [
Annotation(start_offset:0, end_offset:12, text:”Barack Obama”, label:”PER”),
Annotation(start_offset:22, end_offset:35, text:”United States”, label:”LOC”)
])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pydatalanerds-191205153221/85/Building-Named-Entity-Recognition-Models-Efficiently-using-NERDS-19-320.jpg)

![Can we do better?
21
Data: [[“Barack”, “Obama”, “is”, “44th”, “United” “States”, “President”, “.”]]
Labels and Predictions: [[“B-PER”, “I-PER”, “O”, “O”, “B-LOC”, “I-LOC”, “O”, “O”]]
DictionaryNER
I/O
Convert
SpacyNER
I/O
Convert
CrfNER BiLstmCrfNER](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pydatalanerds-191205153221/85/Building-Named-Entity-Recognition-Models-Efficiently-using-NERDS-21-320.jpg)
![ELMo NER Model from Anago
22
DictionaryNER CrfNER SpacyNER BiLstmCrfNER
Data: [[“Barack”, “Obama”, “is”, “44th”, “United” “States”, “President”, “.”]]
Labels and Predictions: [[“B-PER”, “I-PER”, “O”, “O”, “B-LOC”, “I-LOC”, “O”, “O”]]
I/O
Convert
I/O
Convert
ElmoNER](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pydatalanerds-191205153221/85/Building-Named-Entity-Recognition-Models-Efficiently-using-NERDS-22-320.jpg)