The document presents an overview of Learning to Rank (LTR) as a method in information retrieval, detailing its history, algorithms, and practical applications in systems like Solr and Elasticsearch. It explains key concepts including the difference between traditional search techniques and LTR, the various LTR algorithms (pointwise, pairwise, listwise), and their evaluation metrics. Additionally, it discusses practical considerations for implementing LTR, such as acquiring labels and dealing with unbalanced datasets.











![RELXSearchSummIt2018
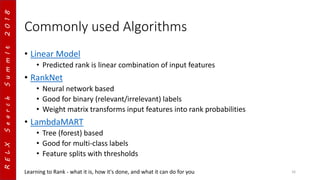
Pairwise Approach
• Input: triples of (query, document pairs) (q, dA, dB)
• Output: one of [-1, 1]
• Model: 𝒇(q, dA, dB) → [-1, 1]
• Classification problem, learn binary classifier to predict [-1, 1] for a
given pair of (query, document pair) triples
• Goal is to minimize average number of inversions in ranking
• Examples: RankNet, RankSVM, LambdaMART
Learning to Rank - what it is, how it's done, and what it can do for you 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/search-summit-2018-ltr-presentation-181002000653/85/Search-summit-2018-ltr-presentation-14-320.jpg)