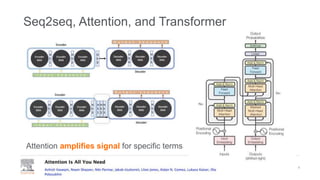
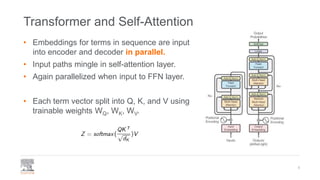
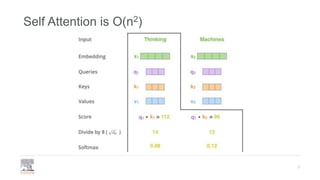
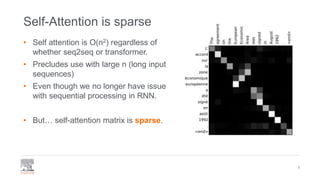
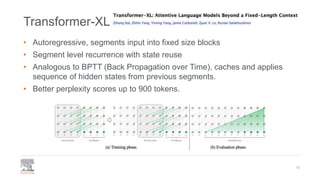
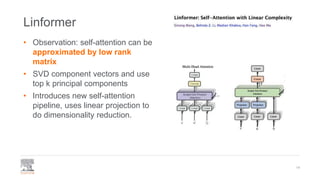
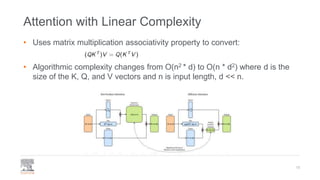
This document provides a comprehensive survey of techniques for adapting transformer models to handle long input sequences, discussing the limitations of self-attention and presenting various approaches to mitigate these issues. It covers advancements such as sparse transformers, transformer-xl, reformer, routing transformer, and longformer, each with distinct algorithmic complexities and methodologies for optimizing attention mechanisms. The document also includes references to foundational research and implementation resources for these transformer variations.





![Longformer
• Sparsify full attention matrix according to ”attention pattern”
• Sliding window of size k (k/2 left, k/2 right) to capture local context
• Optional dilated sliding window at different layers of multi-head attention to get bigger
receptive field
• Additional (task dependent) global attention – [CLS] for classification, question tokens for
QA
• Scales linearly with input length N and sliding window length k (O(n * k)), global context
effect minimal, k << n
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/journal-club-longformer-etc-200917001731/85/Transformer-Mods-for-Document-Length-Inputs-16-320.jpg)
![Big Bird
• Consider self-attention as a DAG and apply graph sparsification principles
• Composed of
• Set of global tokens g that attend to all parts of sequence (ITC – subset of input
tokens, ETC – additional tokens such as [CLS]
• For each Q, set of r random keys it will attend to
• Local neighborhood of size w for each input token
• Complexity is O(n*w) because effect of g and r are negligible, w << n
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/journal-club-longformer-etc-200917001731/85/Transformer-Mods-for-Document-Length-Inputs-17-320.jpg)