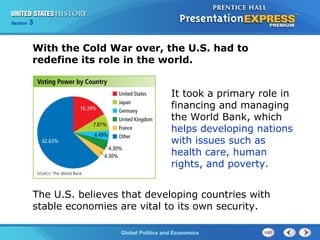
The document summarizes the United States' role in global politics and economics following the end of the Cold War under President Clinton. It discusses how the US supported free trade agreements like NAFTA and signed many trade deals through the WTO to promote globalization and economic growth. It also describes Clinton's foreign policy goals of intervening in conflicts in Somalia, Haiti, and the Balkans through NATO bombings. Additionally, it outlines increasing tensions in the Middle East between Israel and Palestine and the emergence of terrorist threats to the US from groups like al Qaeda.