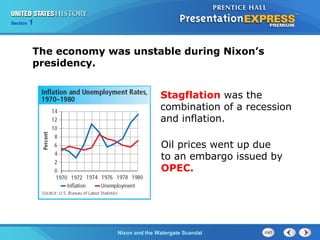
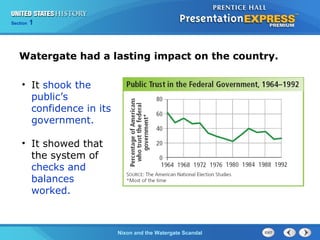
The document summarizes the Watergate scandal that led to Richard Nixon's resignation. It describes how Nixon was reelected in 1972 using a "southern strategy" but his administration was plagued by economic issues like stagflation. In 1972, Nixon's reelection campaign orchestrated a break-in at the Democratic National Committee headquarters, known as the Watergate scandal. Investigations by journalists and a Supreme Court ruling forcing Nixon to release secret tapes revealed his involvement, leading to impeachment and Nixon becoming the only US President to resign from office in 1974.