1. The Allies agreed on a "Europe First" strategy to defeat Germany, viewing it as the most dangerous Axis power. They increased military production and developed technologies like radar to restore supply lines in the Atlantic.
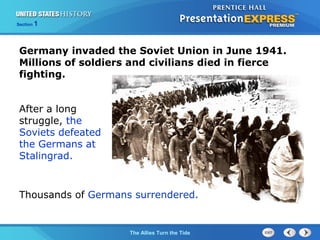
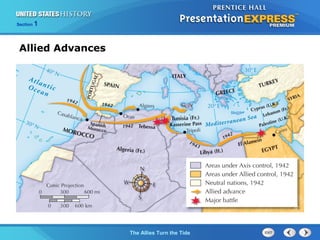
2. The Soviets defeated Germany at Stalingrad in 1943, a major turning point that forced Nazi armies to retreat west. Meanwhile, the Allies defeated German forces in North Africa under Rommel.
3. The Allies launched massive bombing campaigns over Germany and took the air war to Japan, defeating them at the major Battle of Midway in 1942, another turning point that halted Japan's momentum in the Pacific.