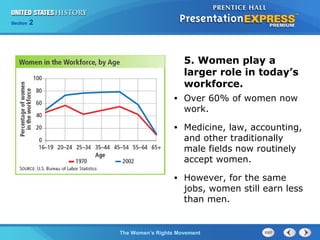
The women's rights movement arose in the 1960s as women examined their roles and sought greater equality. Led by Betty Friedan's book The Feminine Mystique, the movement sought to end discrimination against women through the National Organization for Women and passage of the Equal Rights Amendment. While the ERA failed, the movement succeeded in legalizing abortion with Roe v. Wade and banning sex discrimination in education and the workplace. By the 1970s, these efforts led to more legal rights and opportunities for women, though pay gaps remained, and the movement continued to transform American society.