World War II had significant impacts on American society:
- It opened new jobs and opportunities for women and minorities as men went off to war and industries ramped up production, though discrimination still limited opportunities.
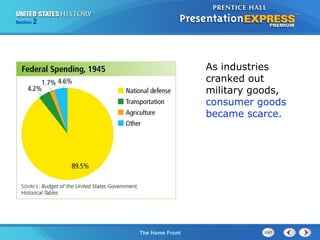
- The war effort changed lives as people moved around the country for jobs, taxes increased, wages and prices were controlled, and consumer goods were rationed to support the war.
- However, the push for civil rights continued, with Executive Order 8802 prohibiting discrimination in defense hiring amid calls for equal treatment of African Americans. Internment of Japanese Americans also showed lingering discrimination.