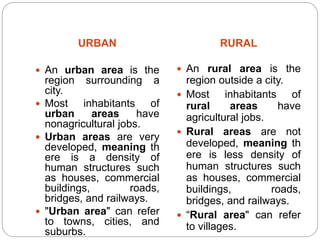
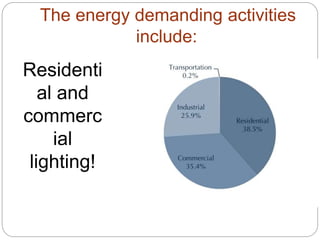
This document discusses energy demand and usage in urban vs rural areas. It notes that urban areas are more developed with non-agricultural jobs, higher population density, and greater energy usage for residential, commercial, industrial, and transportation needs. Rural areas have fewer structures and people working in agriculture with lower energy usage. The document then outlines the major energy demands like lighting, transportation, manufacturing, and waste disposal and how seasons and prevention/control of pollution also impact energy usage.