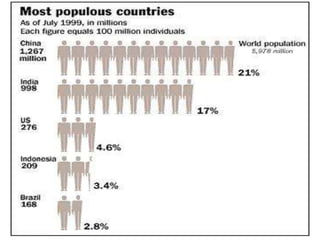
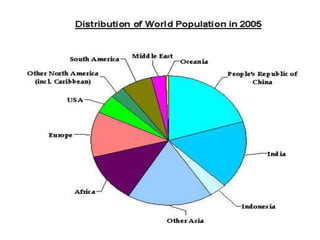
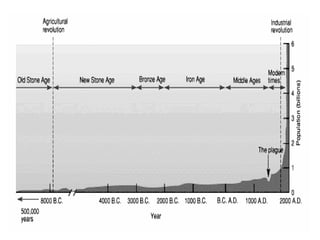
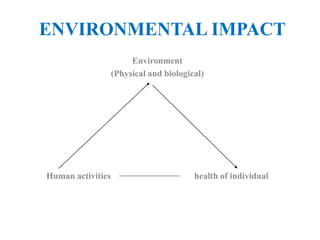
The document discusses various topics related to human population, the environment, and their interrelationships. It begins by providing statistics on global human birth and death rates and explaining concepts like total fertility rate and life expectancy. It then discusses reasons for population growth and the impacts of overpopulation, including threats to natural resources and environmental degradation. The document also covers human rights, the roles of information technology in environmental monitoring and health, policies around women and child welfare, and introduces the concepts of environmental health and hazards.