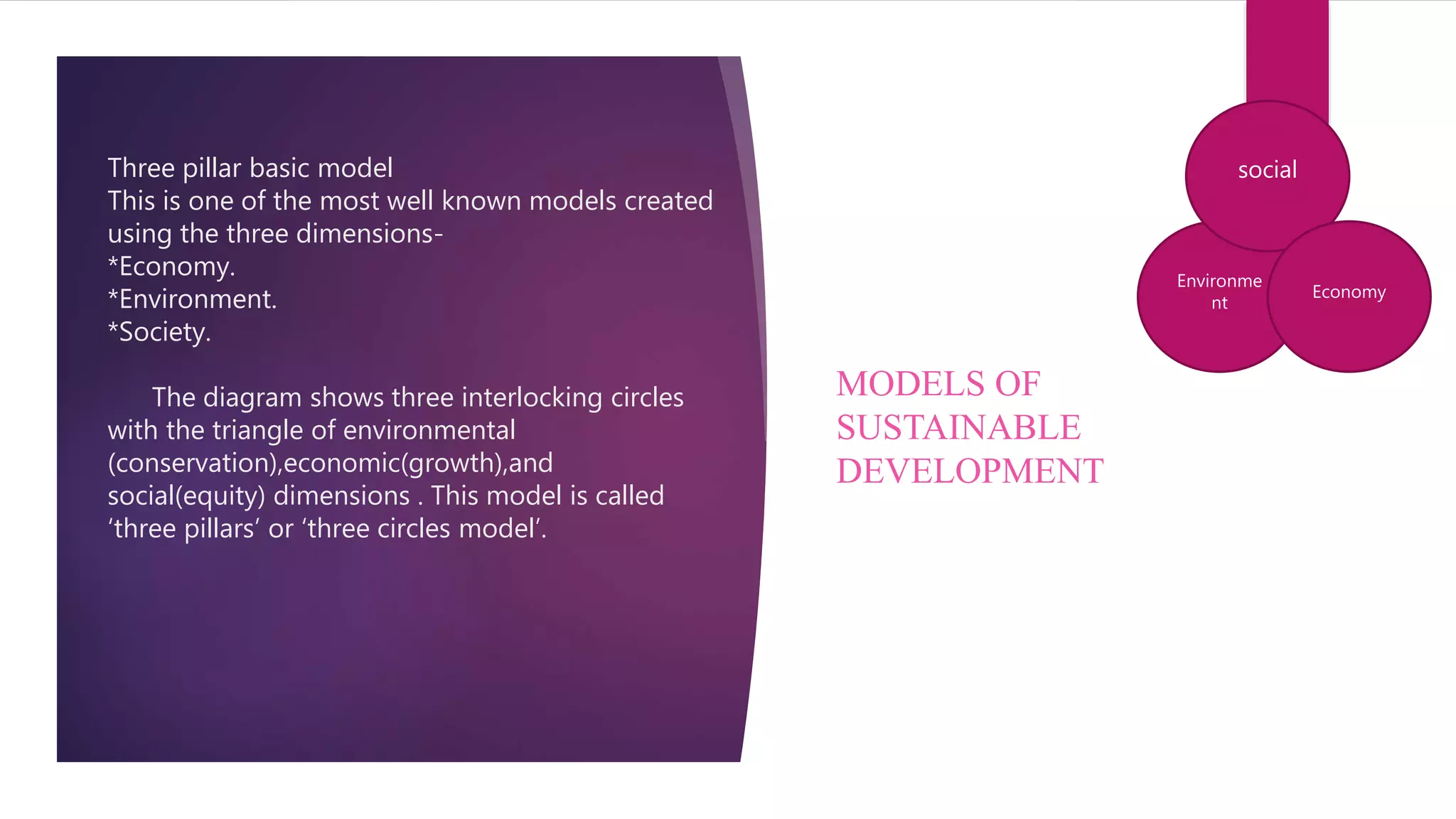
The document discusses the pressing issue of resource scarcity and the principles of sustainable development necessary for a balanced society. It emphasizes the need for sustainable consumption and growth, highlighting various models and indicators for measuring sustainability, like the Gross National Happiness index. It concludes with practical tips for individuals to adopt more sustainable lifestyles to conserve natural resources and protect the environment.