Embed presentation
Download to read offline


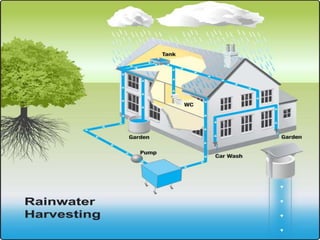







This document discusses various methods of rainwater harvesting and artificial groundwater recharge to meet increasing water demands, raise water tables, and supplement groundwater supplies during dry seasons. These methods include rooftop rainwater harvesting, check dams, embankments, underground tanks, and khadins. Examples are given of projects using these methods in places like the Golden Temple, IIT Delhi, JNU Delhi, Maharashtra, and Jodhpur that have successfully raised local water tables and increased food production. The benefits of these methods are listed as rising water tables, improved groundwater quality, reduced soil erosion, mitigation of drought and flood hazards, lower pumping costs, and sustainable groundwater sources.









