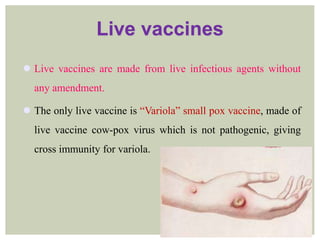
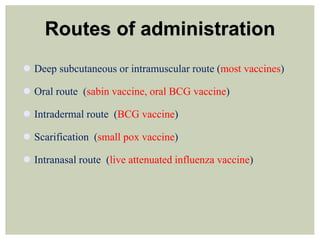
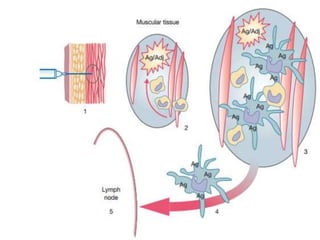
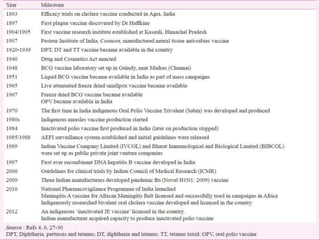
This document provides an overview of vaccination programs and implementation. It discusses vaccine-preventable diseases, types of vaccines, routes of administration, levels of effectiveness, and the history of vaccination programs in India. Key points include: immunization aims to prevent or eradicate diseases; common vaccine-preventable diseases include diphtheria, measles, and polio; vaccines can be live, attenuated, inactivated, or toxoids; and India's vaccination efforts began in the early 1800s with smallpox vaccination and expanded in the late 20th century with the Universal Immunisation Programme.





































































![•REFERENCES
• 1. 3nd ed. Geneva: WHO; 2009. World Health Organization ganization (WHO)
Unicef, World Bank. State of the world's vaccines and immunization.
• 2. Geneva: WHO; 2012. Mar, [accessed on May 30, 2012]. World Health
Organization. Global immunization data 2011. Available from:
www.who.int/hpvcentre/Global_Immunization_Data.pdf .
• 3. Fenner F, Henderson DA, Arita I, Jezek Z, Ladnyi ID. Geneva: World Health
Organization; 1988. Smallpox and its eradication; pp. 369–71.
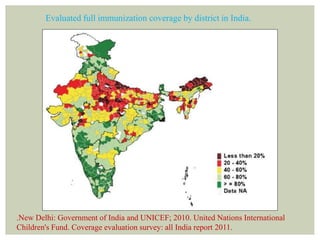
• 4. New Delhi: Government of India and UNICEF; 2010. United Nations
International Children's Fund. Coverage evaluation survey: all India report 2009.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sem9vaccinationprogramme-160201175351/85/Vaccination-programmes-89-320.jpg)



