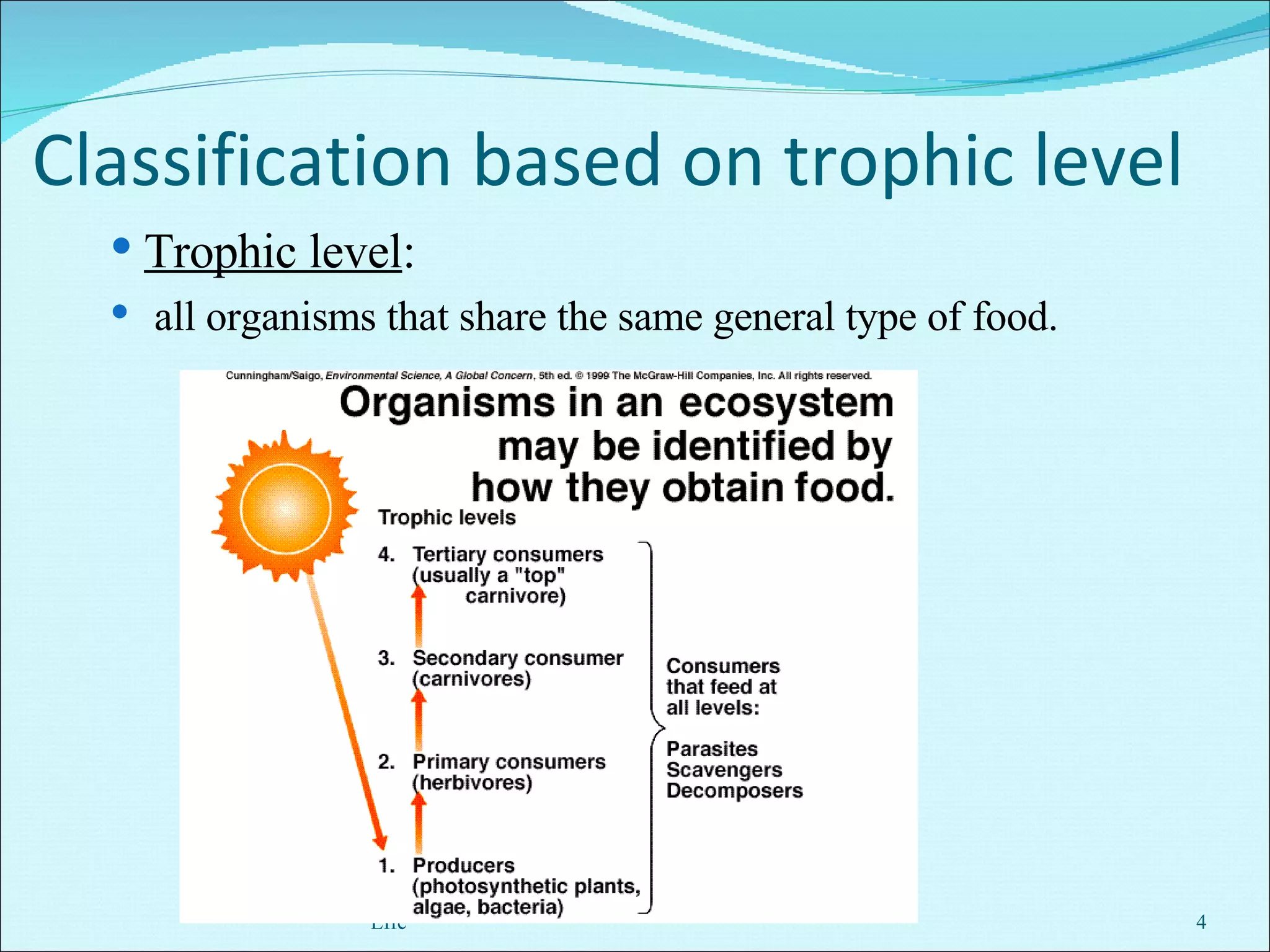
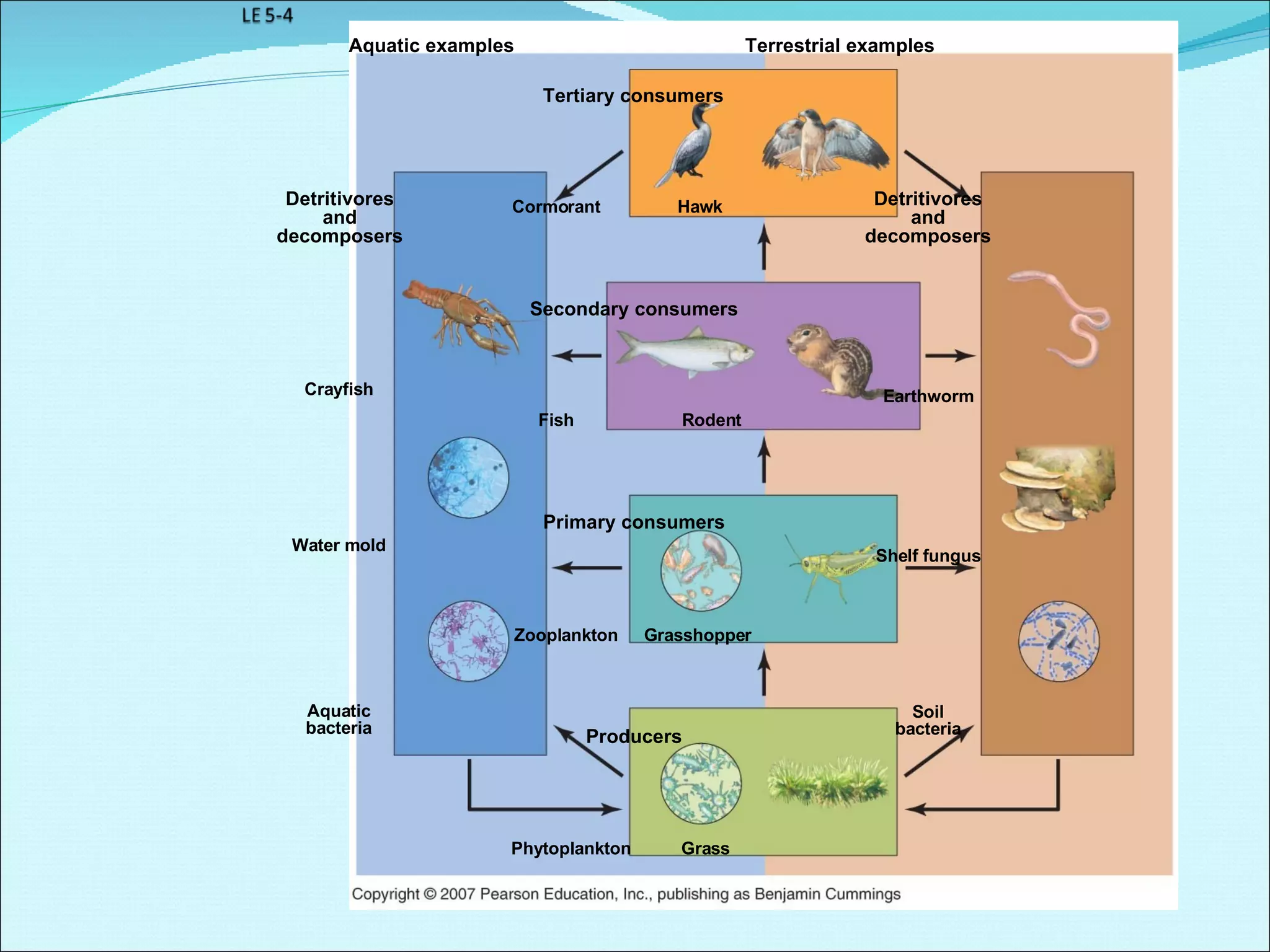
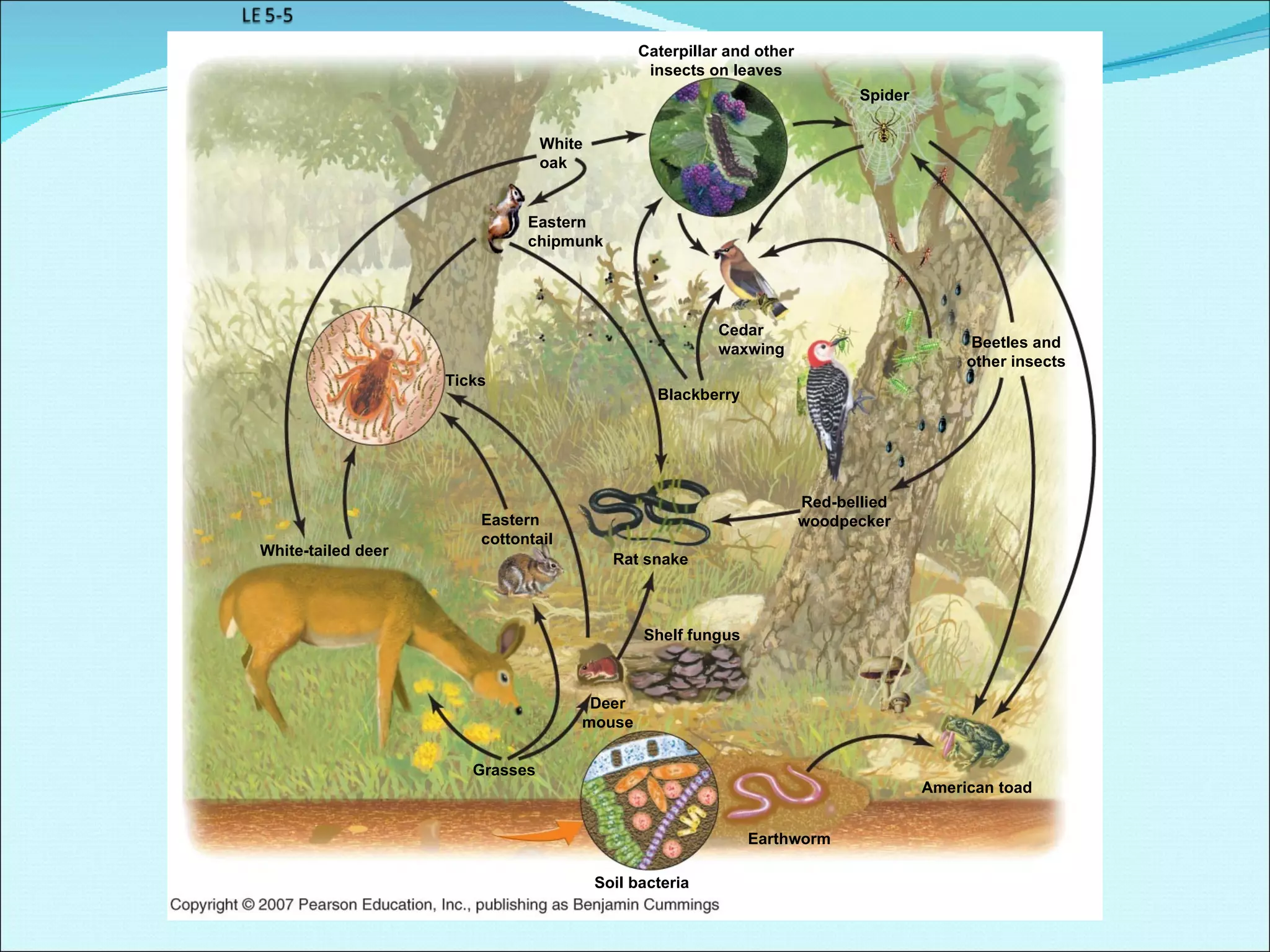
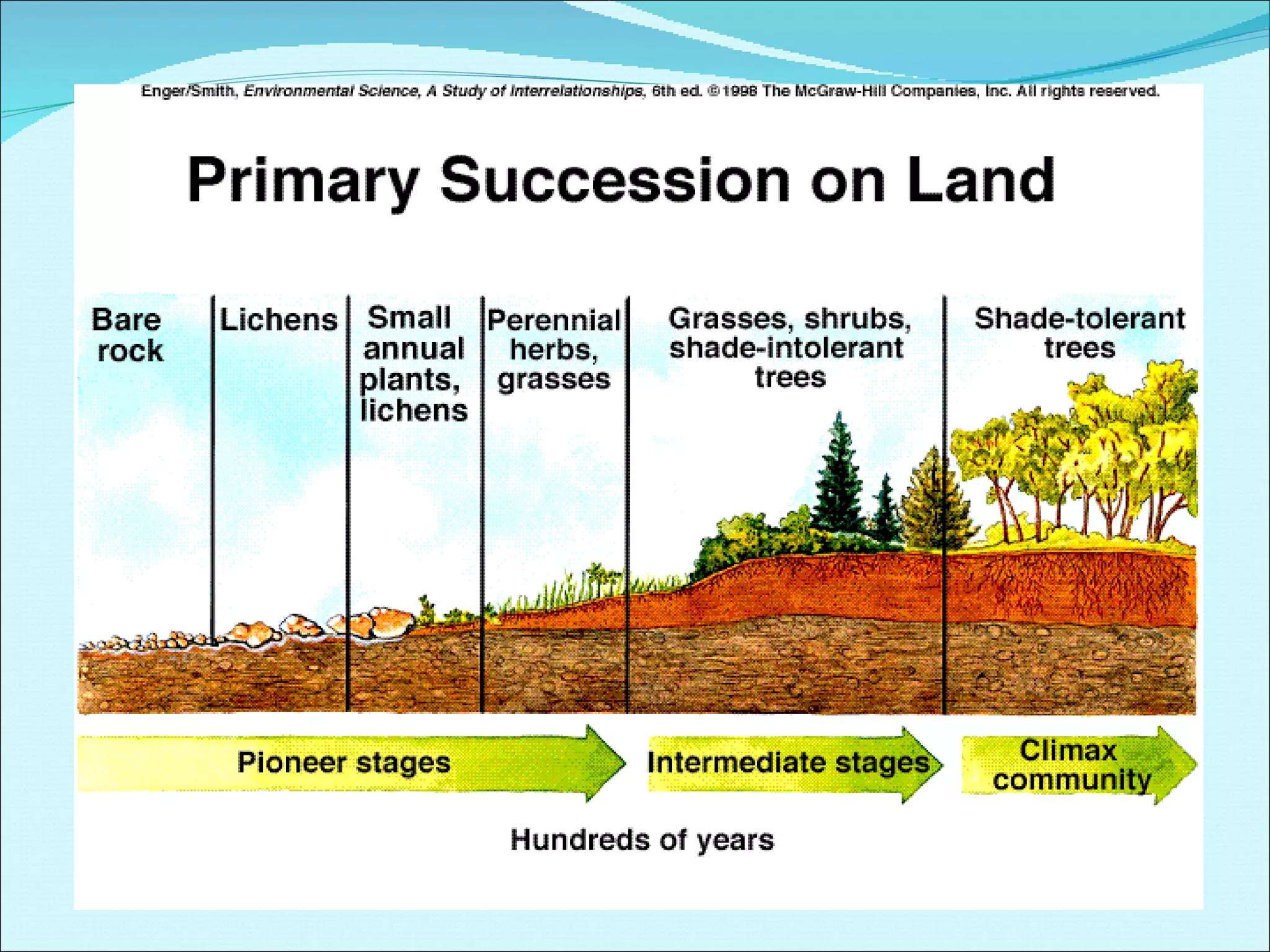
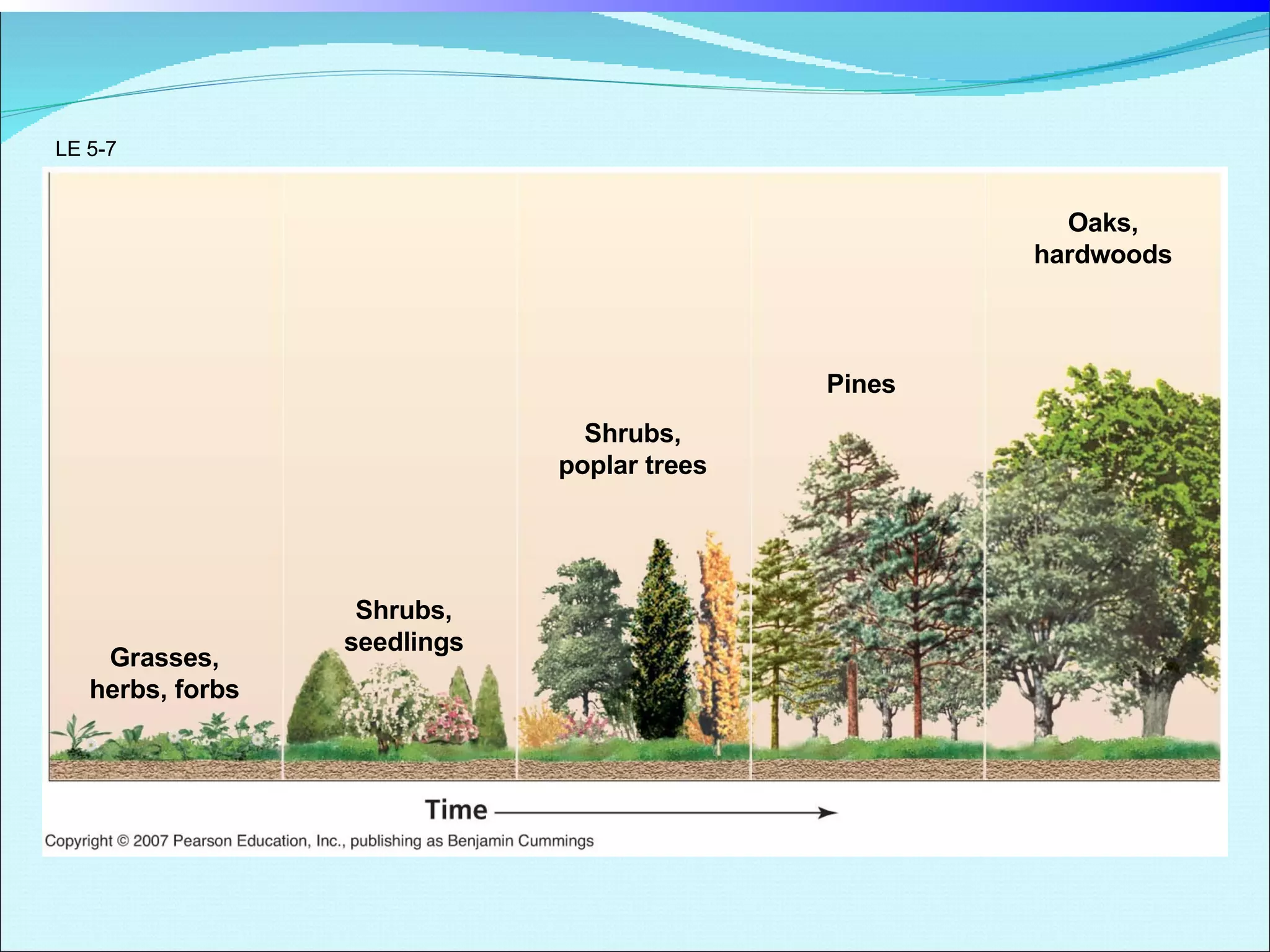
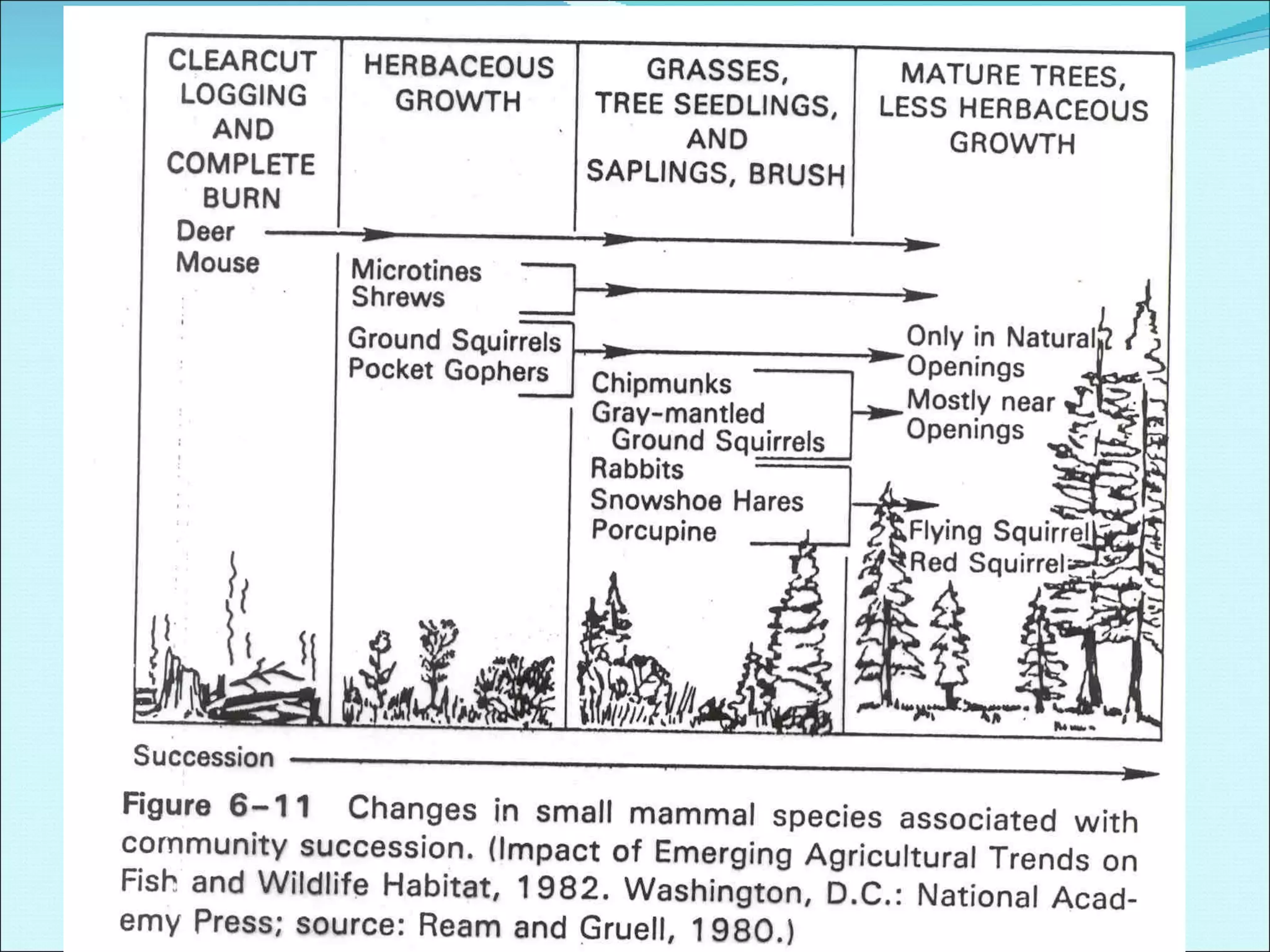
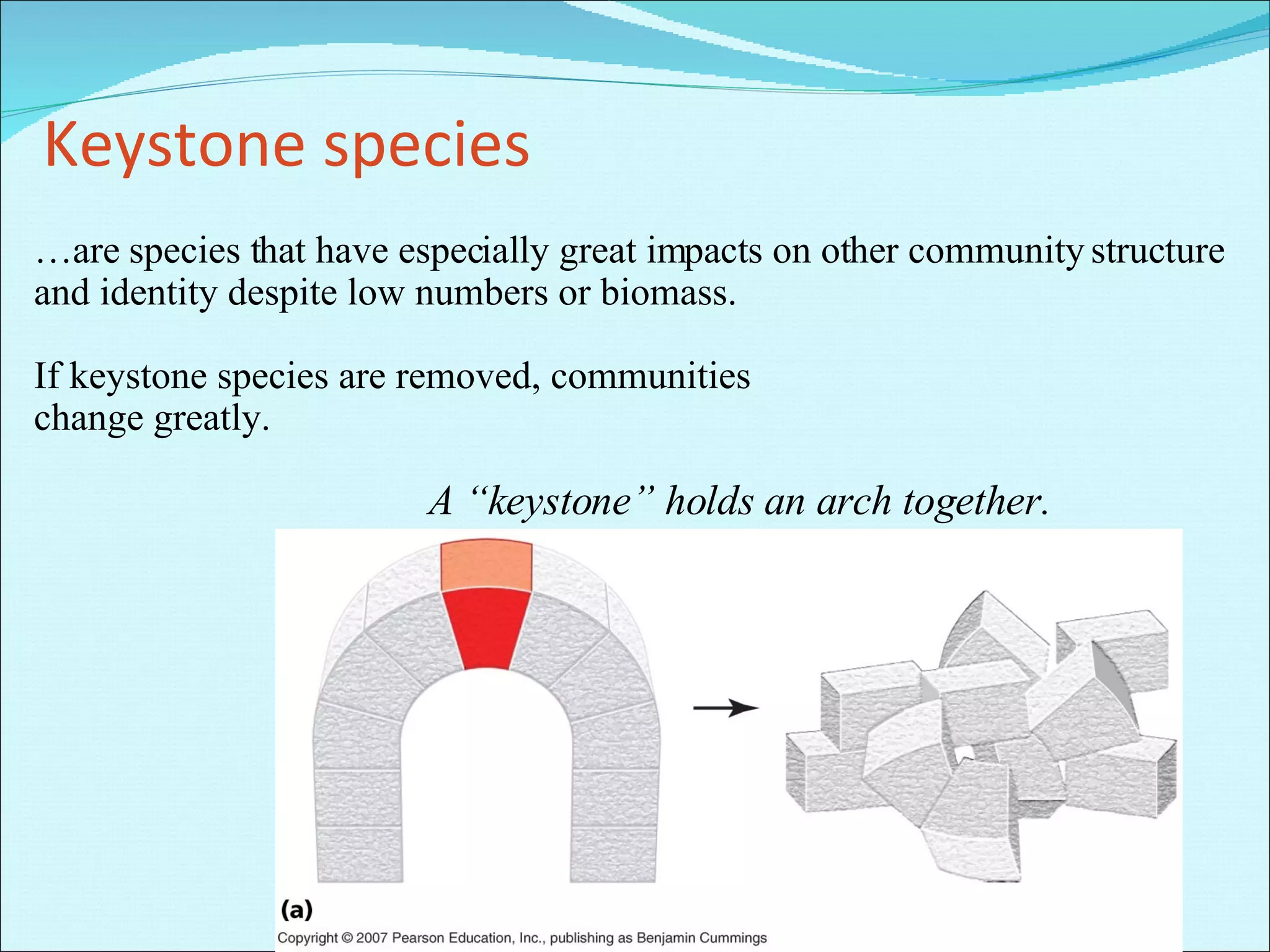
Community ecology examines how species interact and relate to one another within biological communities. Ecologists represent feeding interactions through food chains and complex food webs. Organisms are classified based on trophic levels according to their position in the food web. Communities experience natural and human-caused disturbances and undergo succession over time. Some species have outsized impacts on community structure as keystone species, ecosystem engineers, or foundation species. Community ecologists study how communities resist or recover from disturbances.