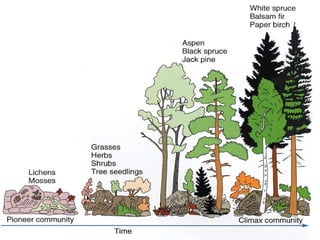
Community interactions powerfully affect ecosystems through various types of relationships between species including competition, predation, herbivory, symbiosis, and disease. These interactions drive community structure and dynamics. Communities tend to have short food chains due to inefficiencies in energy transfer and limits to animal size. Dominant, keystone, and foundation species play important roles in determining community composition through competitive and facilitative effects. Ecological succession involves predictable changes in communities over time in response to disturbances.