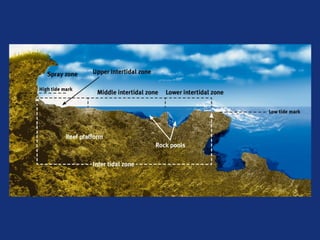
There are different types of intertidal zones including rocky shores, sandy beaches, and mangrove swamps. Each habitat presents unique challenges for organisms to adapt to, such as shifting sands or exposure to air and waves. The intertidal zone can be further divided into subzones from the spray zone to the lower intertidal zone. Organisms in each subzone have developed adaptations like thick shells or burrowing to survive in their particular environment and deal with changes from tides.