The document discusses various topics related to nuclear power plants including:
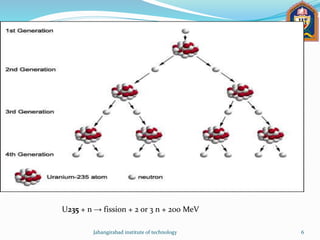
1) Nuclear fuel such as Uranium-235 and Plutonium-239 that can undergo fission chain reactions to produce energy.
2) How nuclear fission of heavy elements like Uranium releases heat and how this can be used to create a sustained nuclear chain reaction in a nuclear reactor.
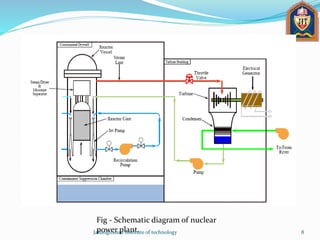
3) The basic components of a nuclear power plant including the nuclear reactor, control rods, steam generators, turbines, pumps and cooling towers.