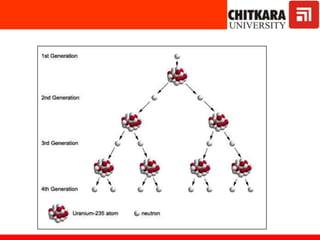
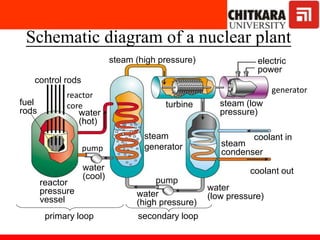
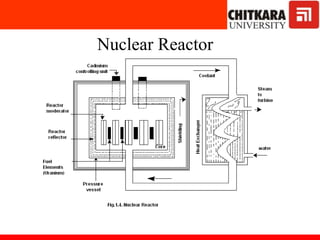
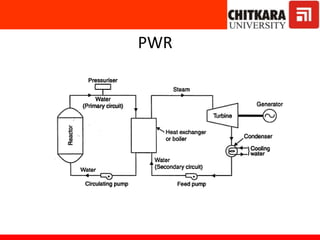
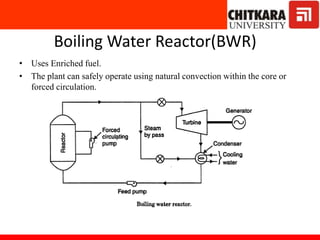
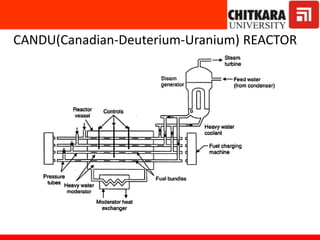
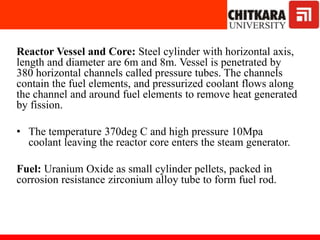
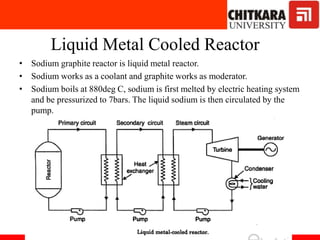
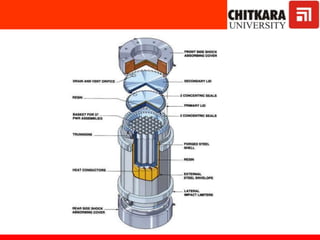
The document discusses nuclear fuels used in nuclear power plants such as uranium-235 and plutonium-239, how nuclear fission produces energy through a self-sustaining chain reaction, and the key components of nuclear reactors including the reactor core, control rods, moderator, coolant, and safety measures. It also covers different types of nuclear reactors like pressurized water reactors and boiling water reactors, as well as waste disposal and the future prospects of nuclear power.