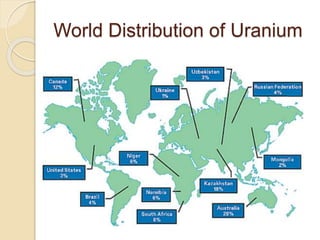
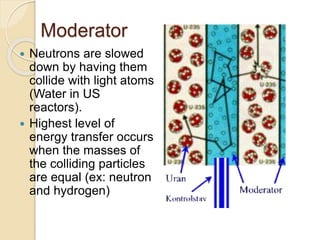
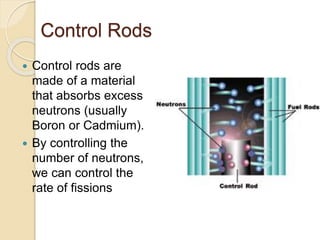
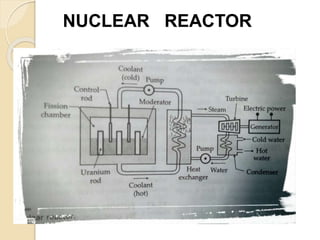
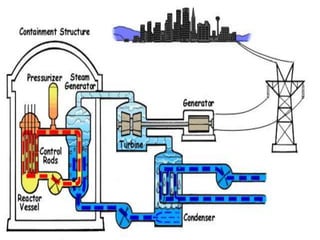
Fission is the splitting of a nucleus into smaller parts that releases energy. It can occur through nuclear chain reactions where neutrons produced in one fission induce additional fissions. Uranium-235 is commonly used as it can undergo fission when struck by slow neutrons. This results in fission products like krypton and strontium, more neutrons on average, and a large amount of energy. A controlled chain reaction in a nuclear reactor uses fissionable material as fuel, neutron moderators to slow neutrons, control rods to regulate the reaction, coolants to remove heat, and shielding to protect from radiation. Nuclear power plants generate electricity by using the heat from fission in a reactor to