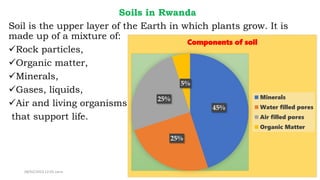
The document discusses the types of soils present in Rwanda, including their characteristics, formation, and distribution. It highlights the impact of climate, parent rock, and topography on soil formation, as well as the causes and effects of soil erosion in the region. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of soil conservation methods to mitigate the adverse effects of erosion and improve agricultural productivity.