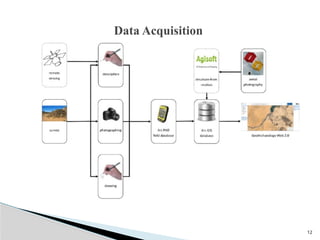
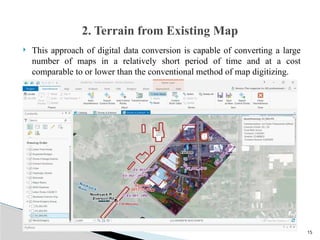
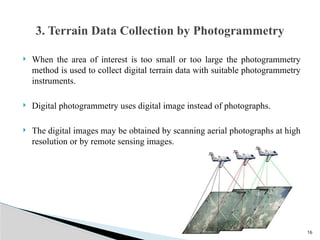
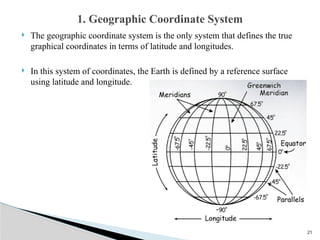
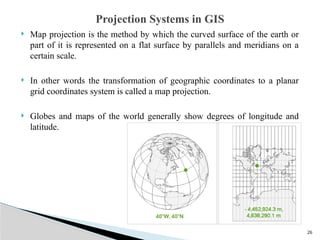
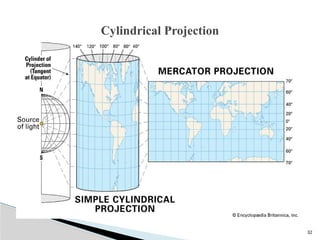
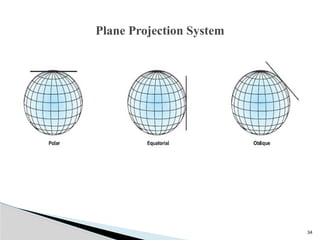
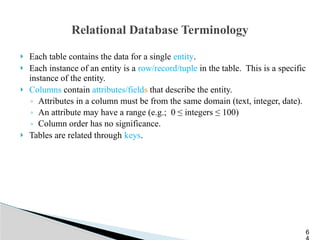
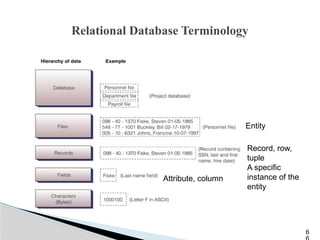
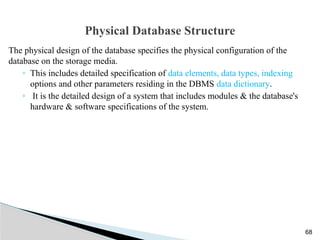
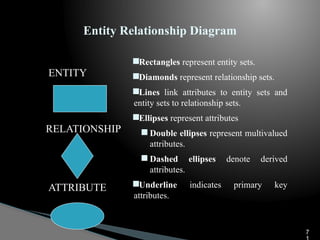
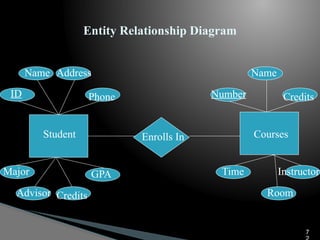
The document outlines the components, types, and applications of geographic information systems (GIS) data, emphasizing the distinction between spatial and attribute data. It discusses data acquisition methods, data models (raster and vector), and the importance of georeferencing, map projections, and database structures involved in GIS. The advantages and disadvantages of different data models and storage methods are also examined, providing a comprehensive overview of GIS data management and representation.