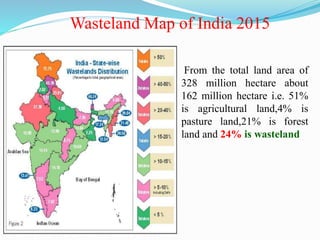
This document discusses wastelands in India. It states that 24% of India's total land area is classified as wasteland. Wastelands are degraded lands that can be rehabilitated through reasonable efforts. They are caused by overuse of land through practices like overcultivation, deforestation, overgrazing, and improper irrigation. Degradation leads to issues like soil erosion. Wastelands are categorized based on difficulty of reclamation - easily reclaimable through practices like reducing salt content, reclaimable with some difficulty using agroforestry, and reclaimable with extreme difficulty through activities like forestry or ecosystem recreation. Various methods of reclamation are discussed, including afforestation, re