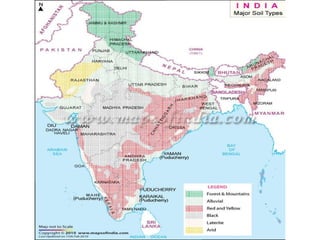
The document discusses different types of soils found in India. It describes alluvial soil, which is the most widely spread soil deposited by river systems. Alluvial soil is further divided into old alluvial and new alluvial soils. Black soil is volcanic in origin and ideal for growing cotton. Red and yellow soil develops on igneous rock in low rainfall areas of the Deccan plateau. The types of soil are determined by factors like climate, vegetation, parent rock type and relief of the land.