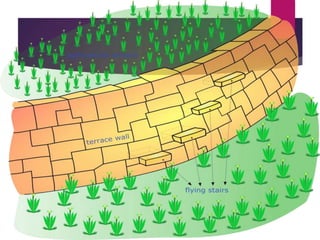
This document discusses various techniques for soil conservation to prevent erosion and maintain fertility. It describes contour plowing, terrace farming, keyline design, perimeter runoff control, windbreaks, crop rotation, and mulching as organic farming practices that conserve the soil. It also recommends preventing overgrazing, re-establishing forest cover, and maintaining soil pH levels. The document concludes by mentioning engineering structures like gabion walls, retaining walls, breast walls, check dams, and weep holes that can further control soil erosion.