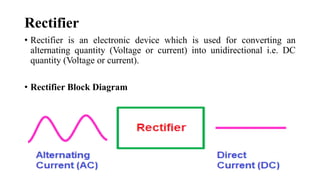
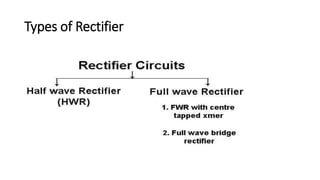
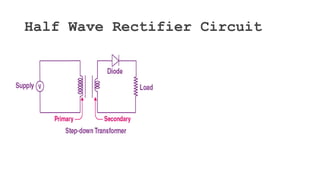
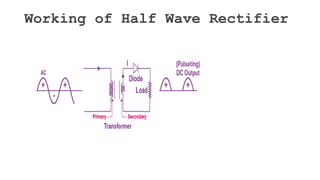
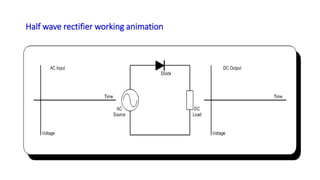
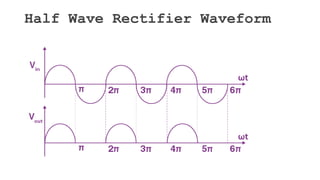
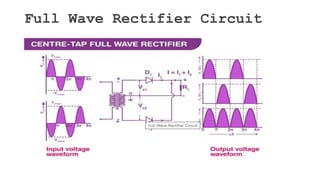
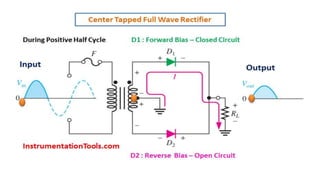
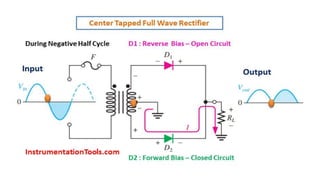
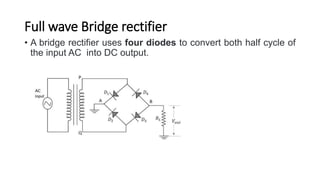
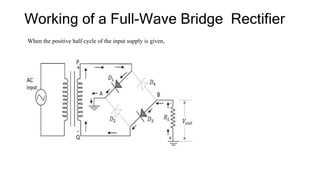
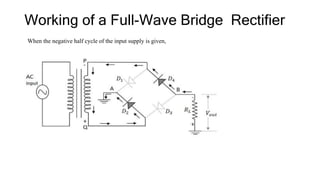
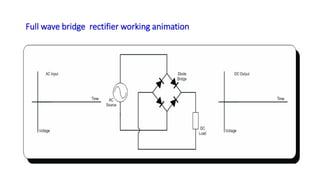
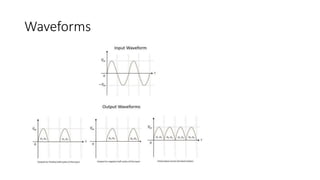
The document discusses different types of rectifiers. It describes half-wave rectifiers, full-wave center-tapped rectifiers, and full-wave bridge rectifiers. For each type, it provides the circuit diagram, explains how it works during each half-cycle of the AC input, and lists the advantages and disadvantages as well as common applications.