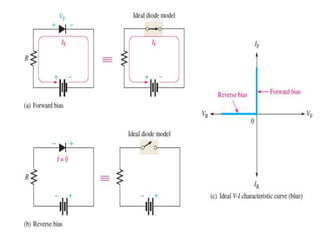
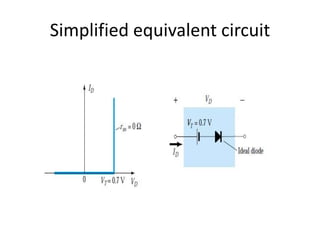
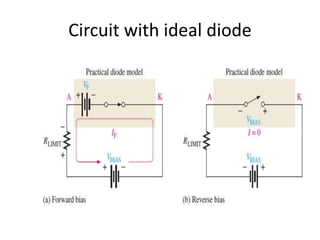
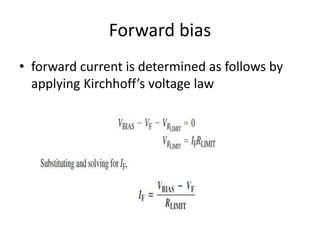
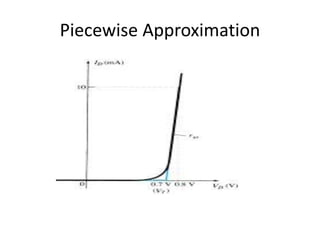
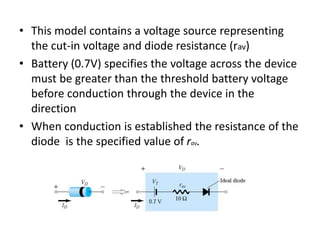
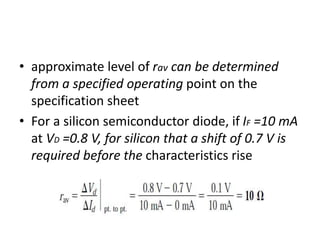
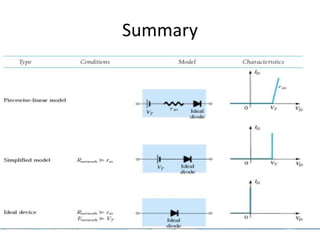
This document discusses diode equivalent circuit models, which are used to approximate the nonlinear behavior of real diodes for circuit analysis purposes. It describes three common diode models: the ideal diode model, which represents a diode as a simple switch; the practical (or simplified) model, which includes a 0.7V voltage drop; and the piecewise linear model, which approximates the diode curve as a series of linear segments. The document explains that diode models allow the use of conventional linear circuit analysis by replacing the nonlinear diode with an equivalent linear circuit representation.