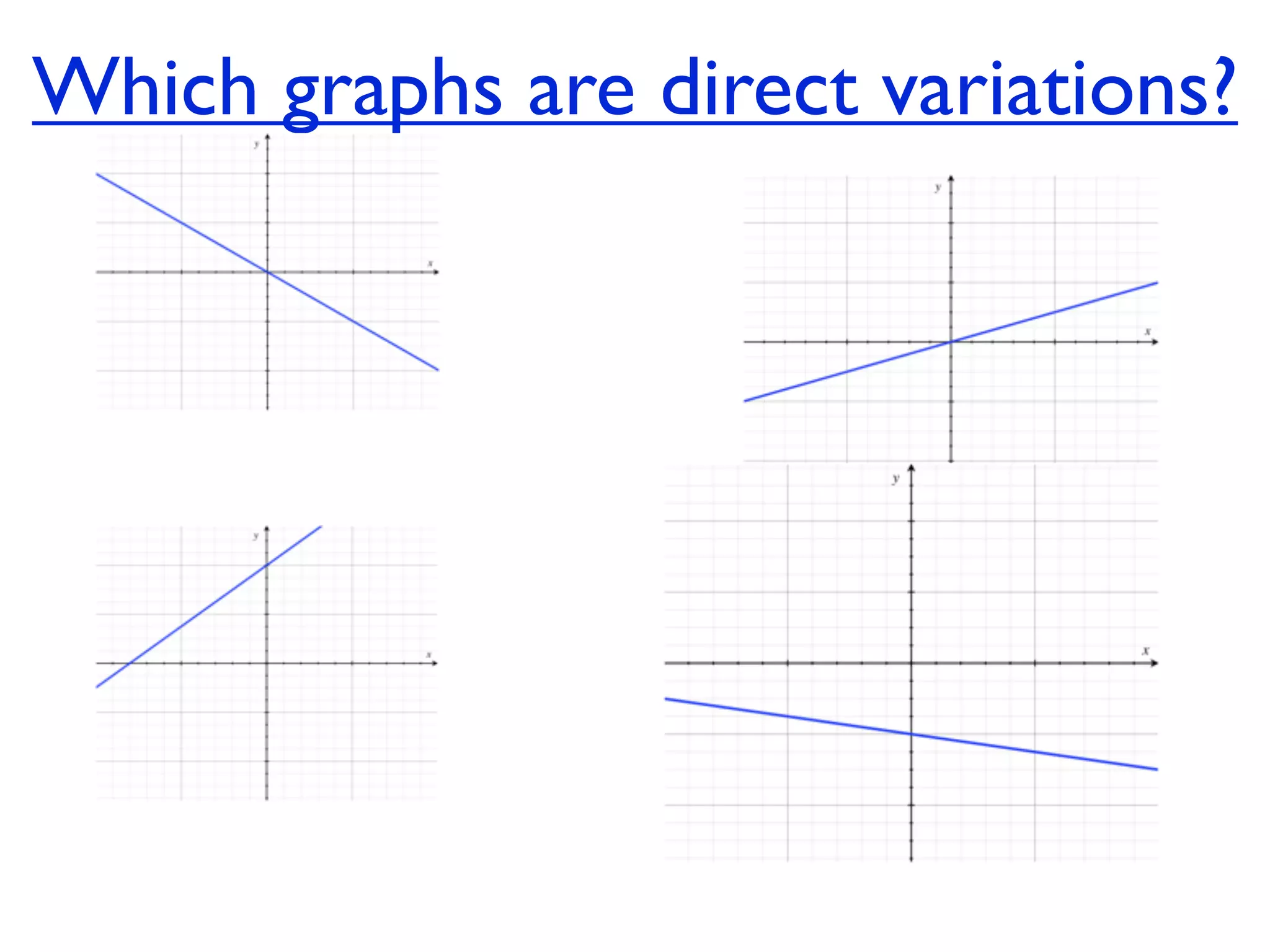
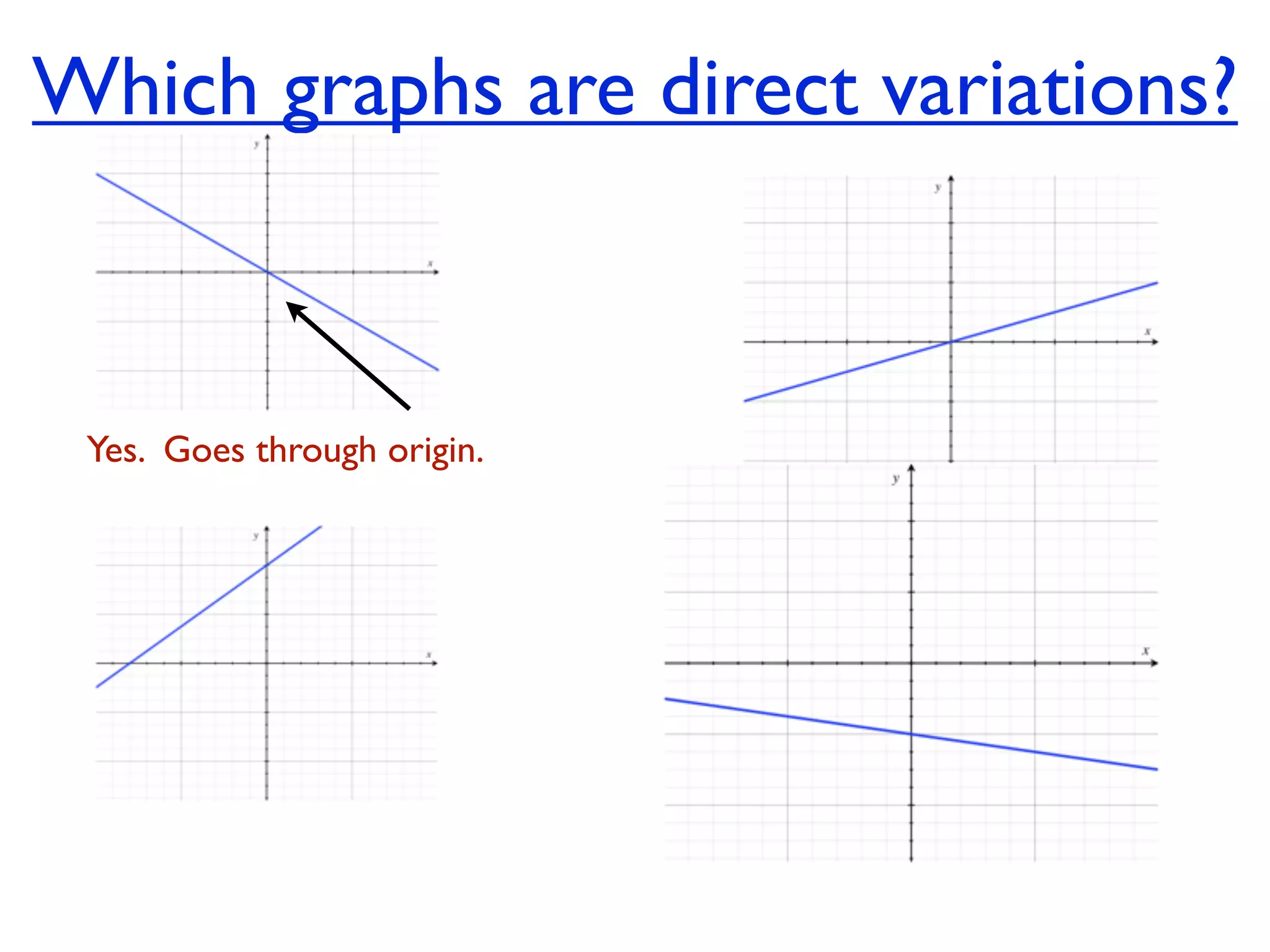
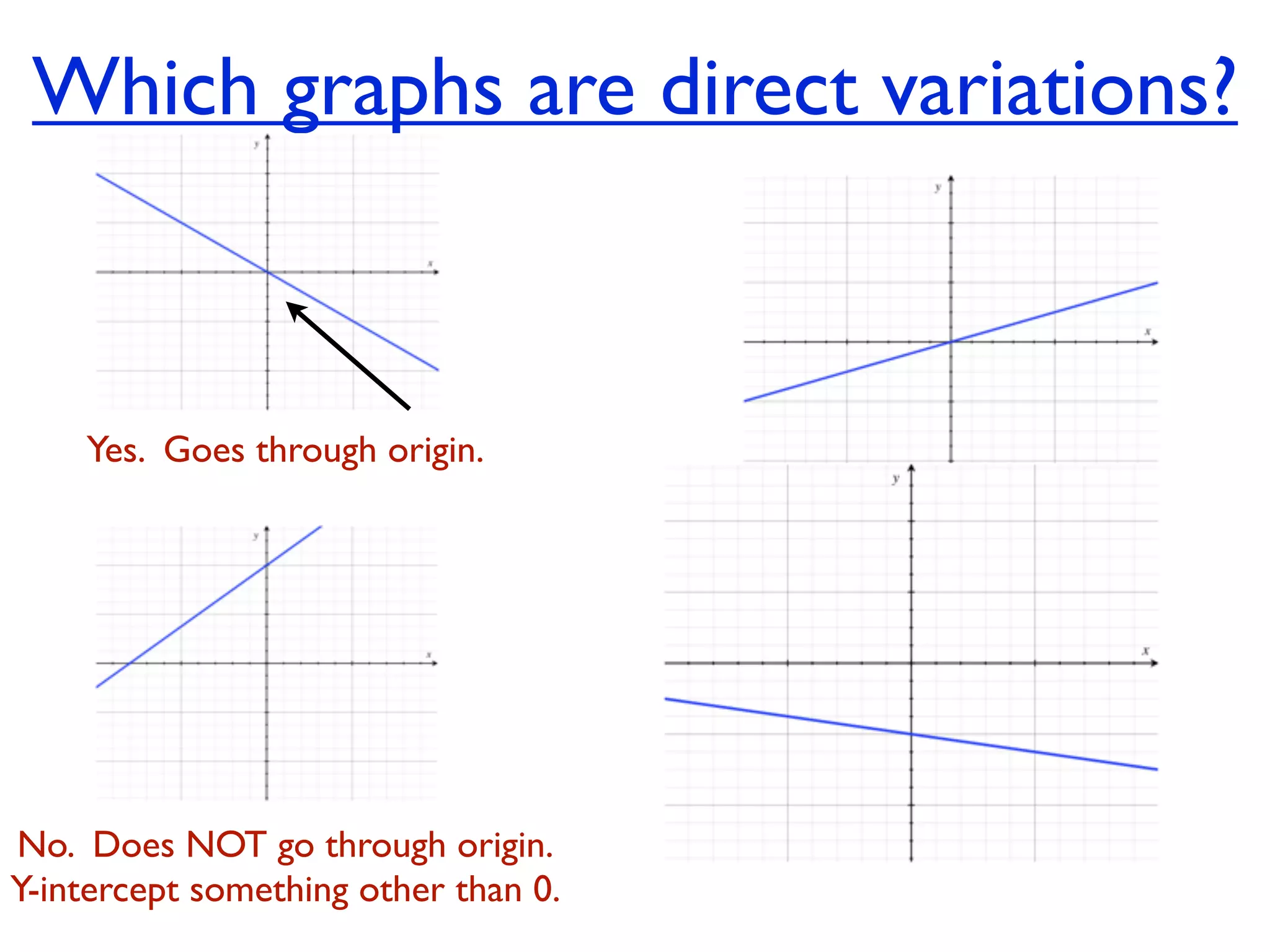
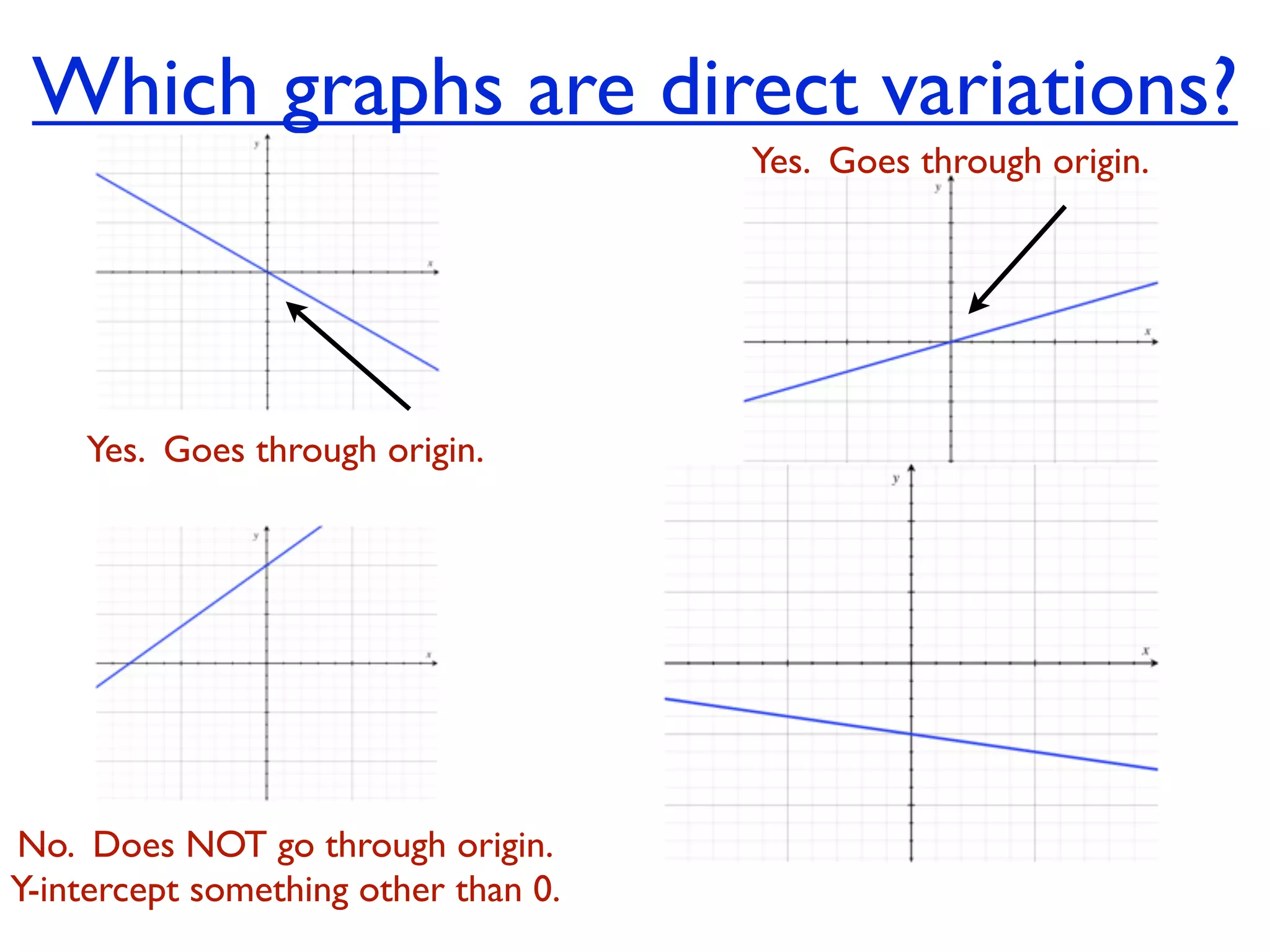
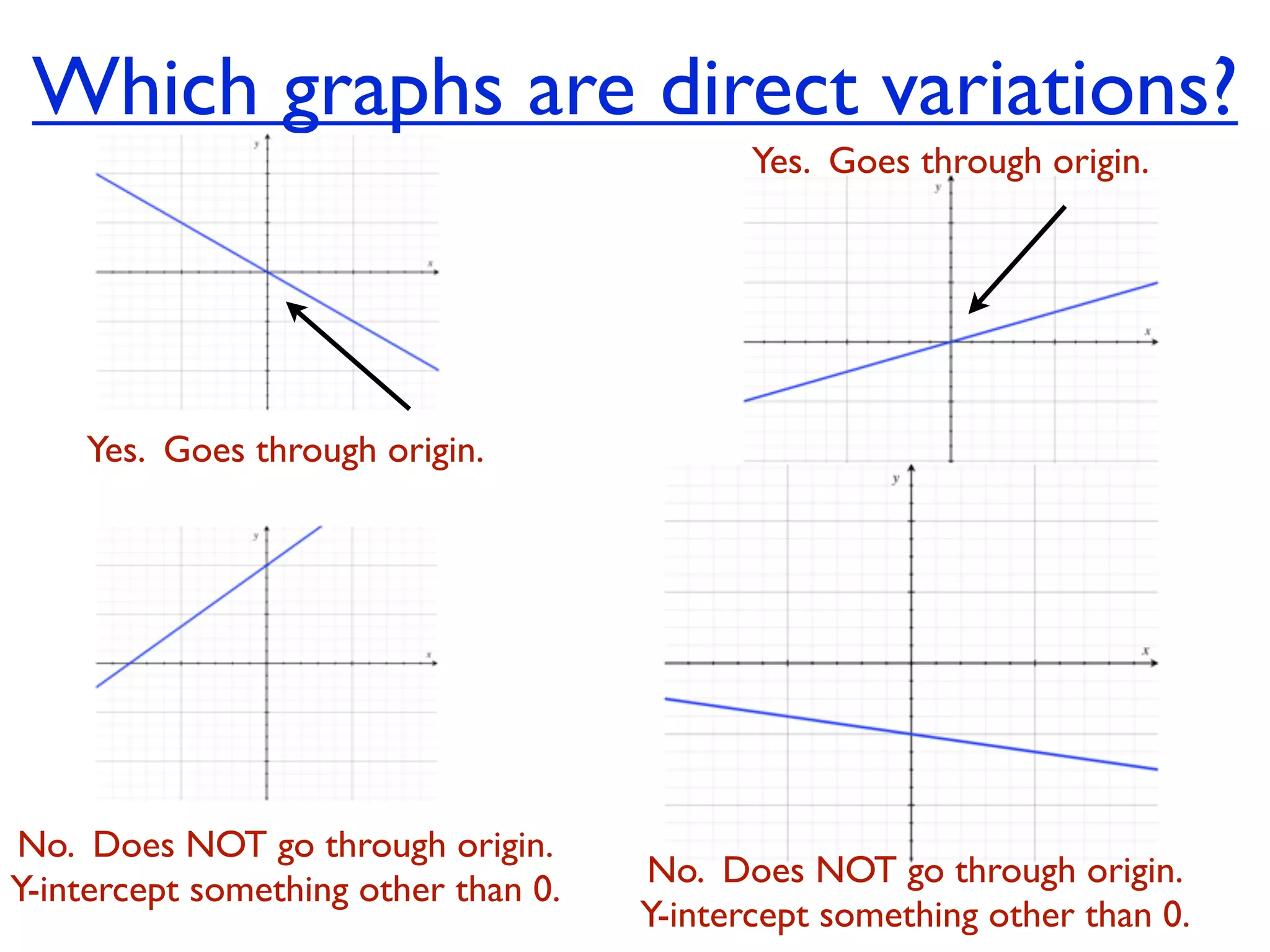
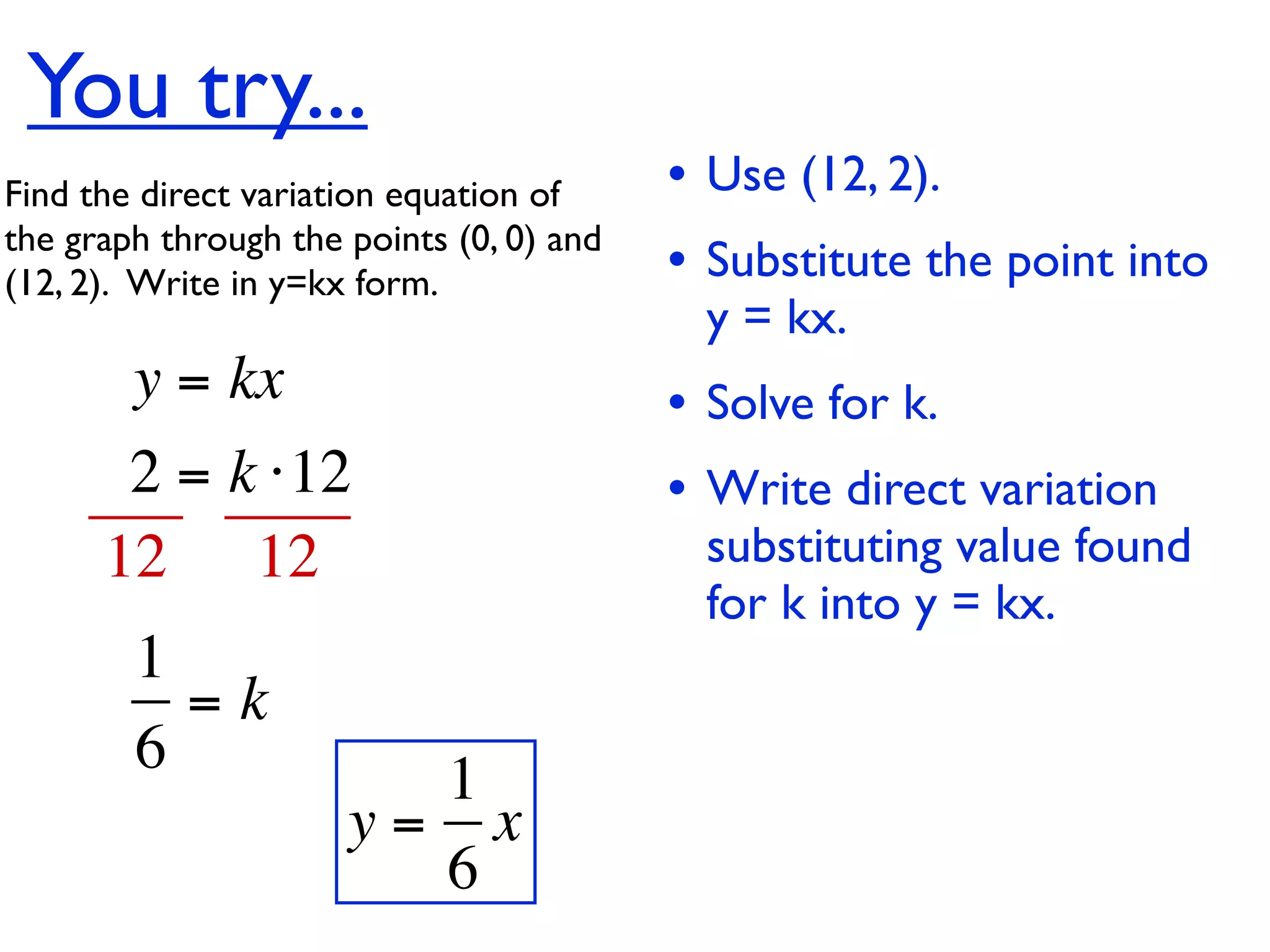
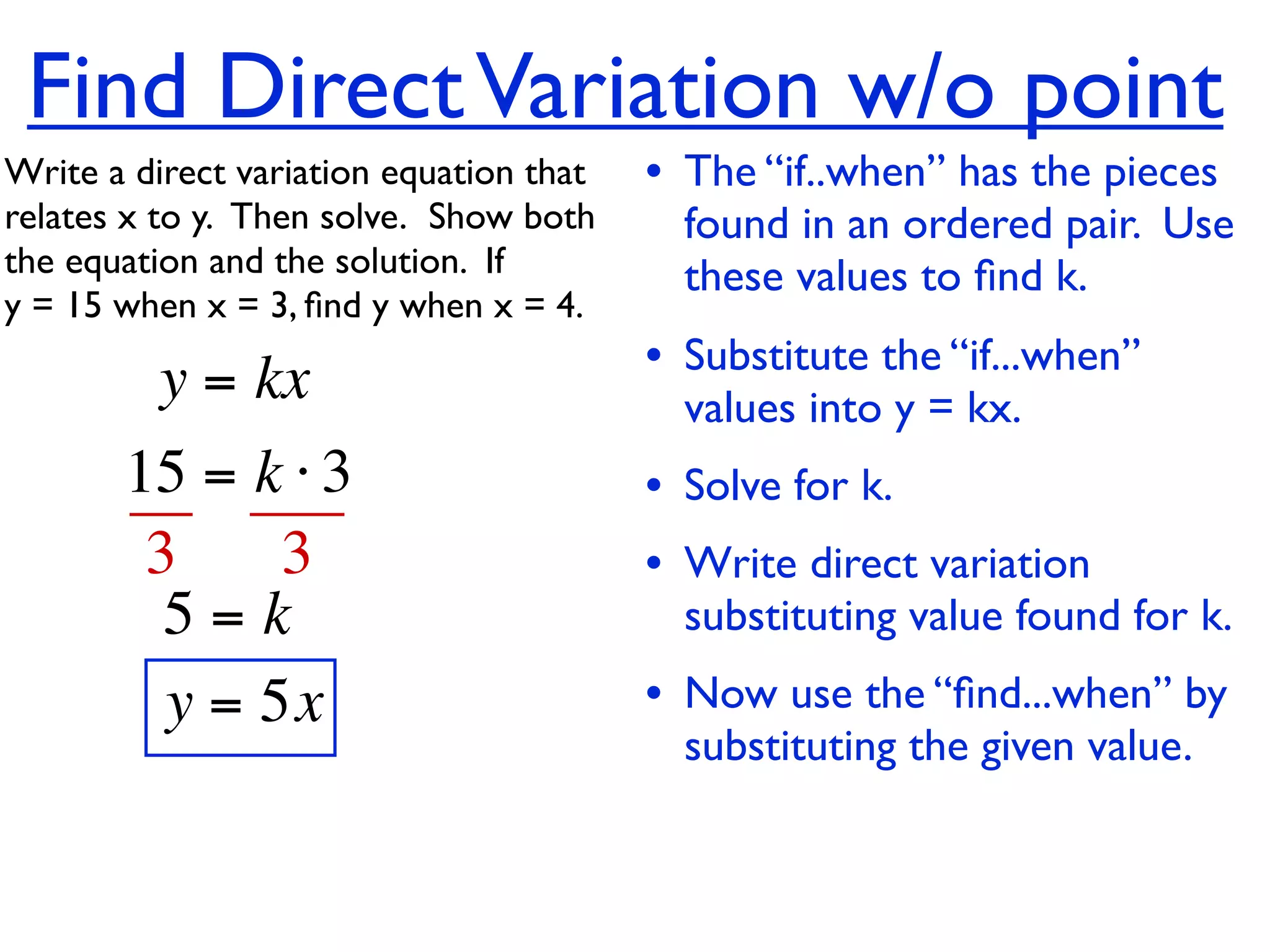
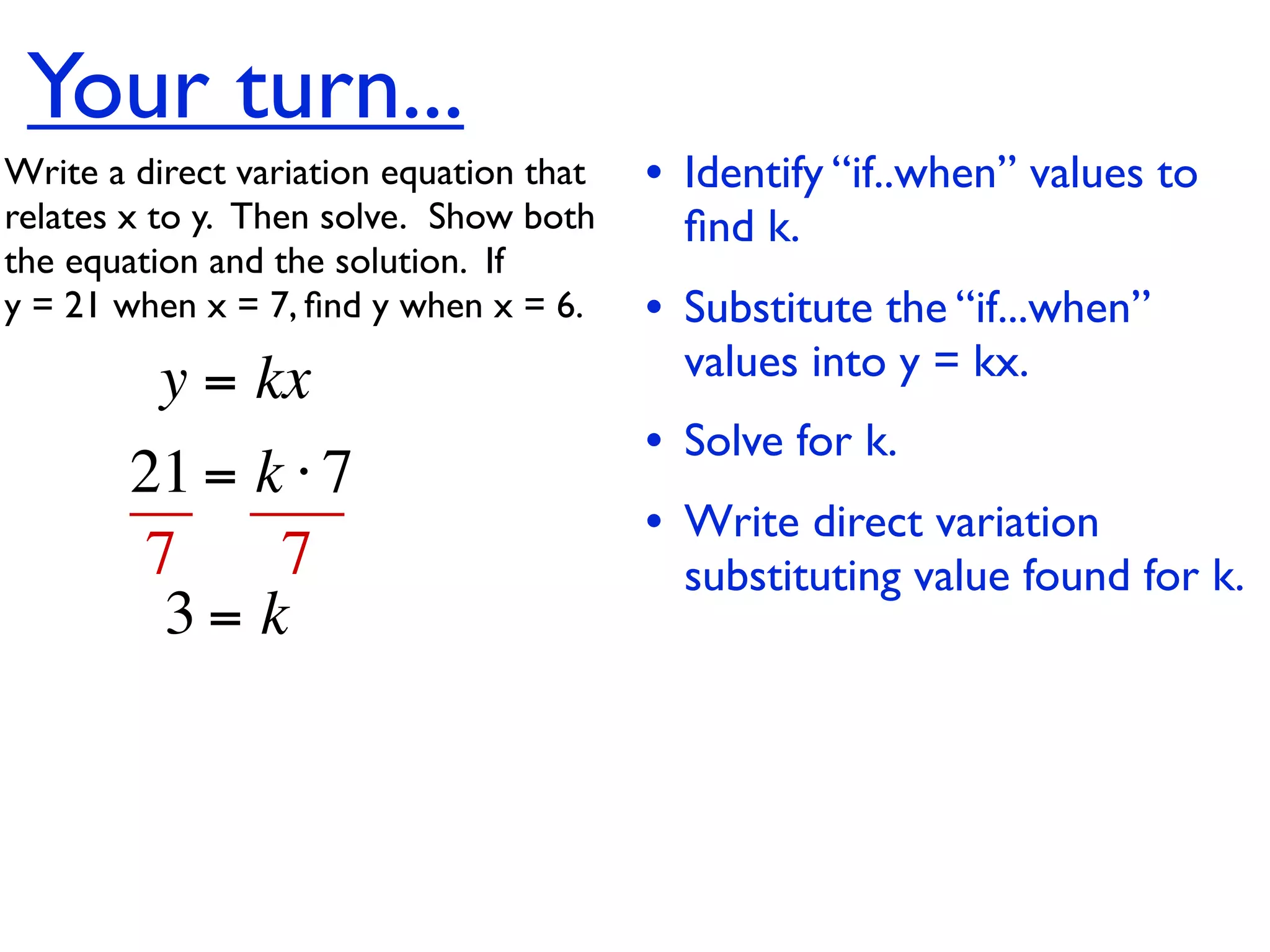
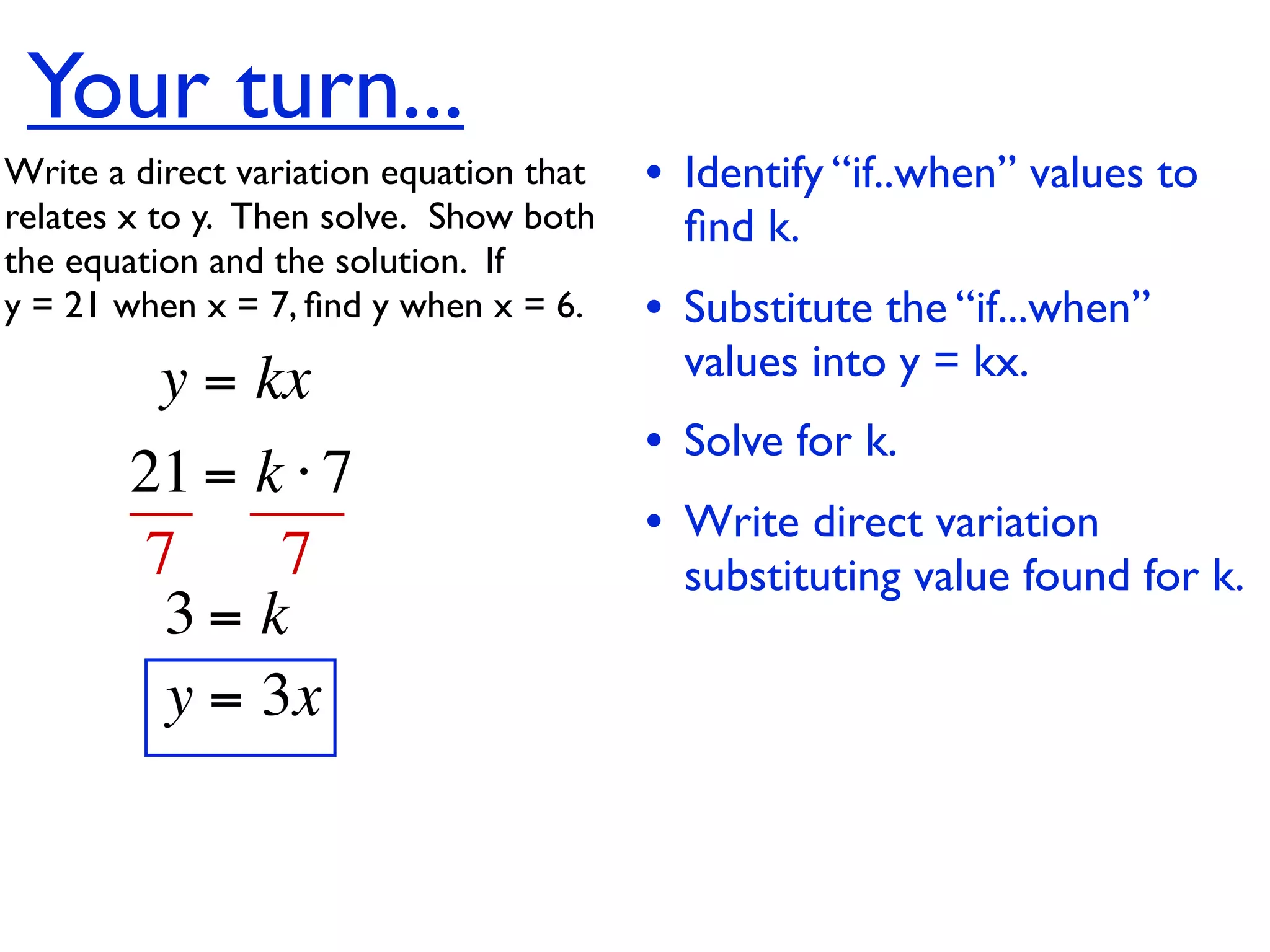
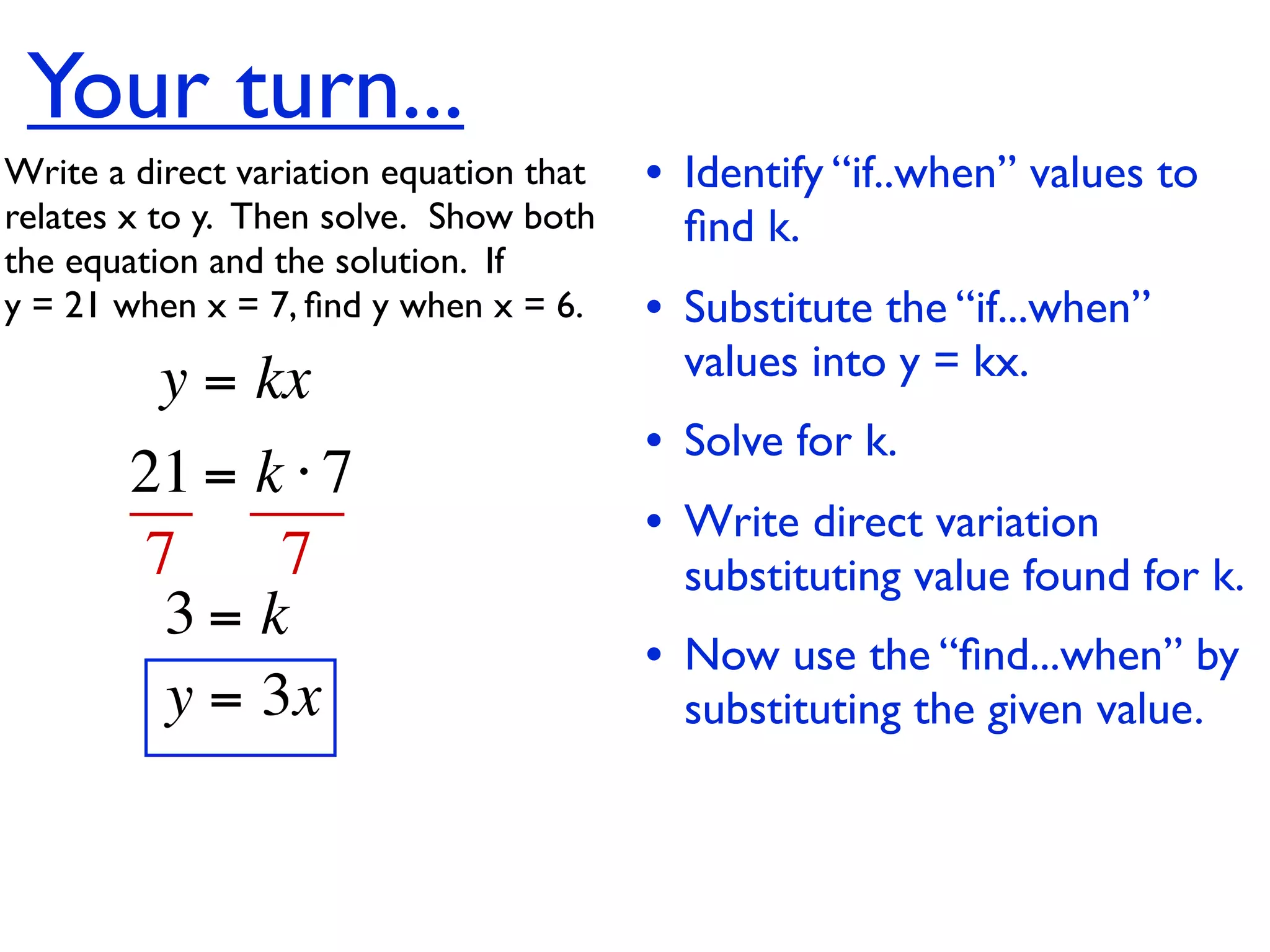
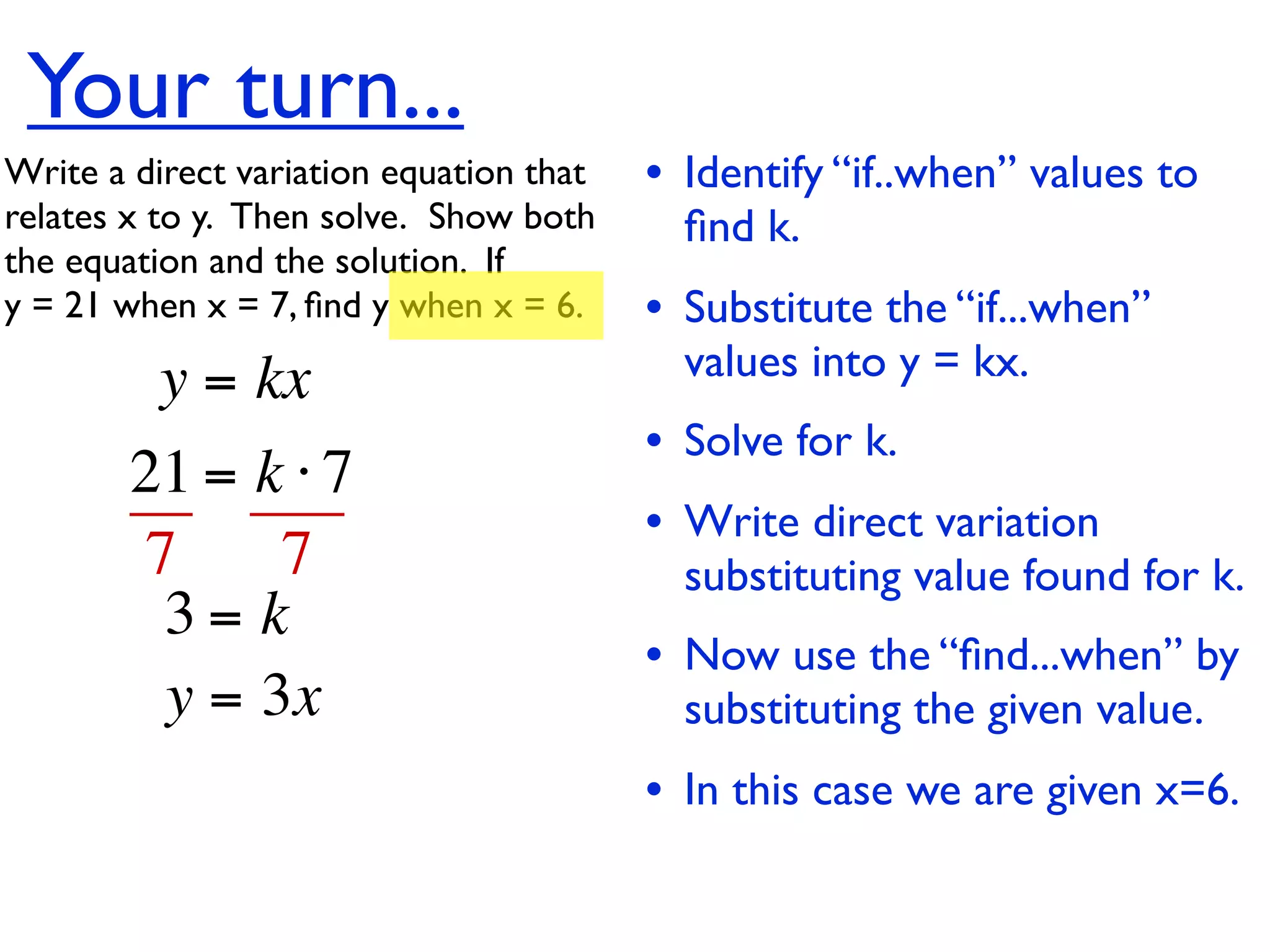
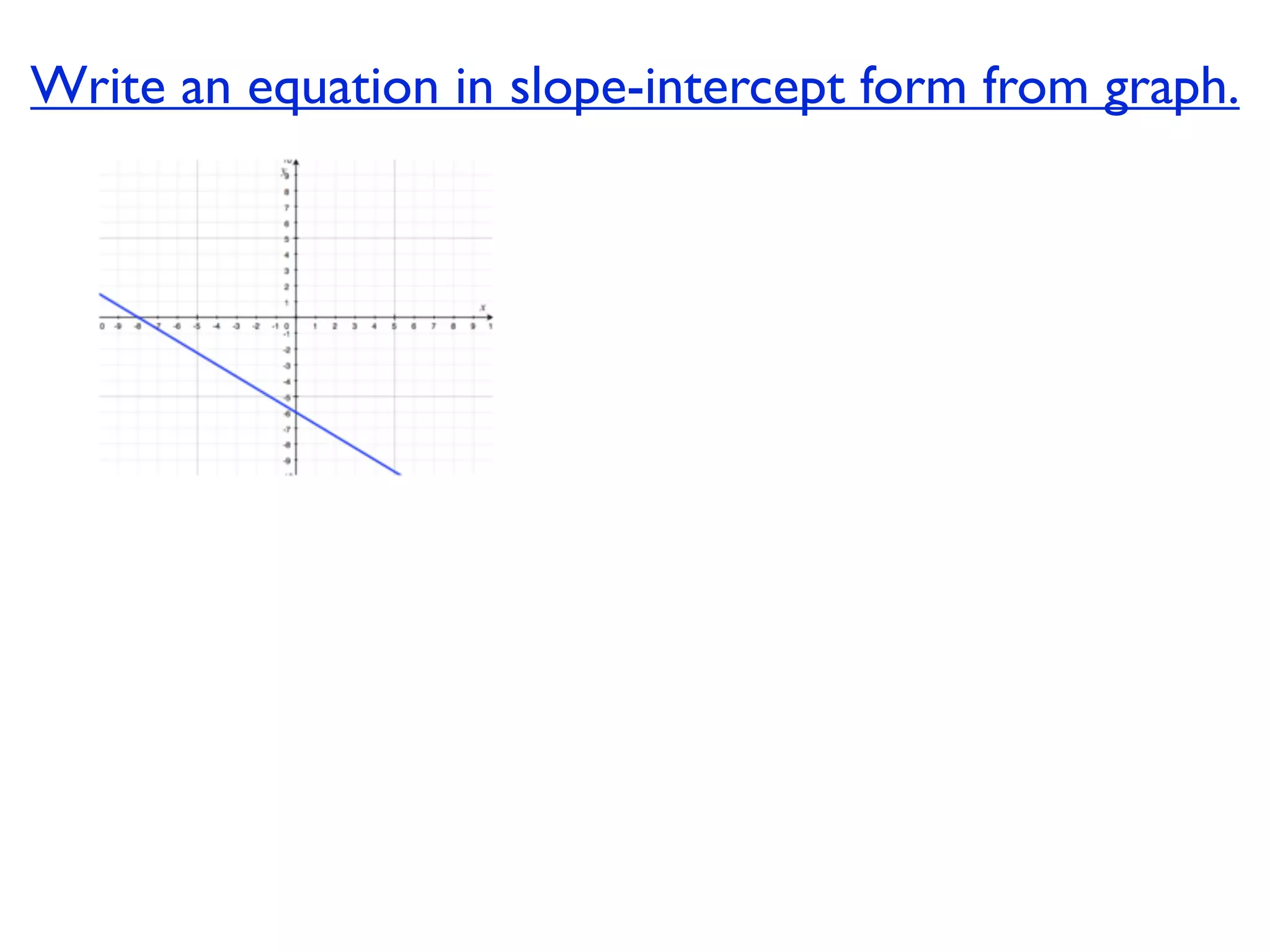
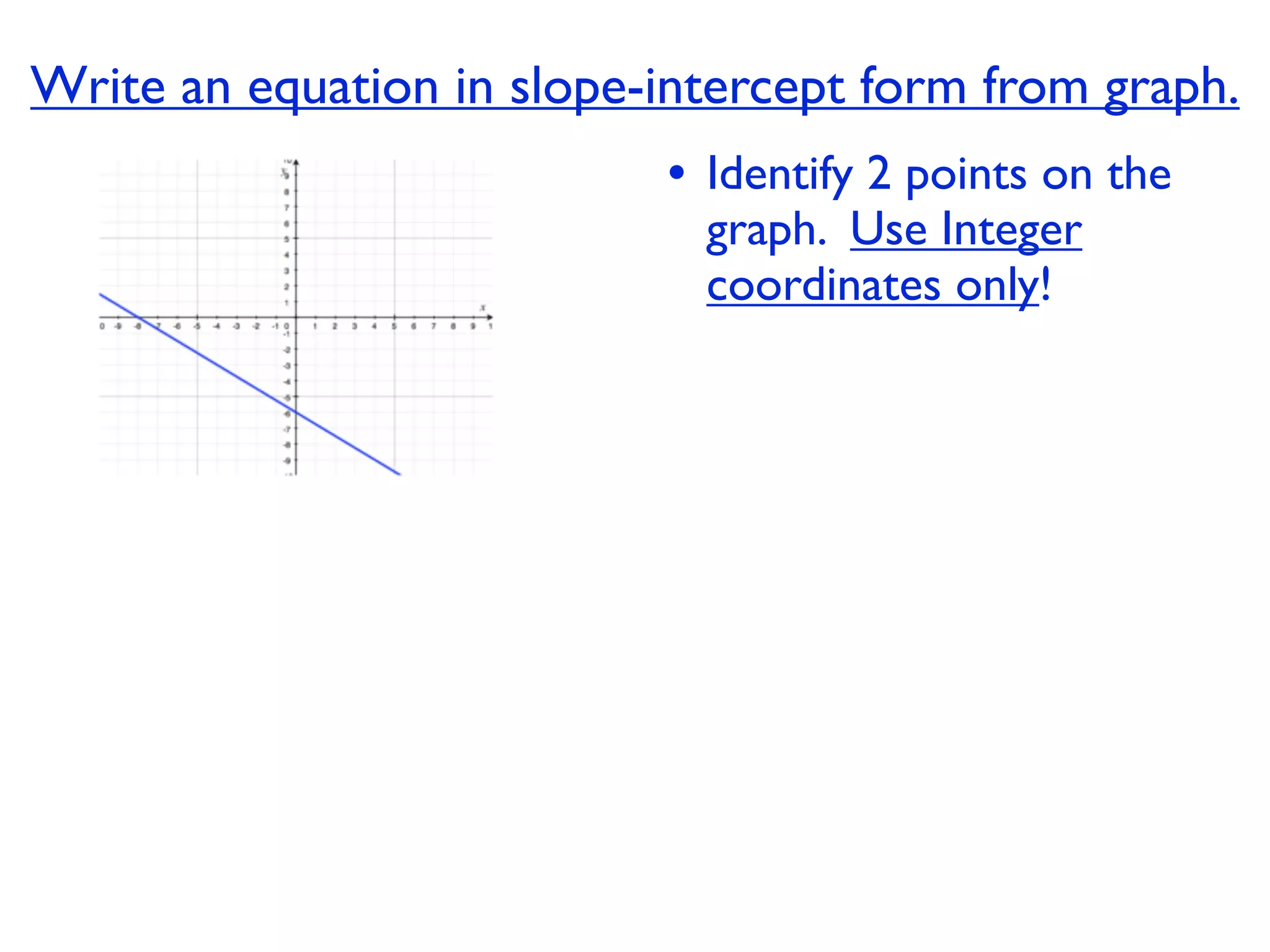
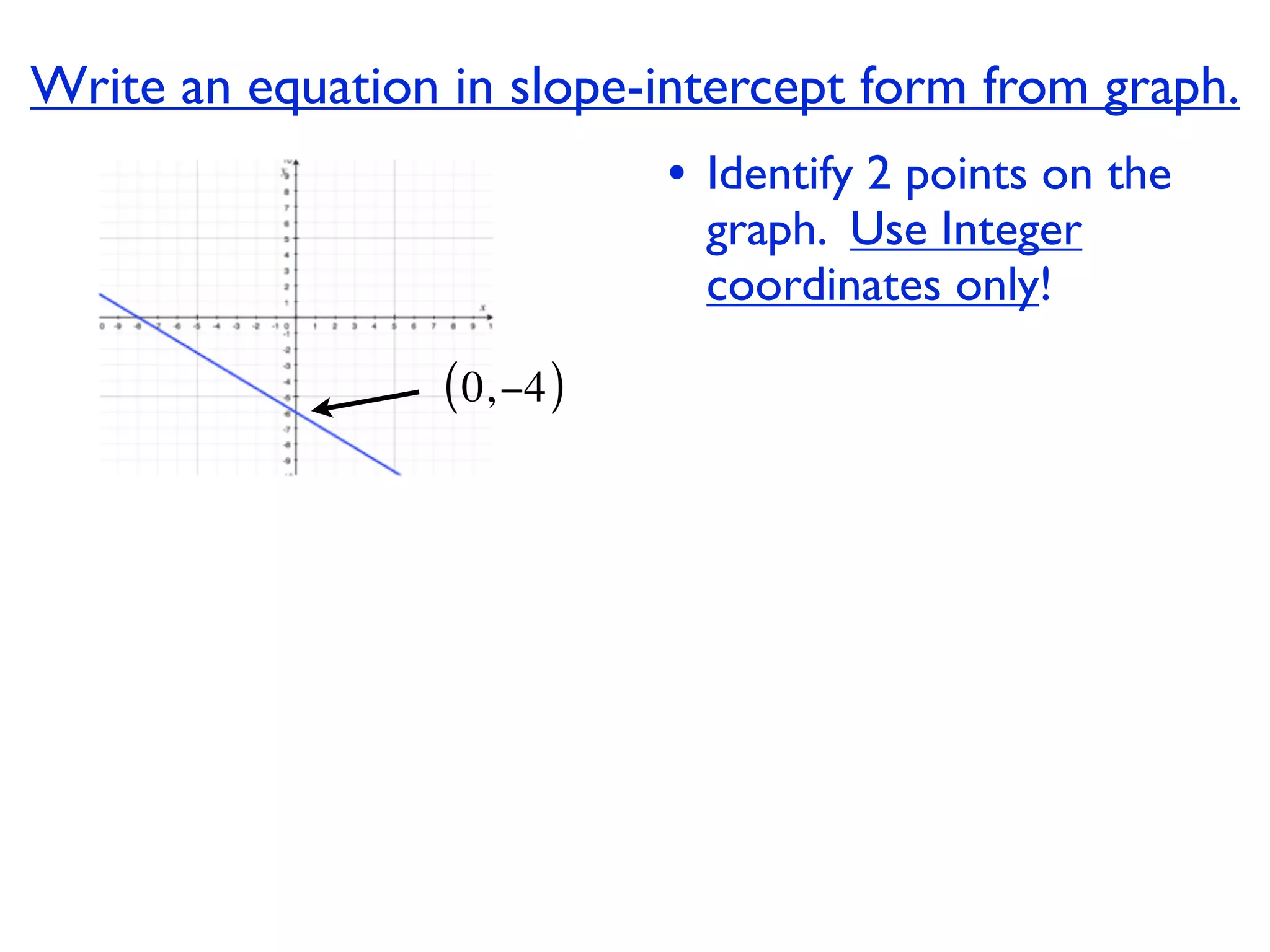
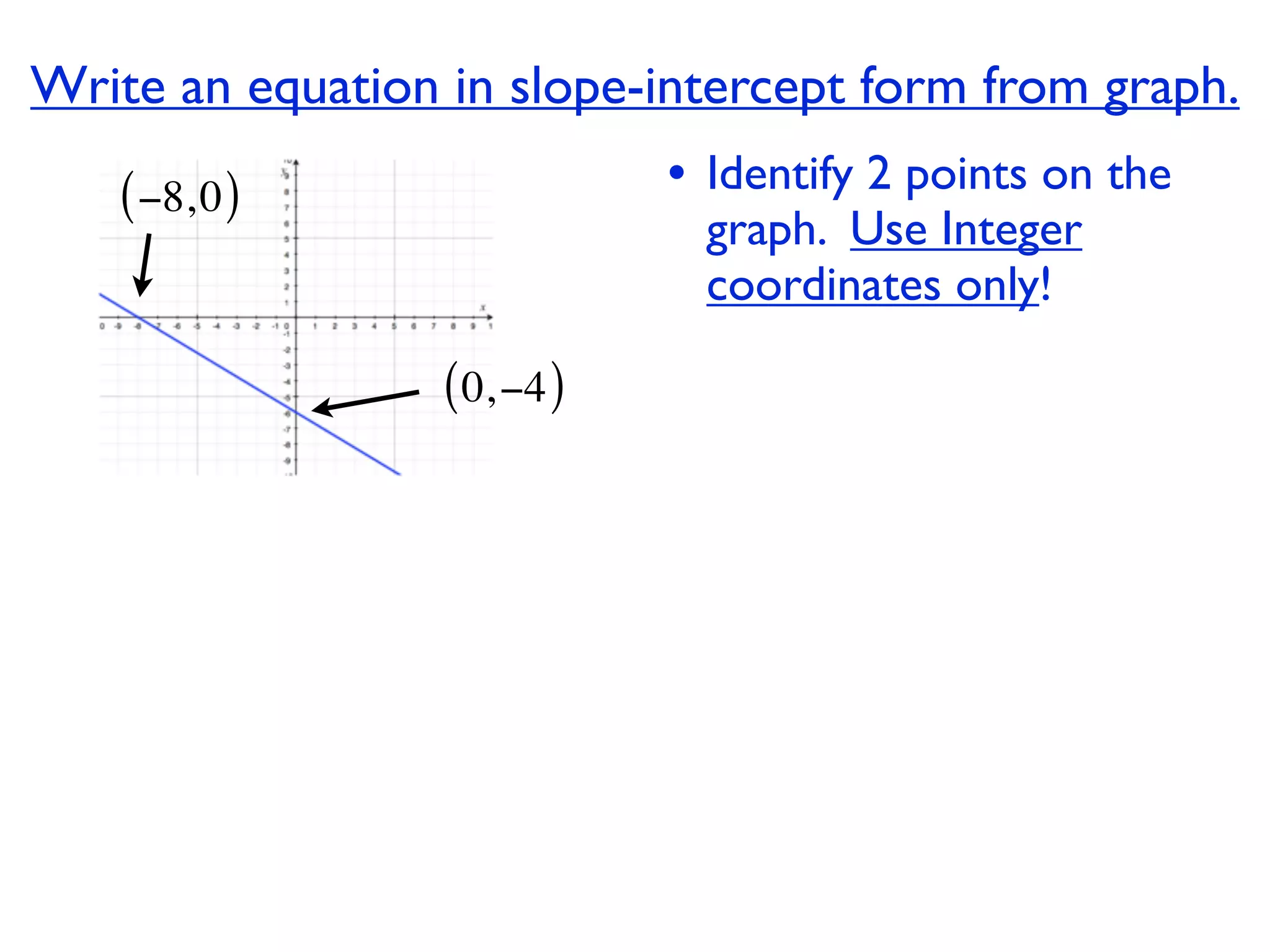
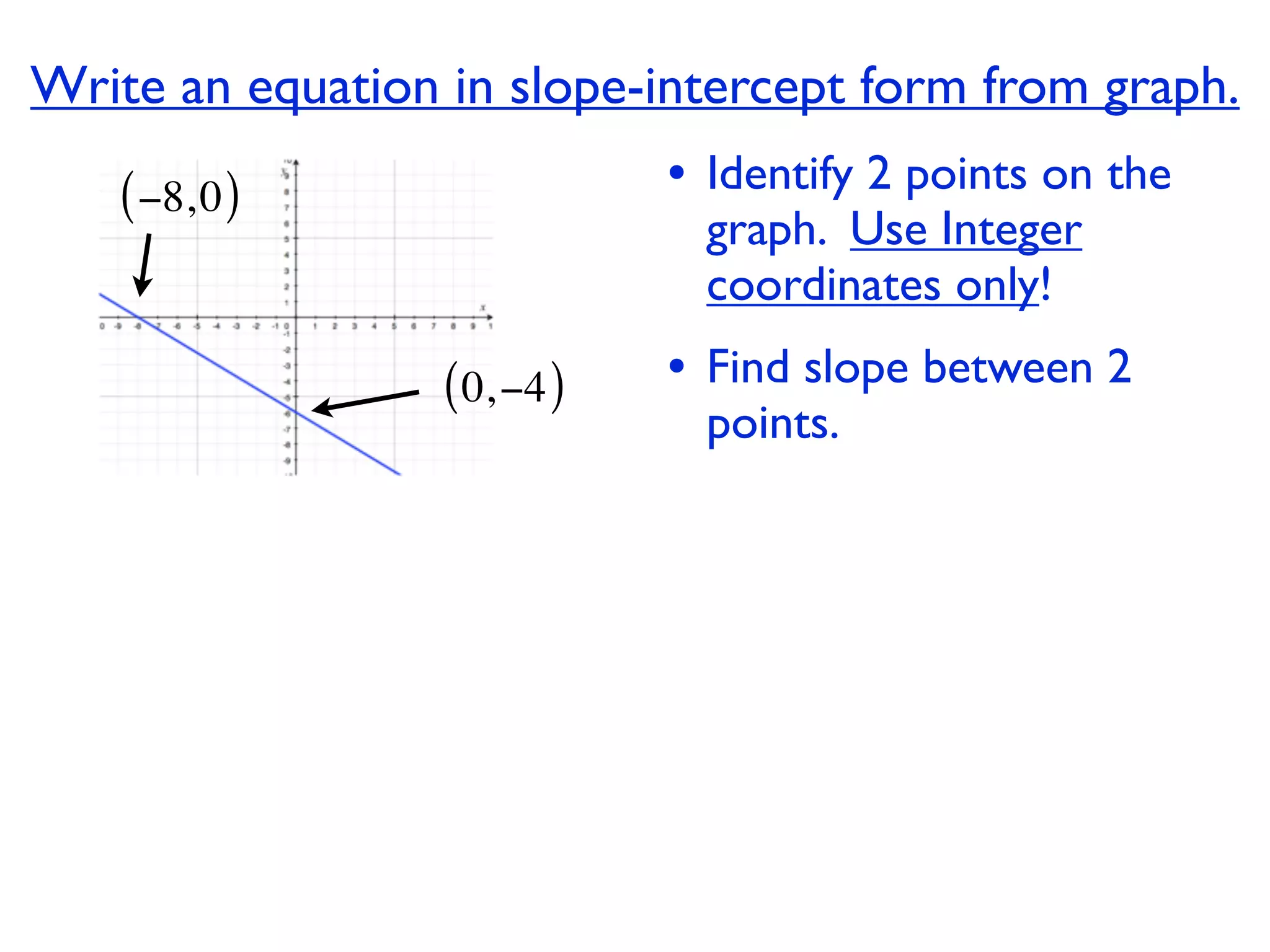
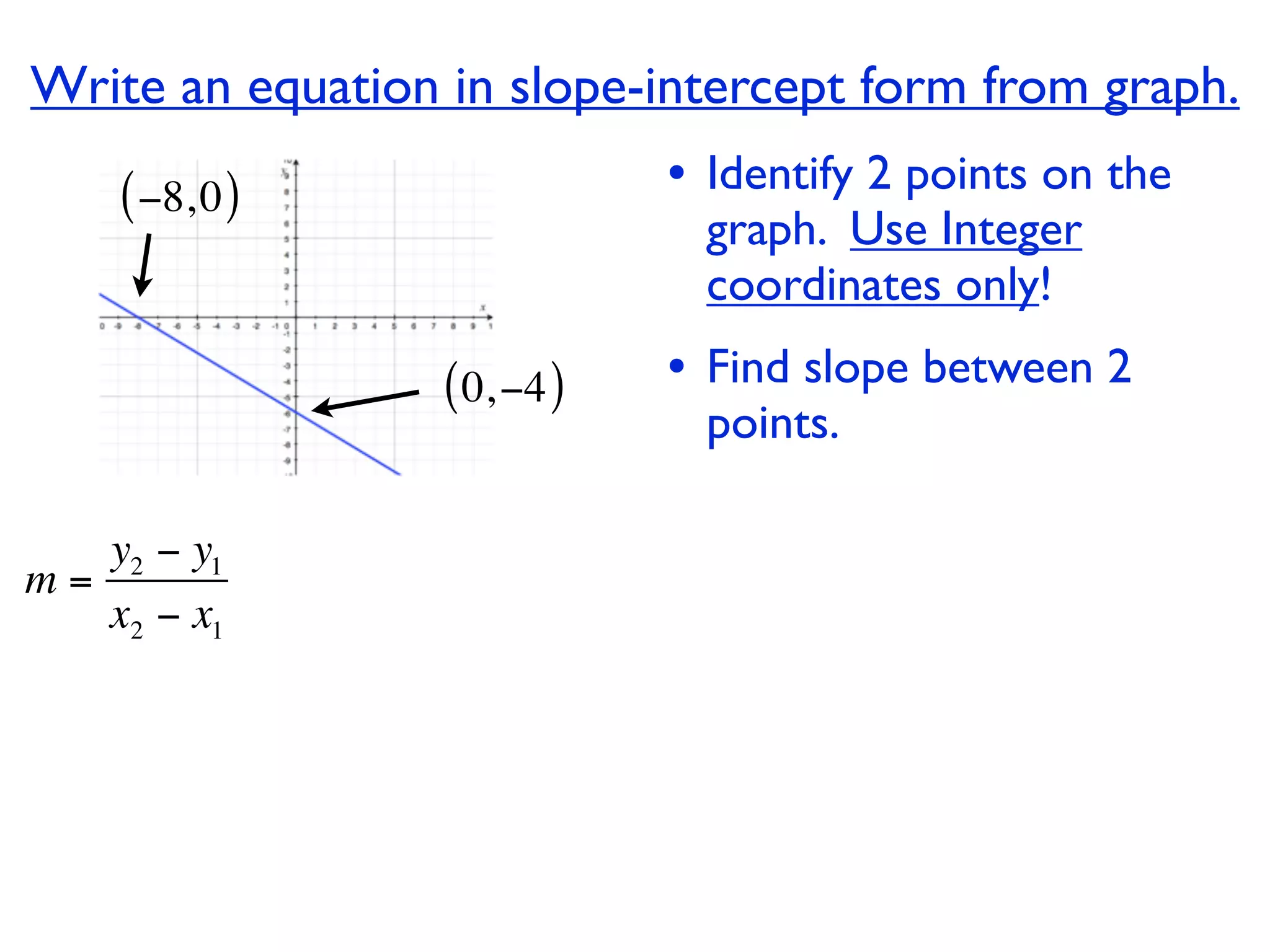
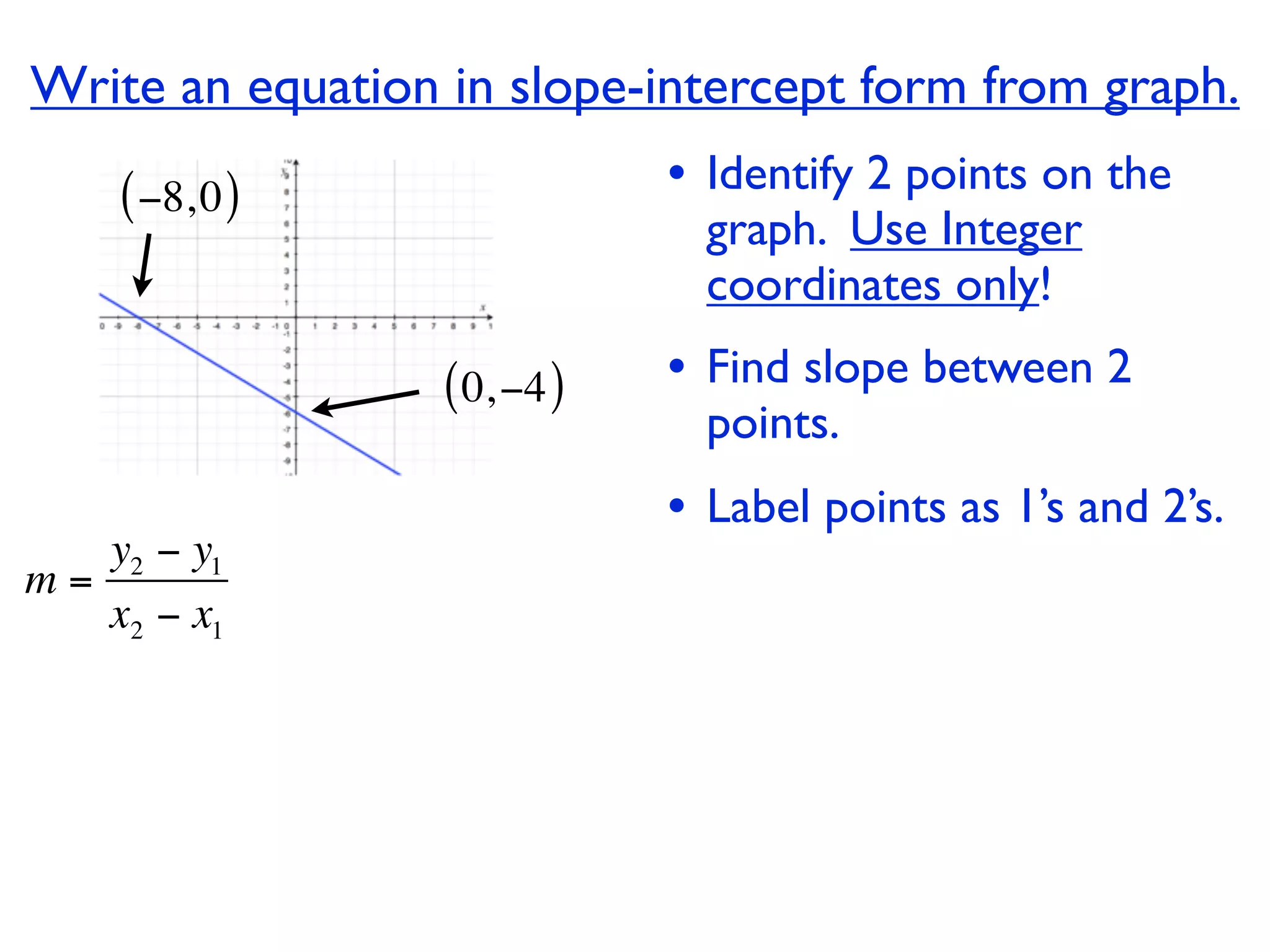
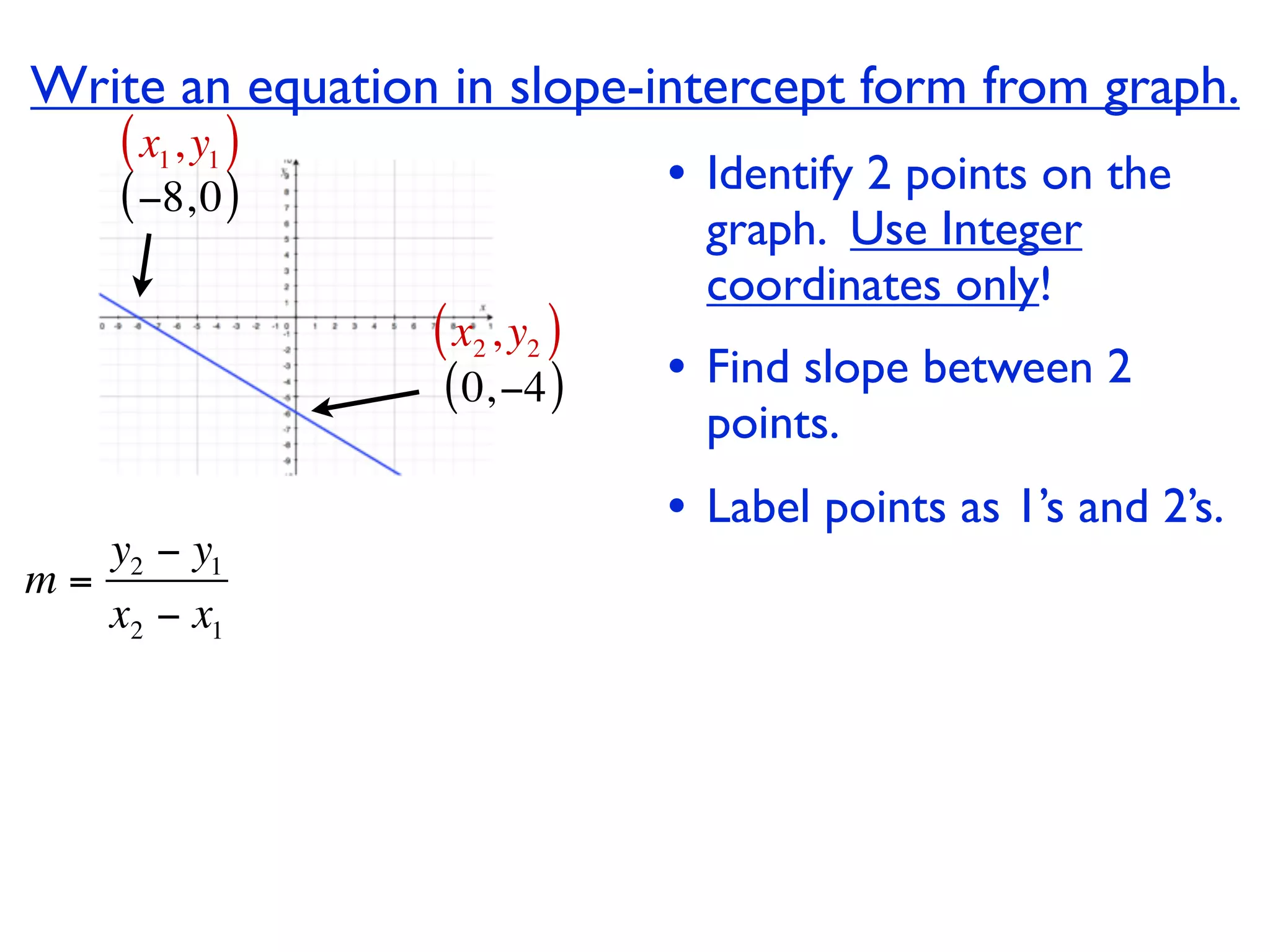
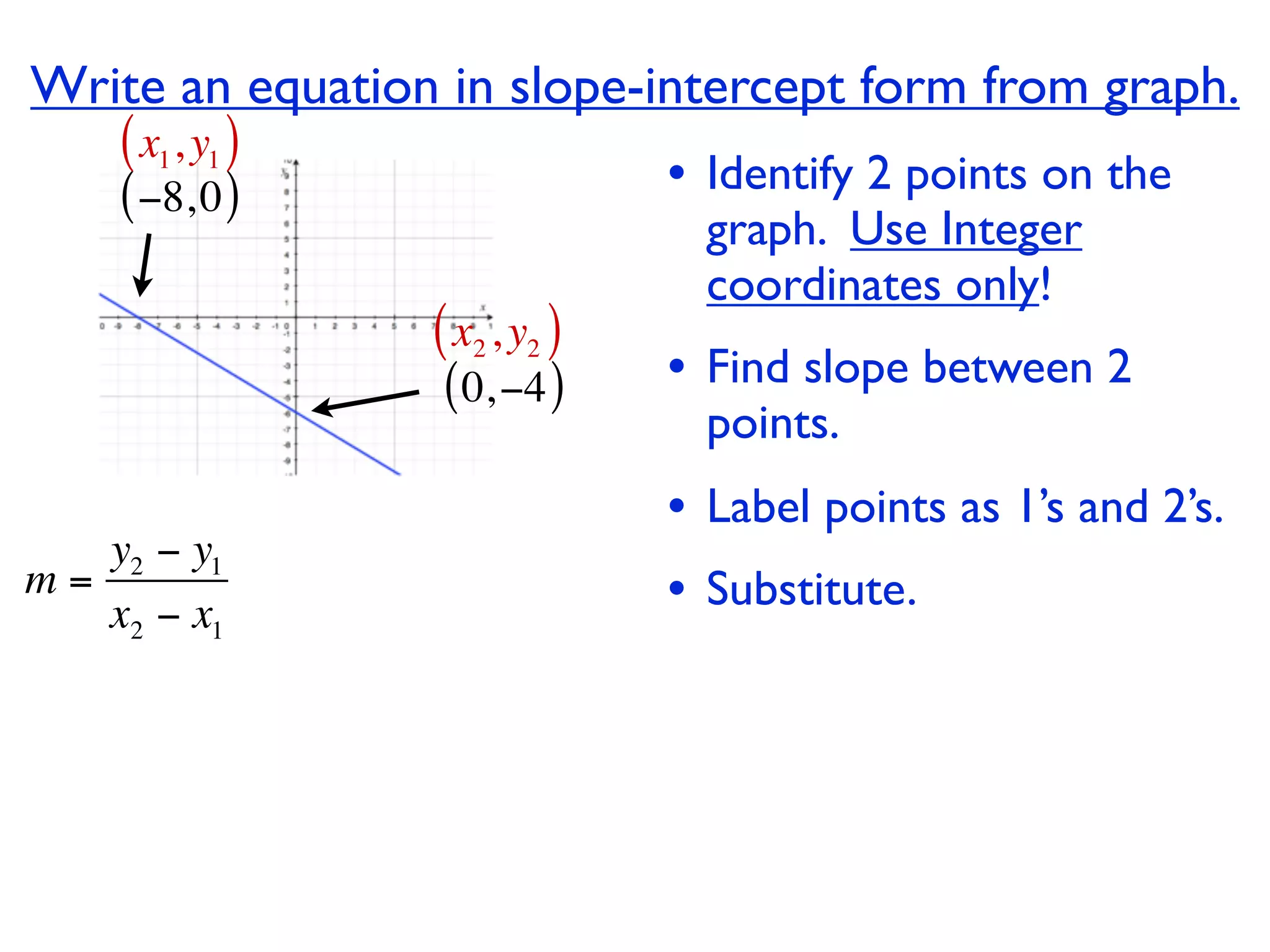
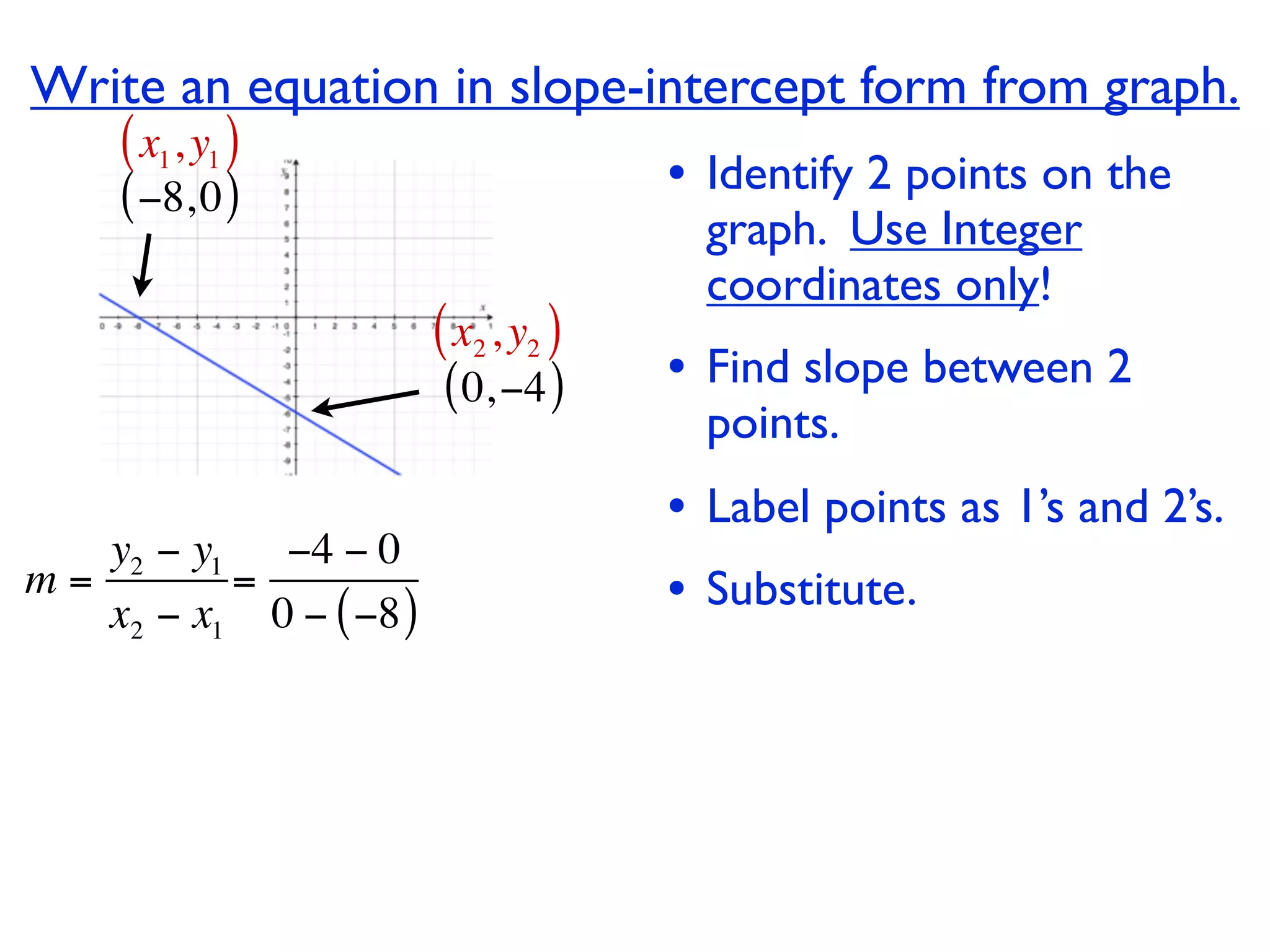
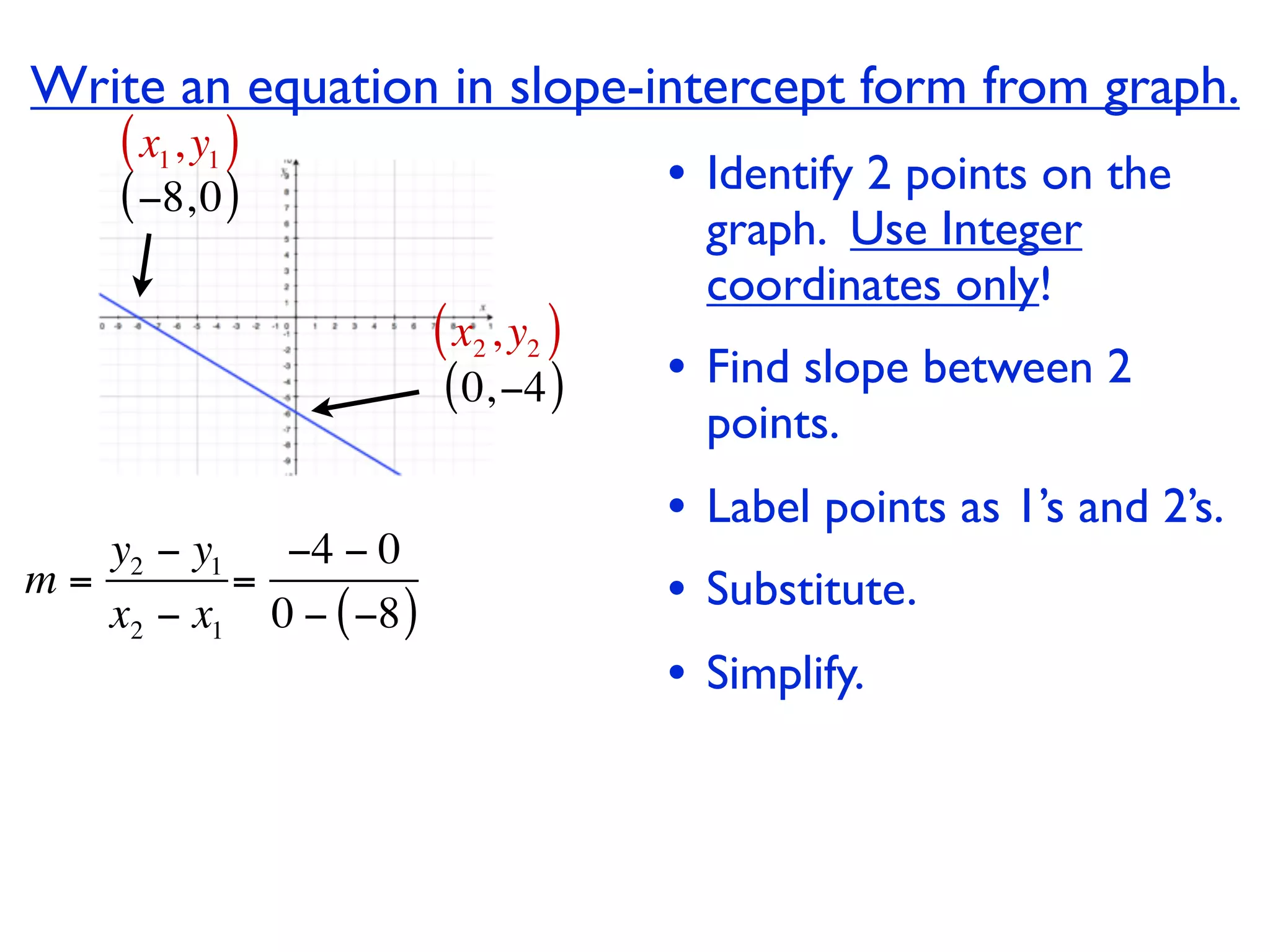
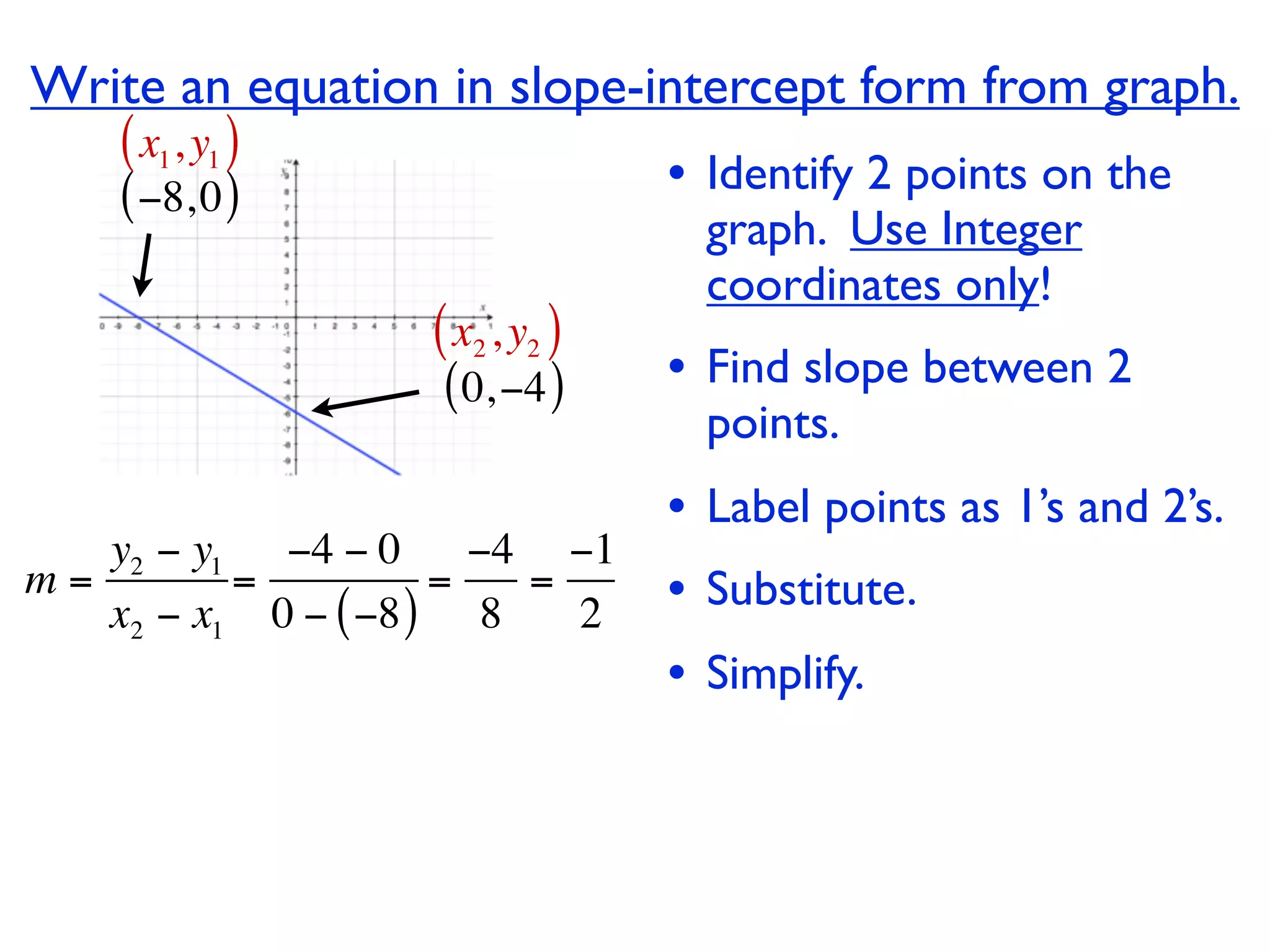
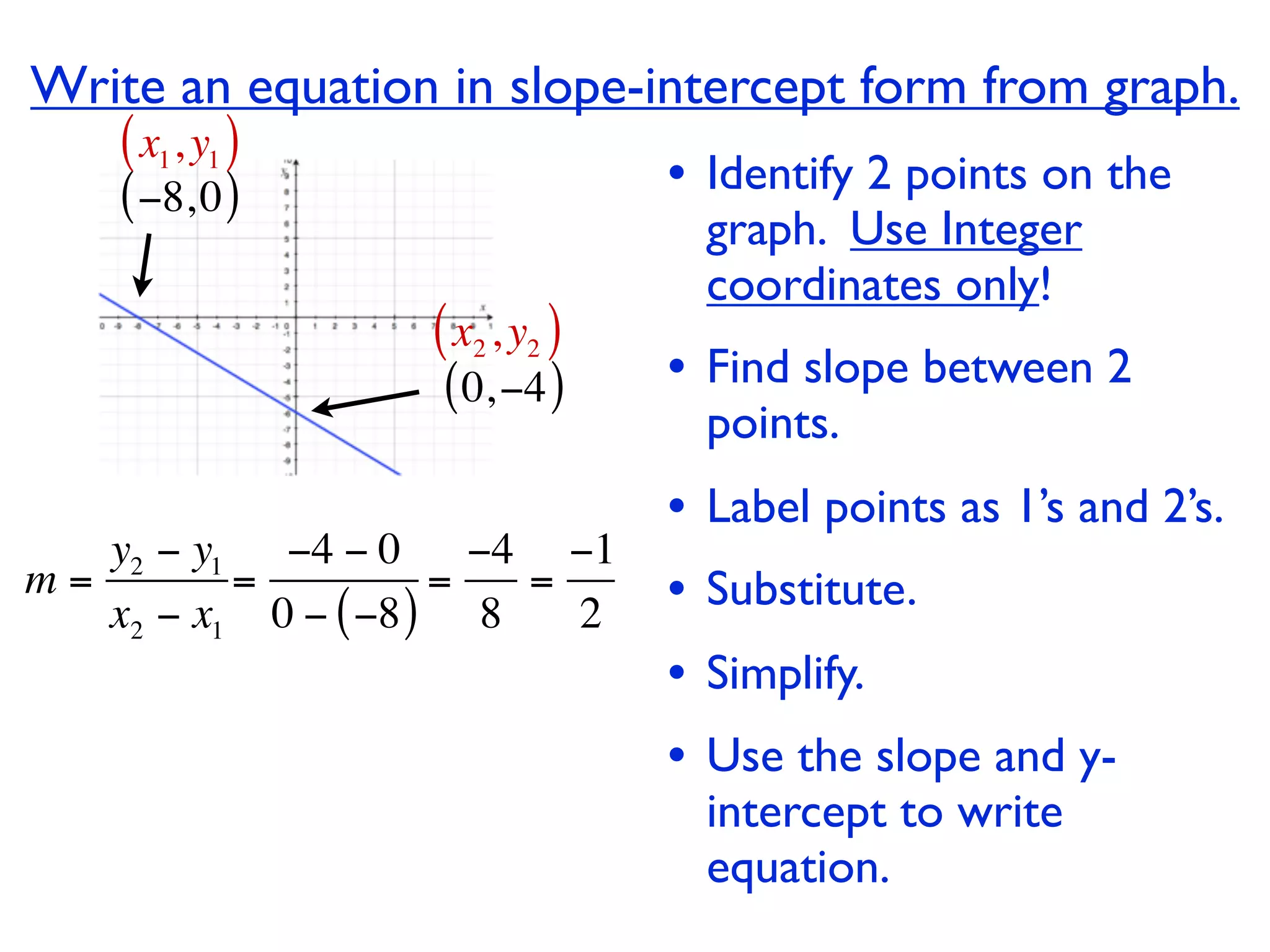
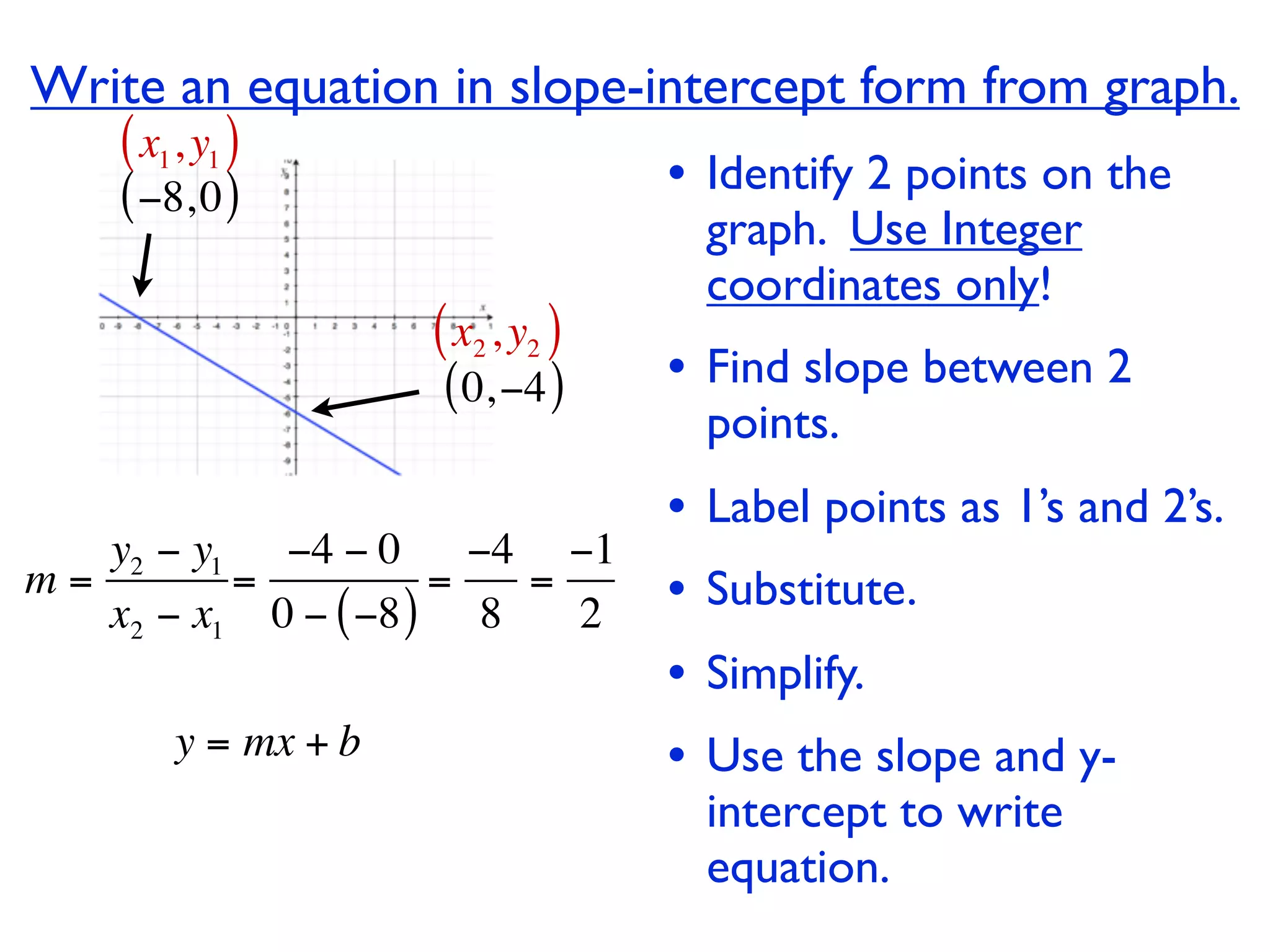
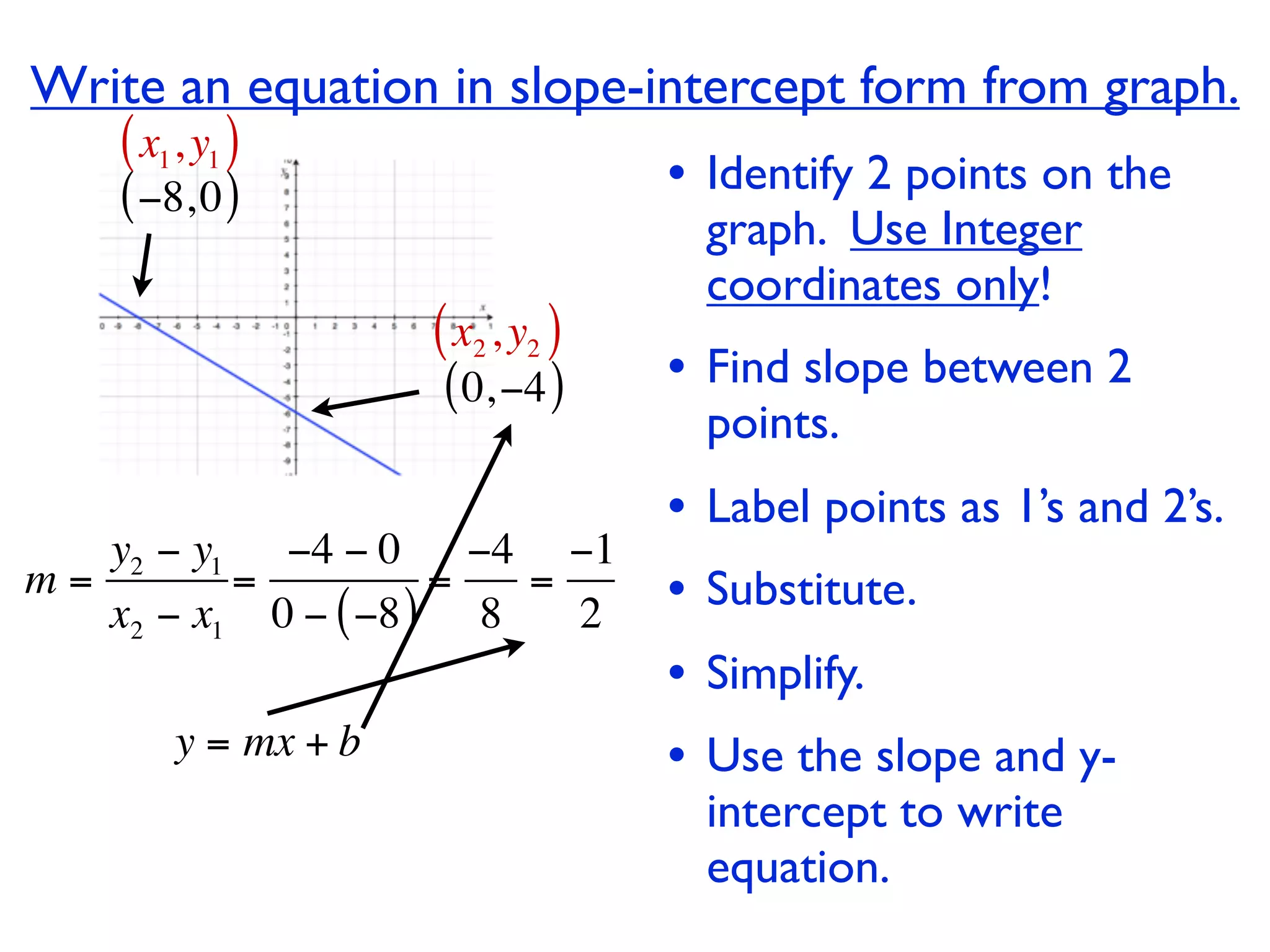
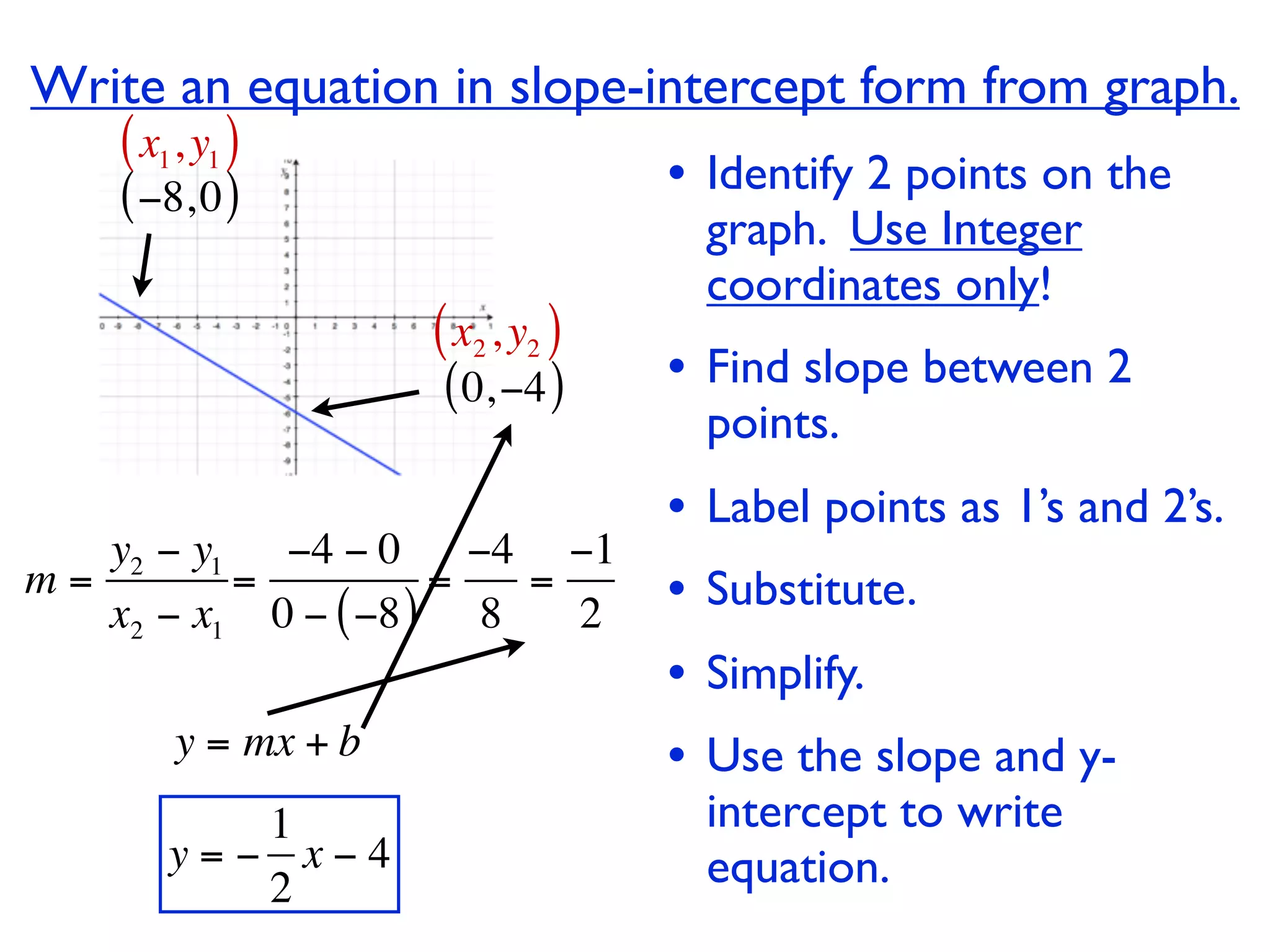
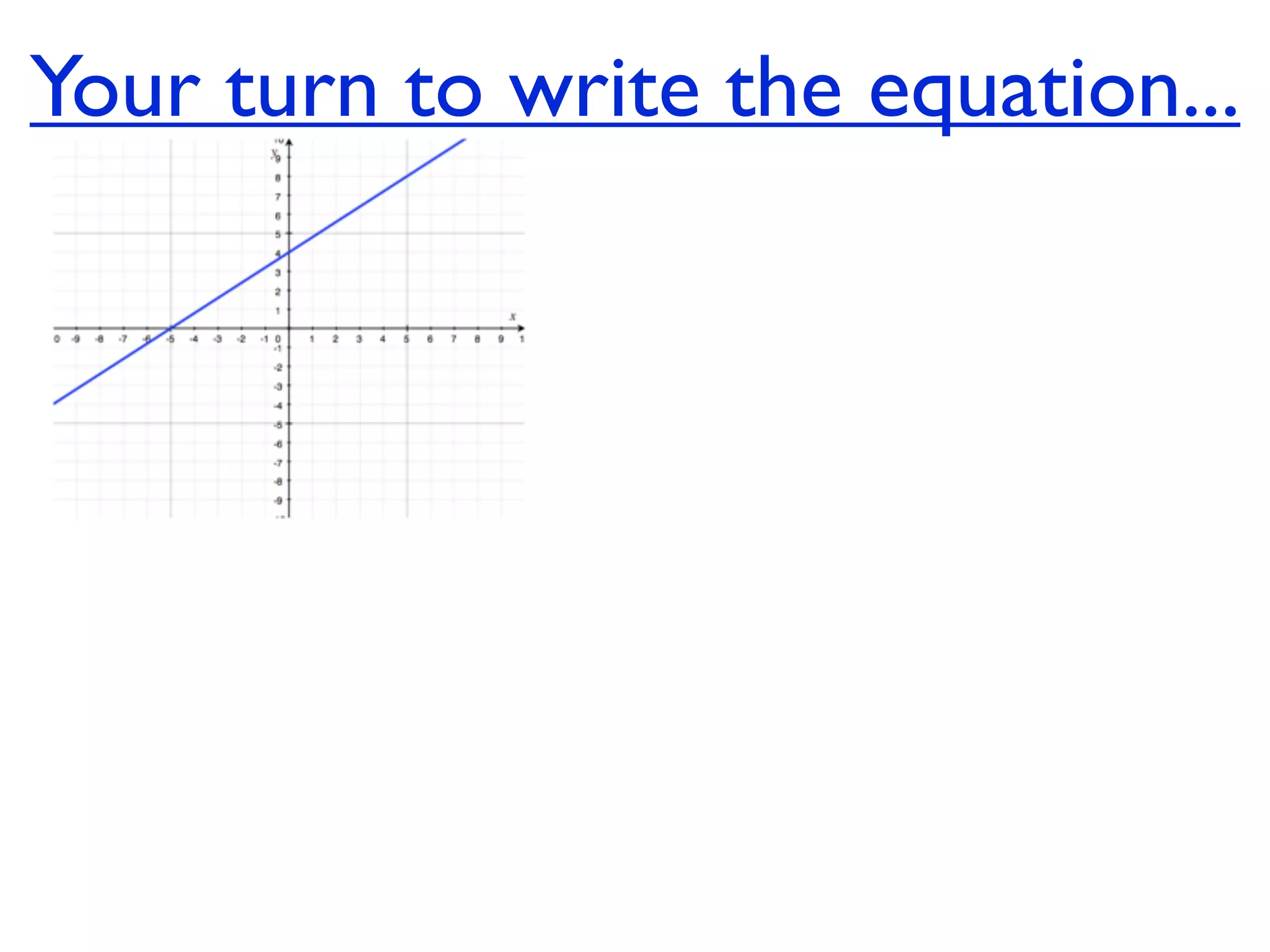
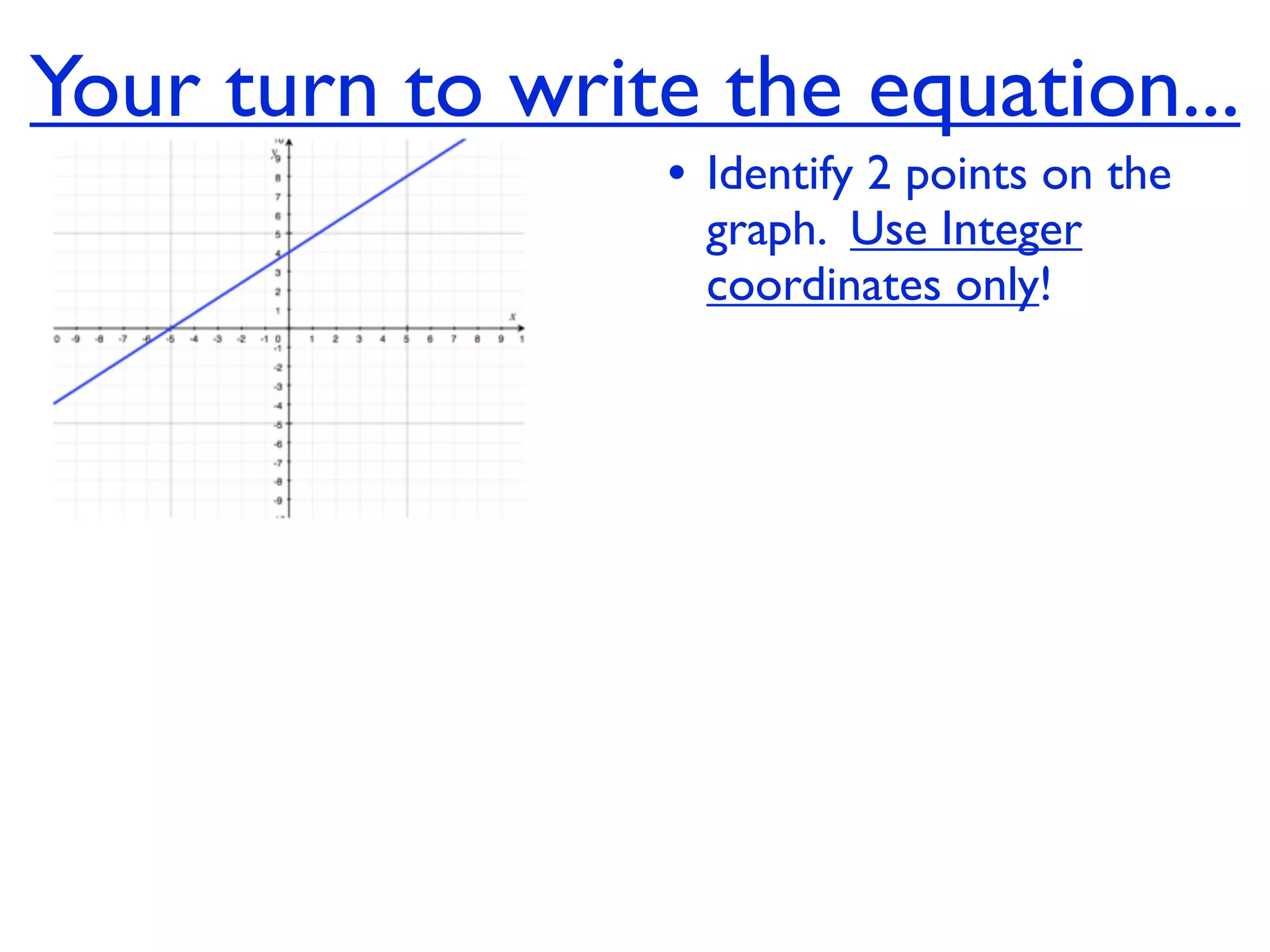
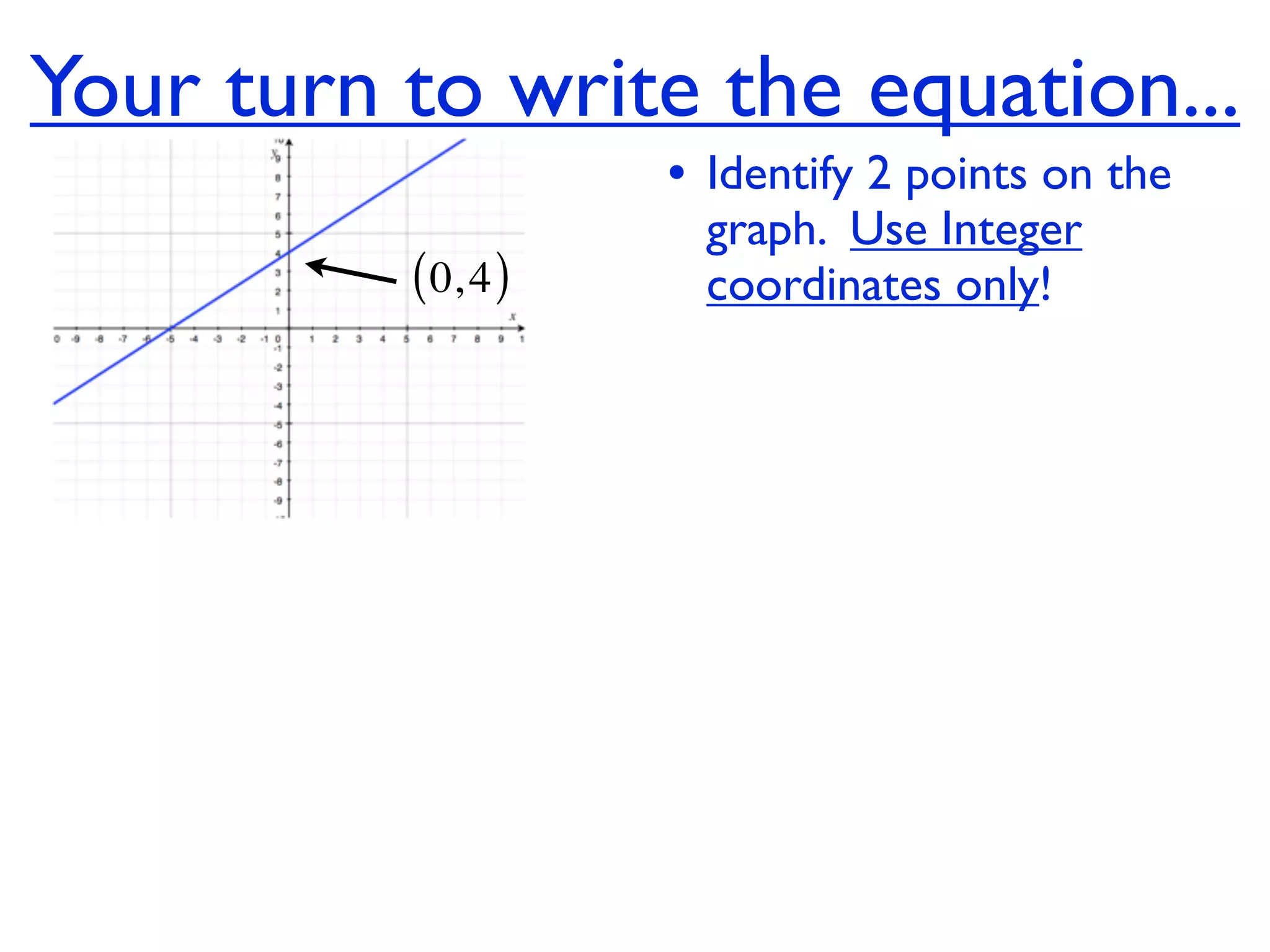
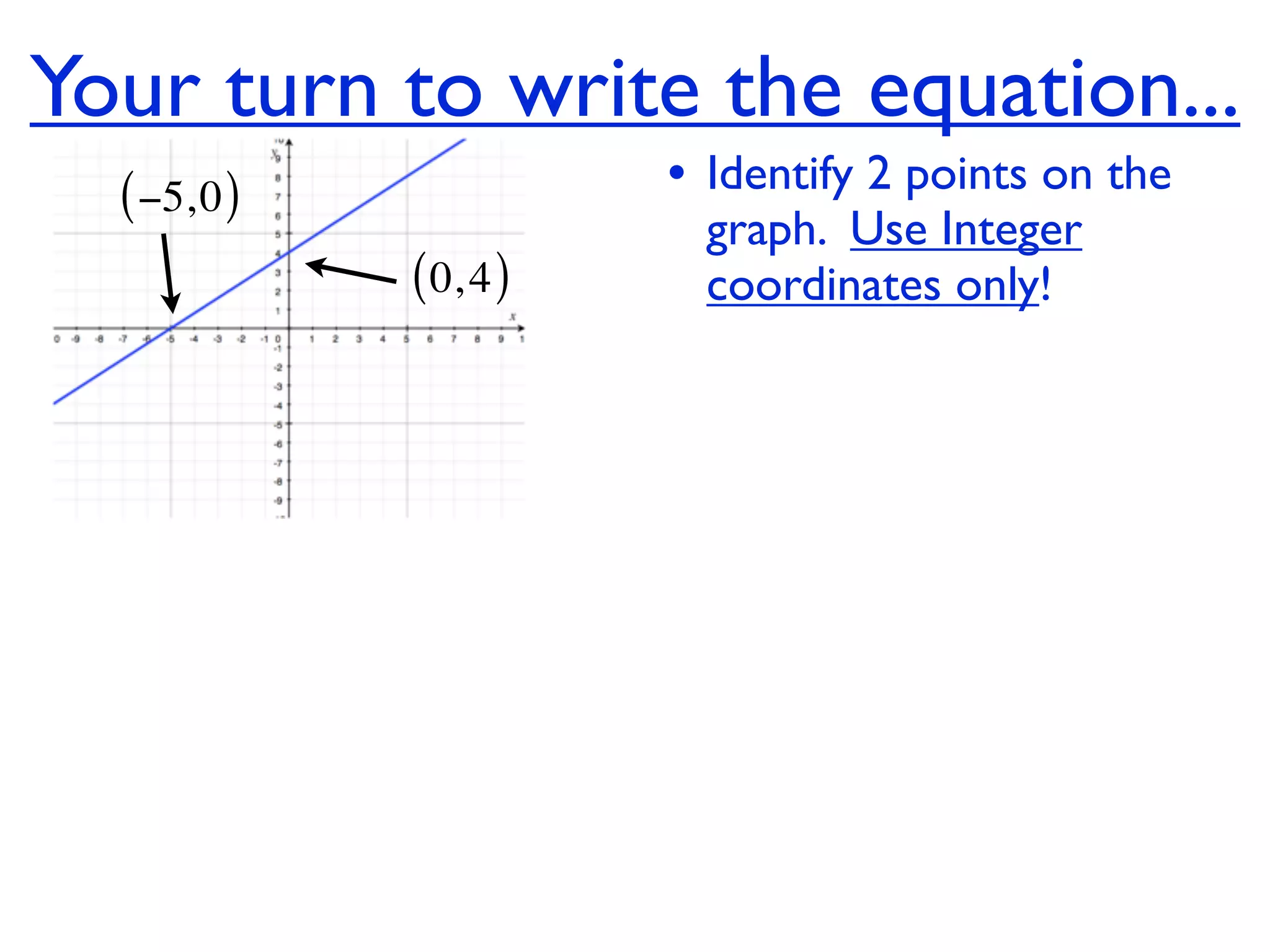
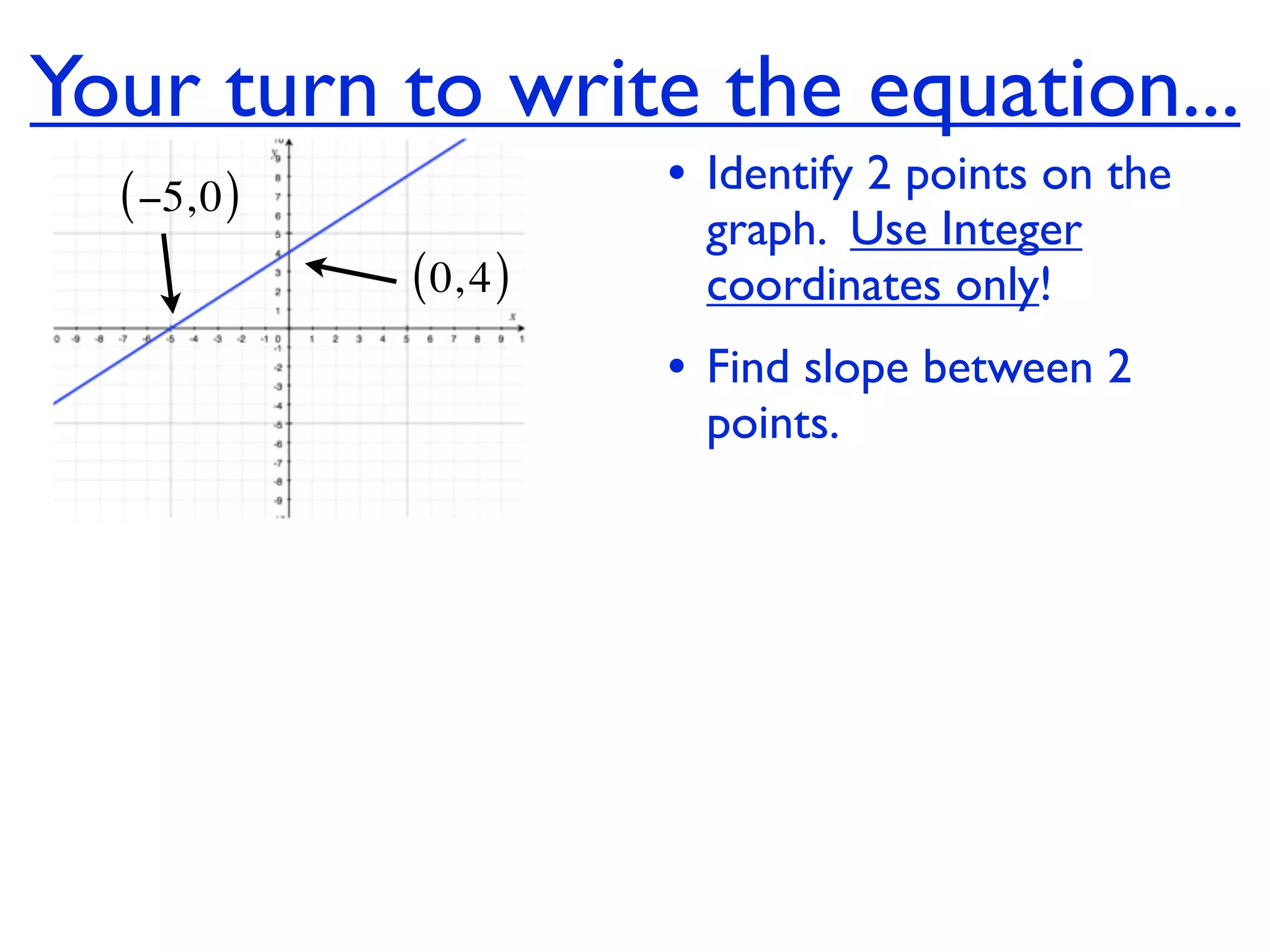
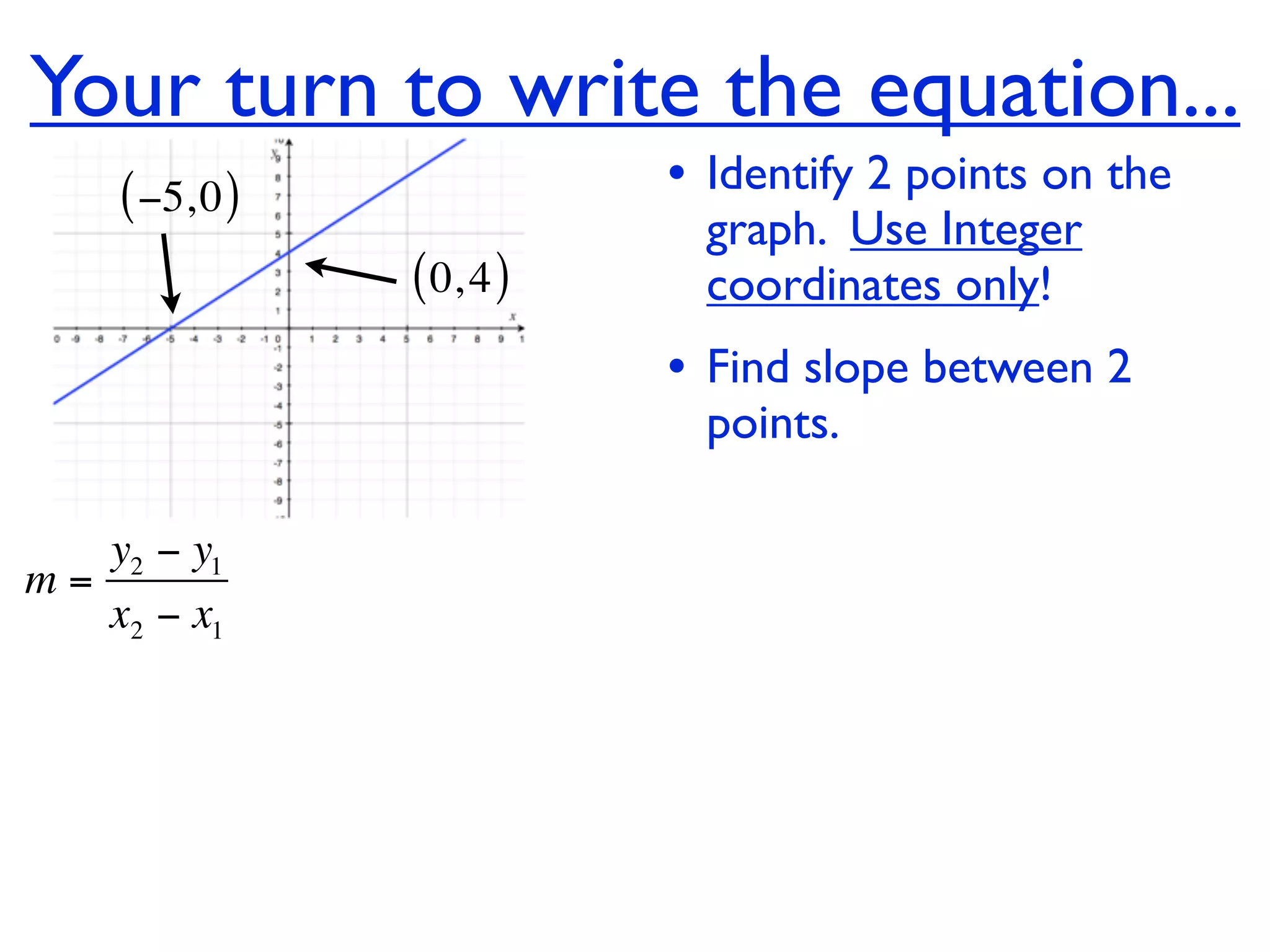
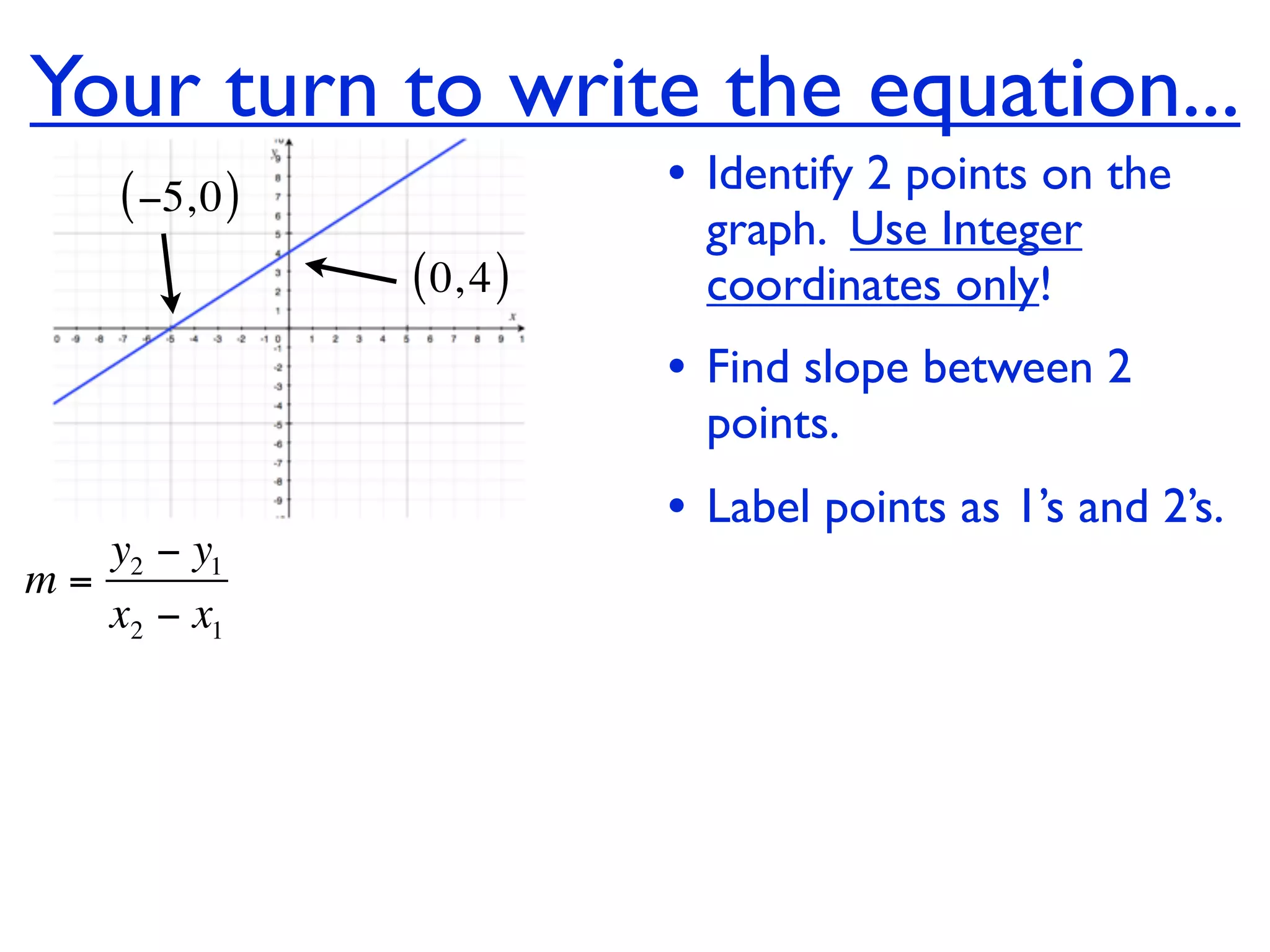
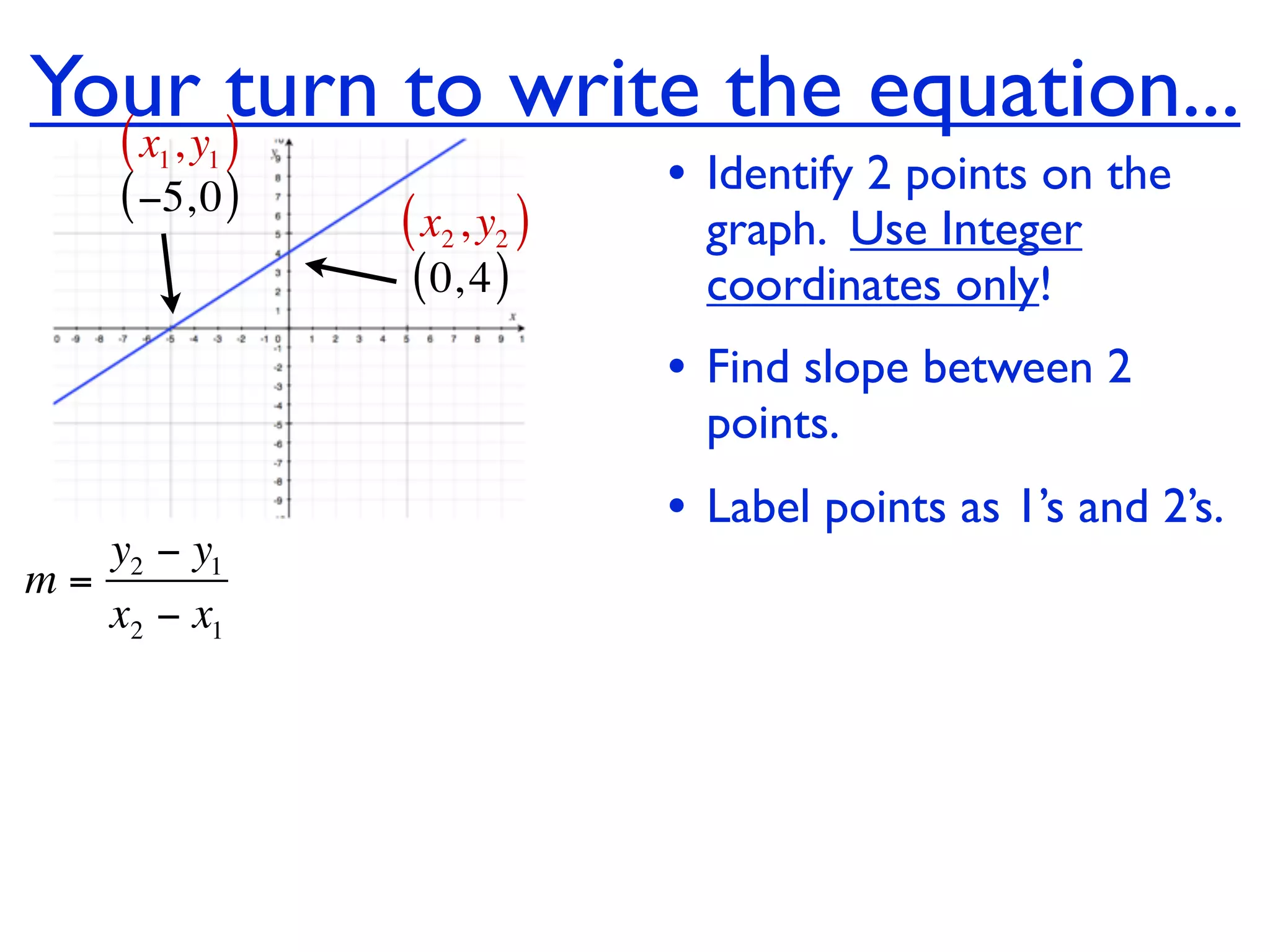
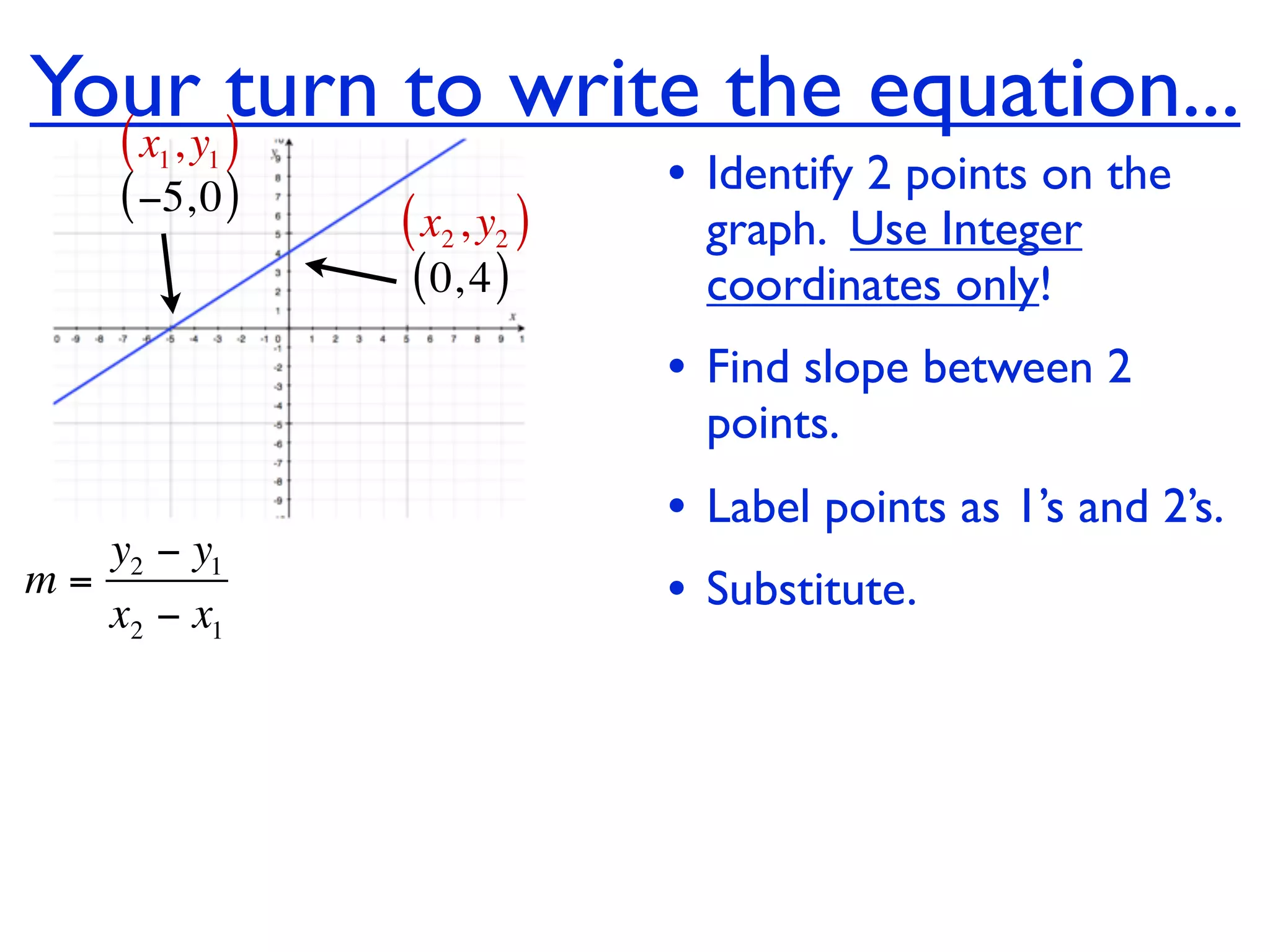
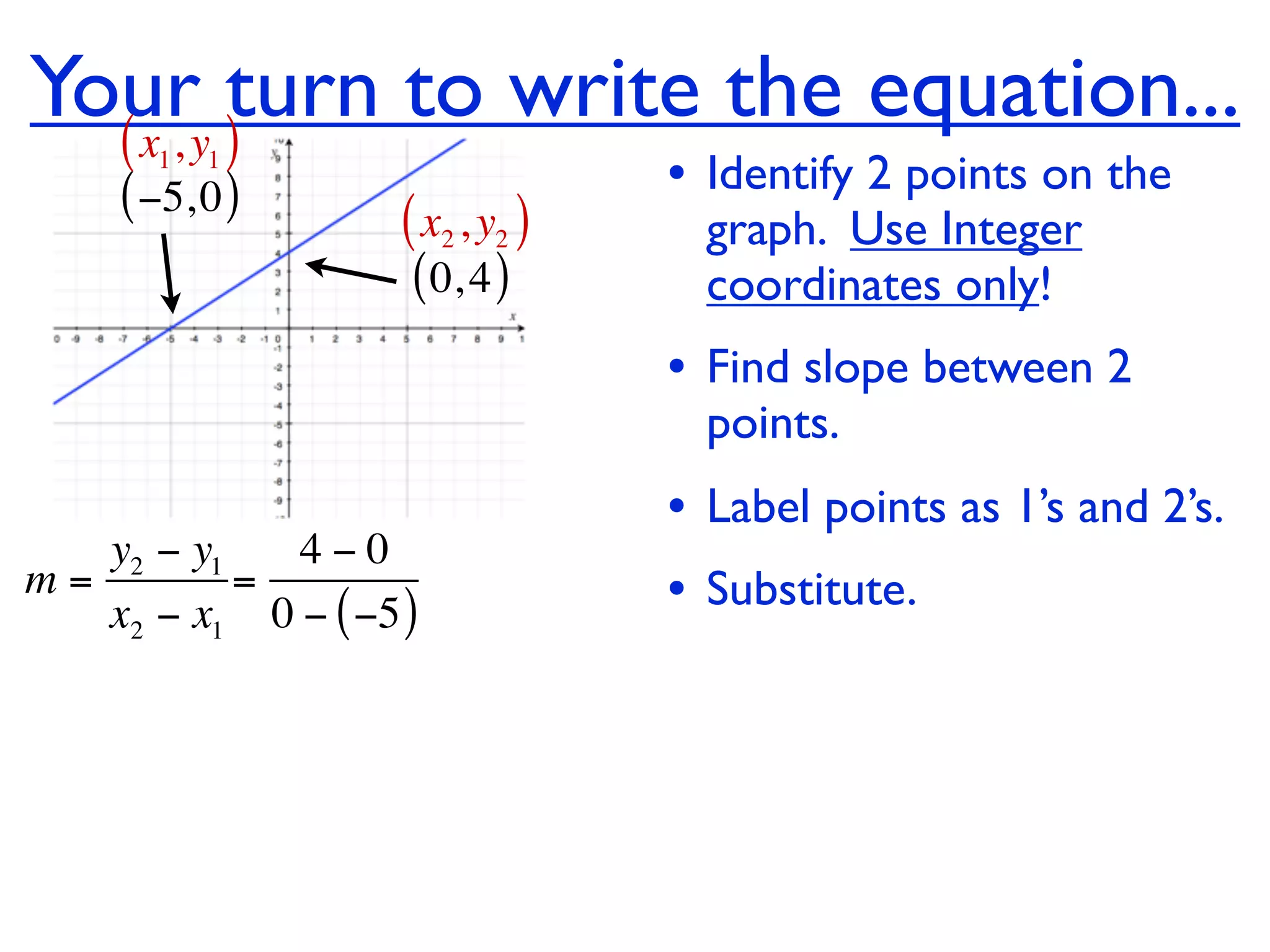
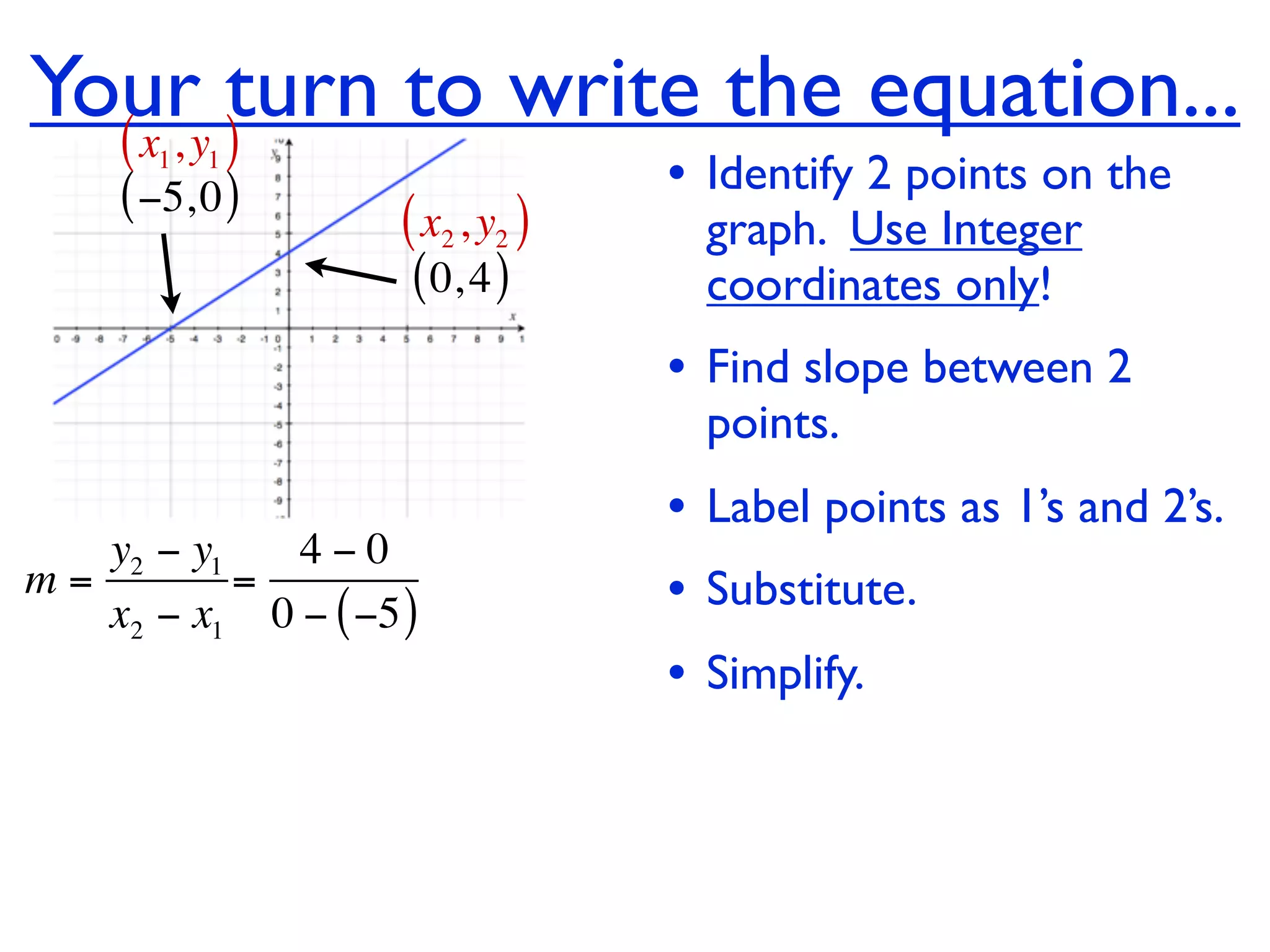
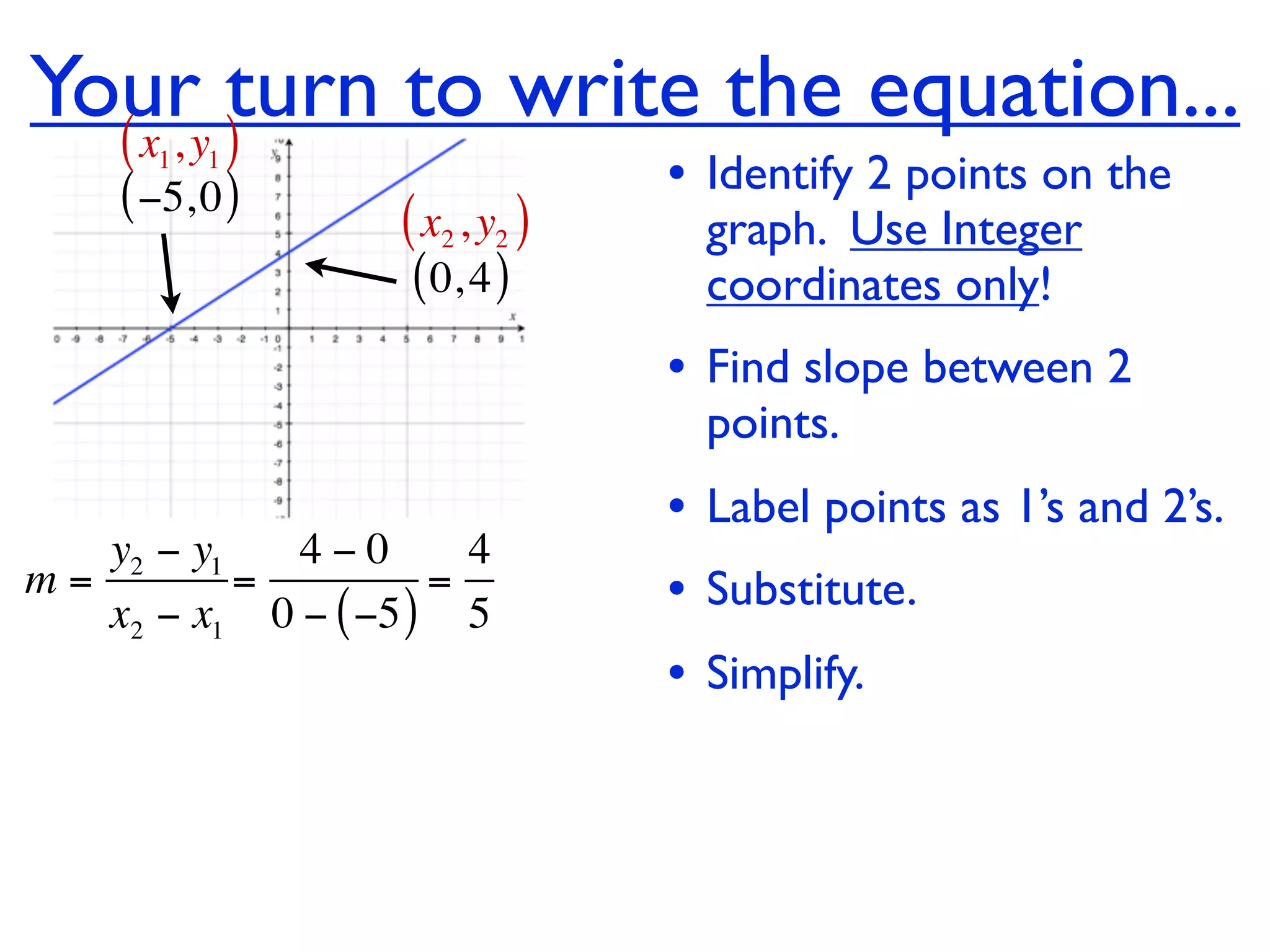
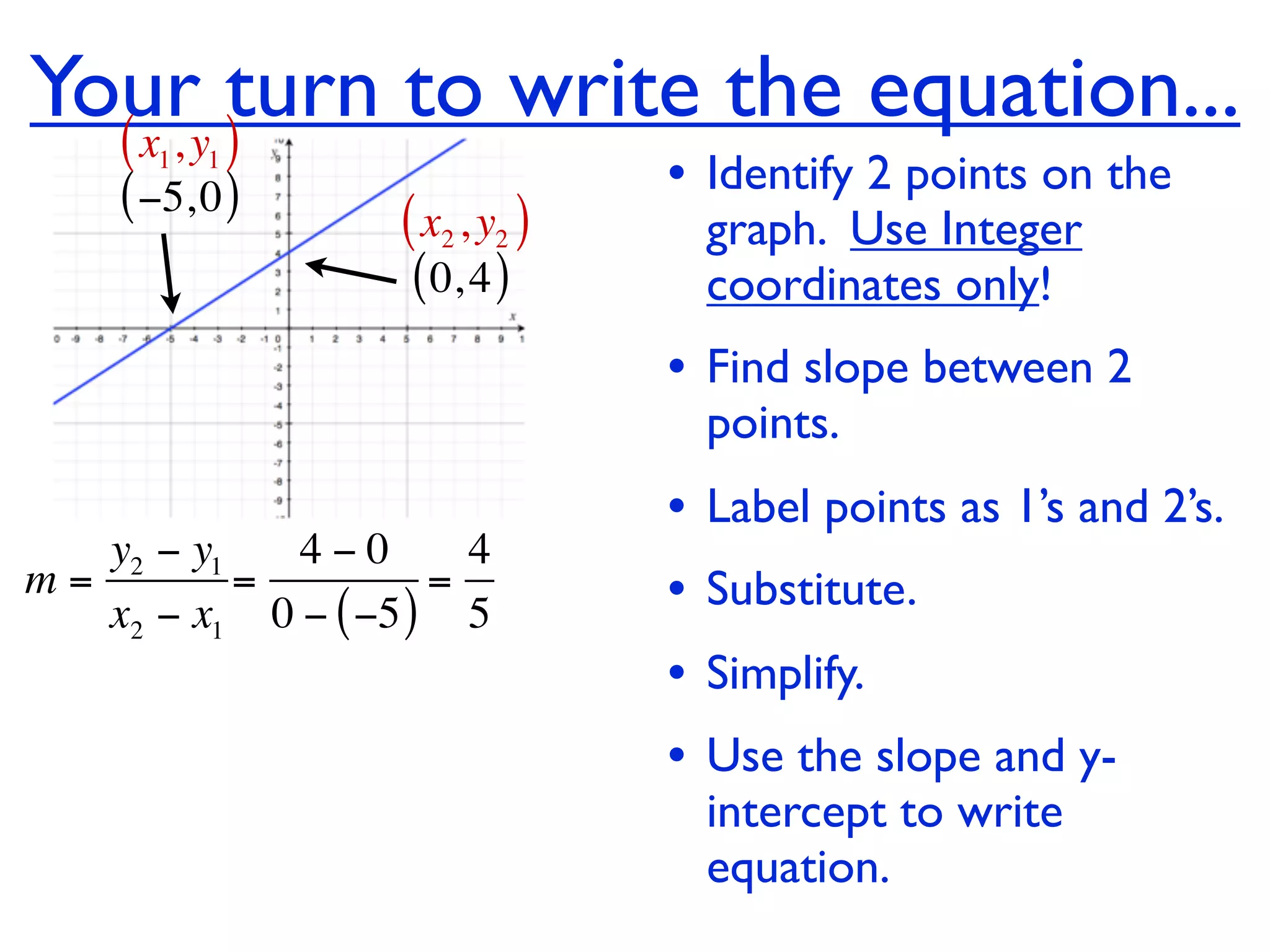
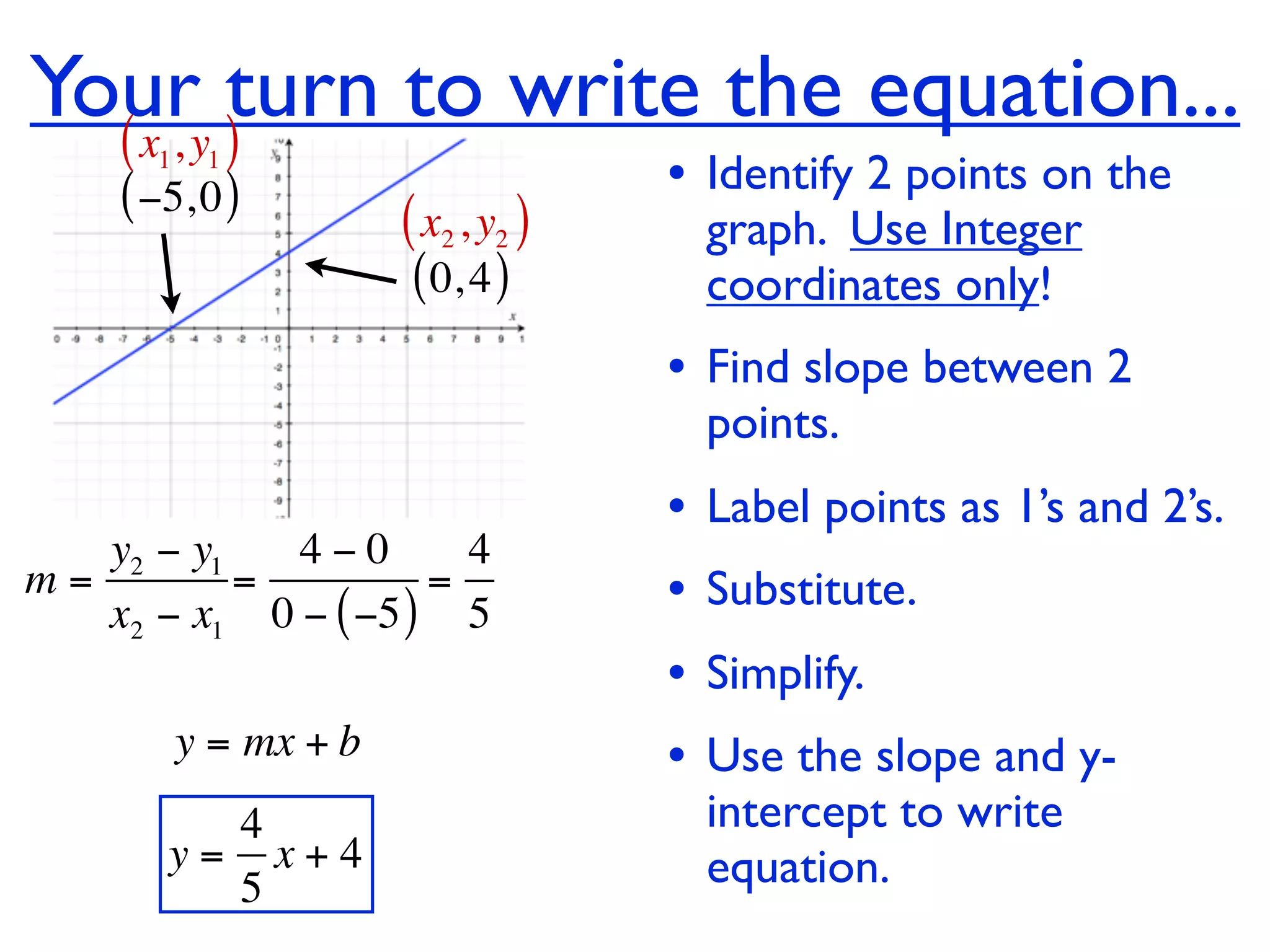
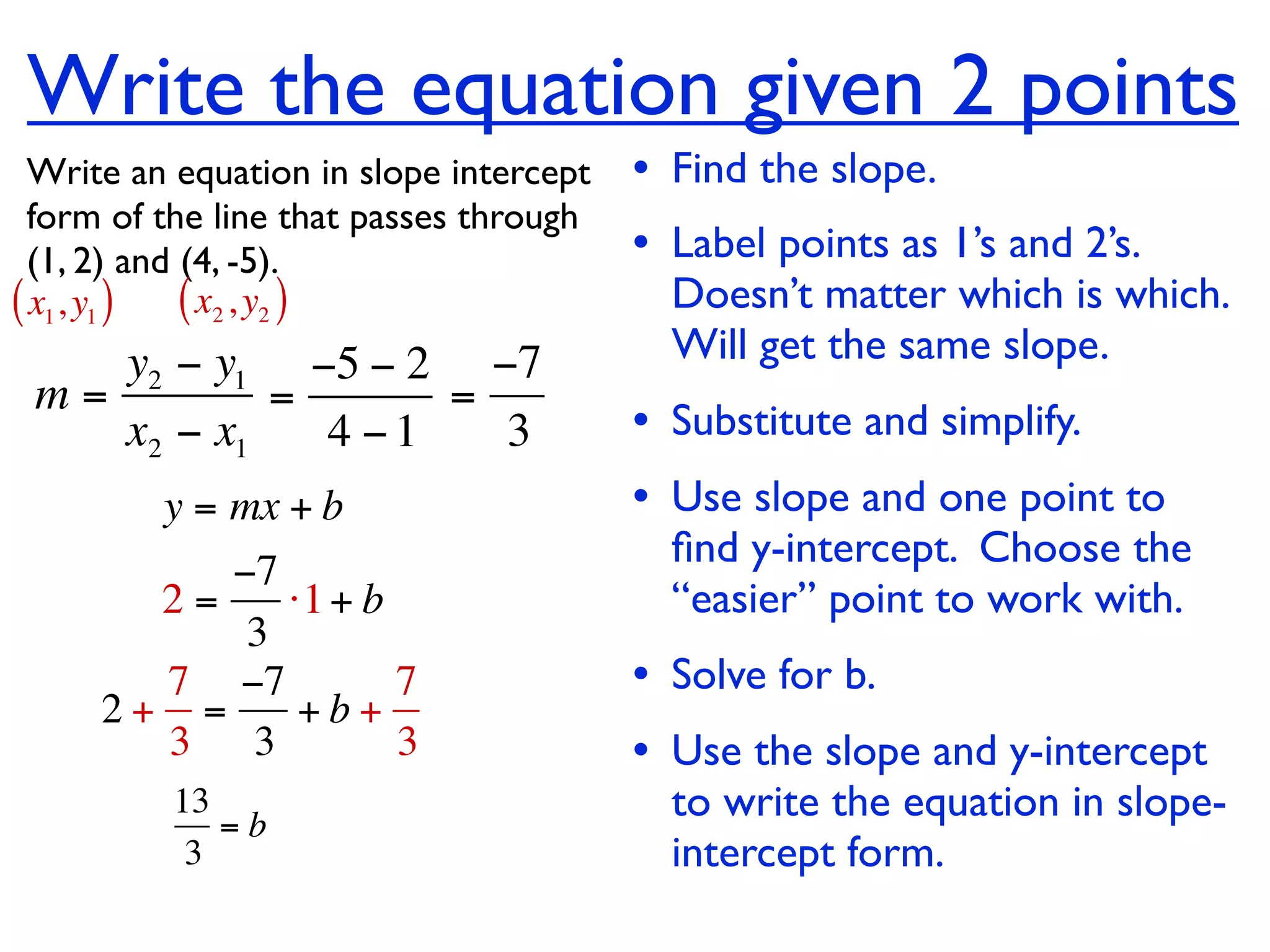
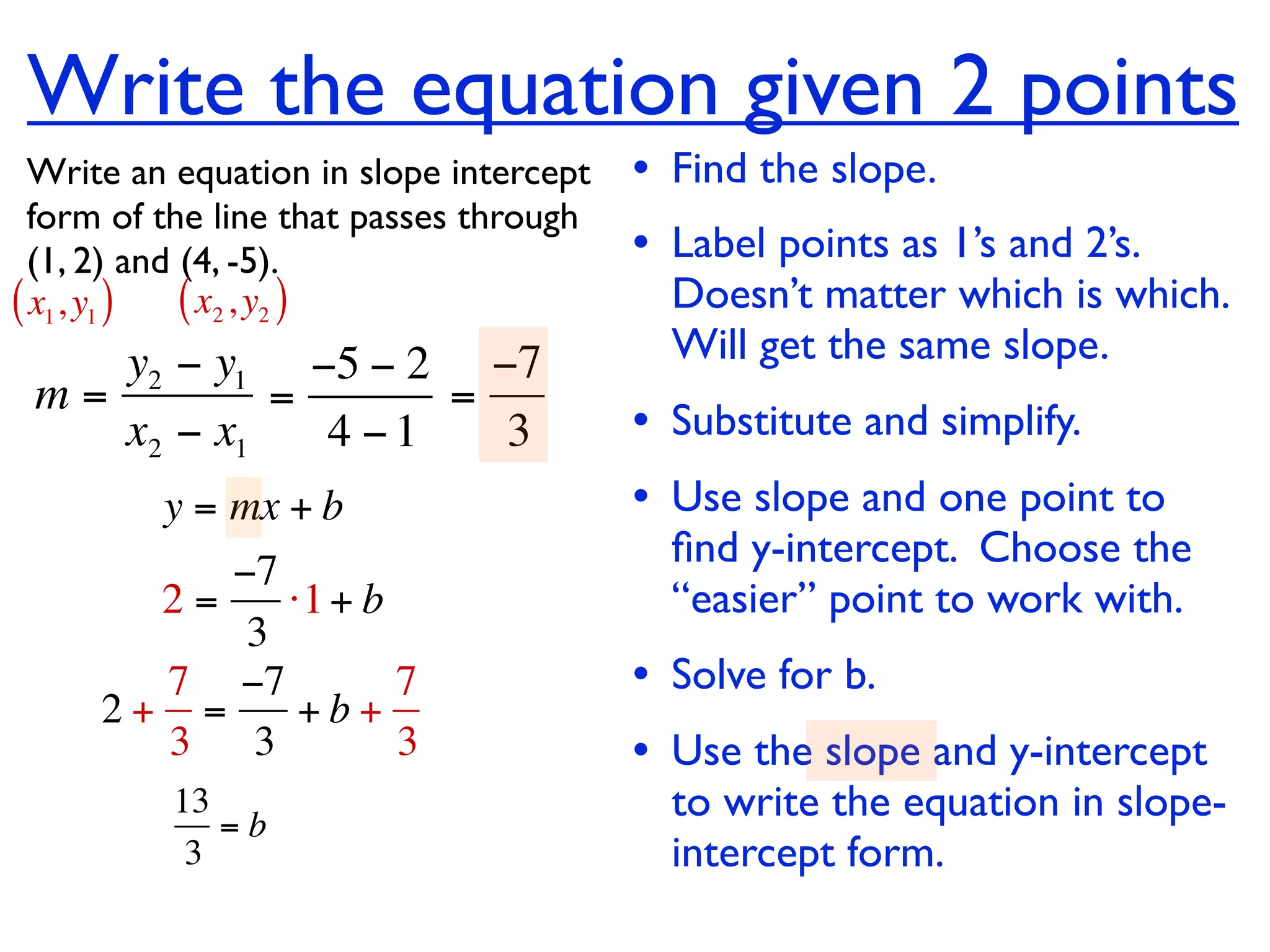
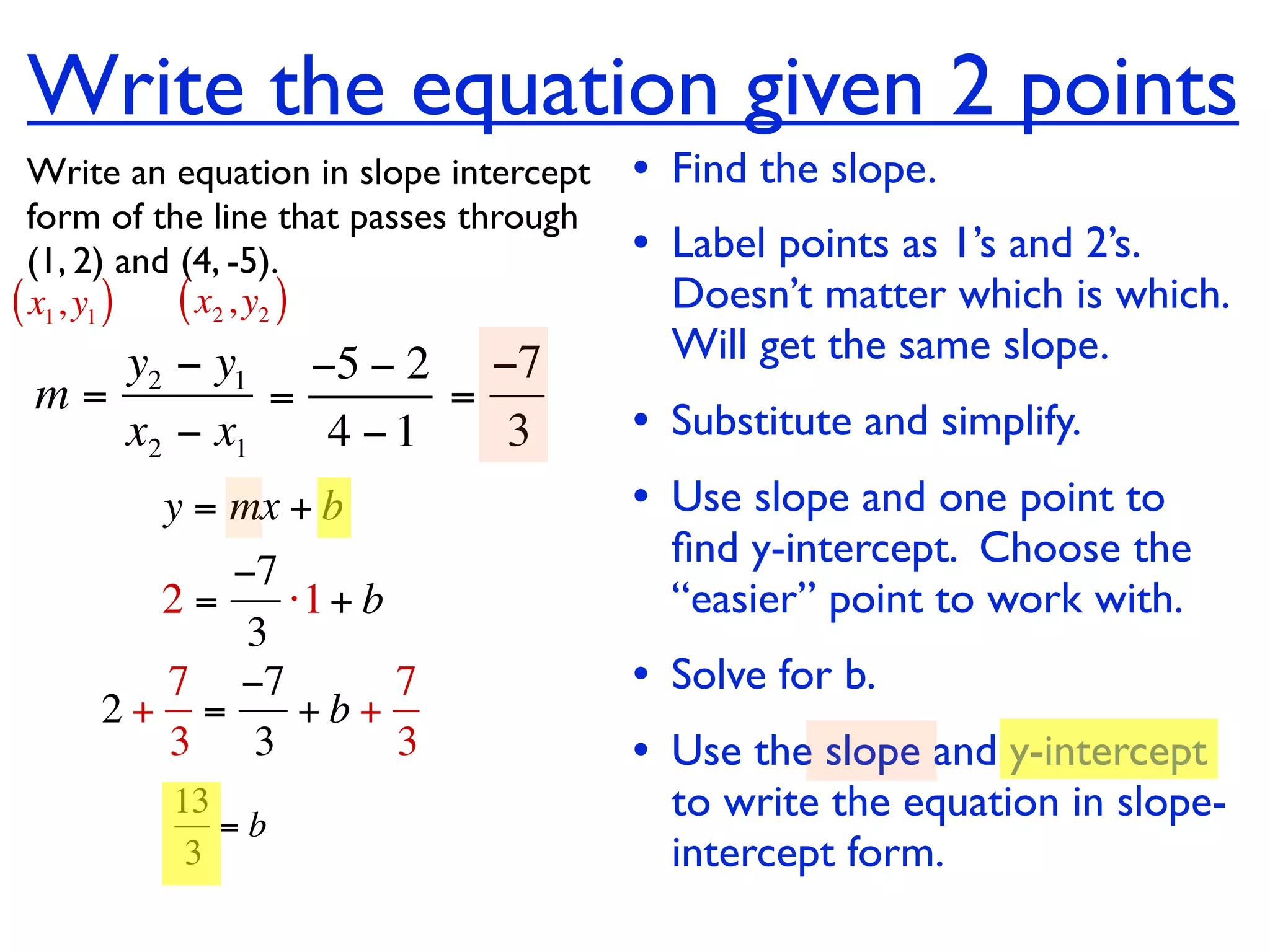
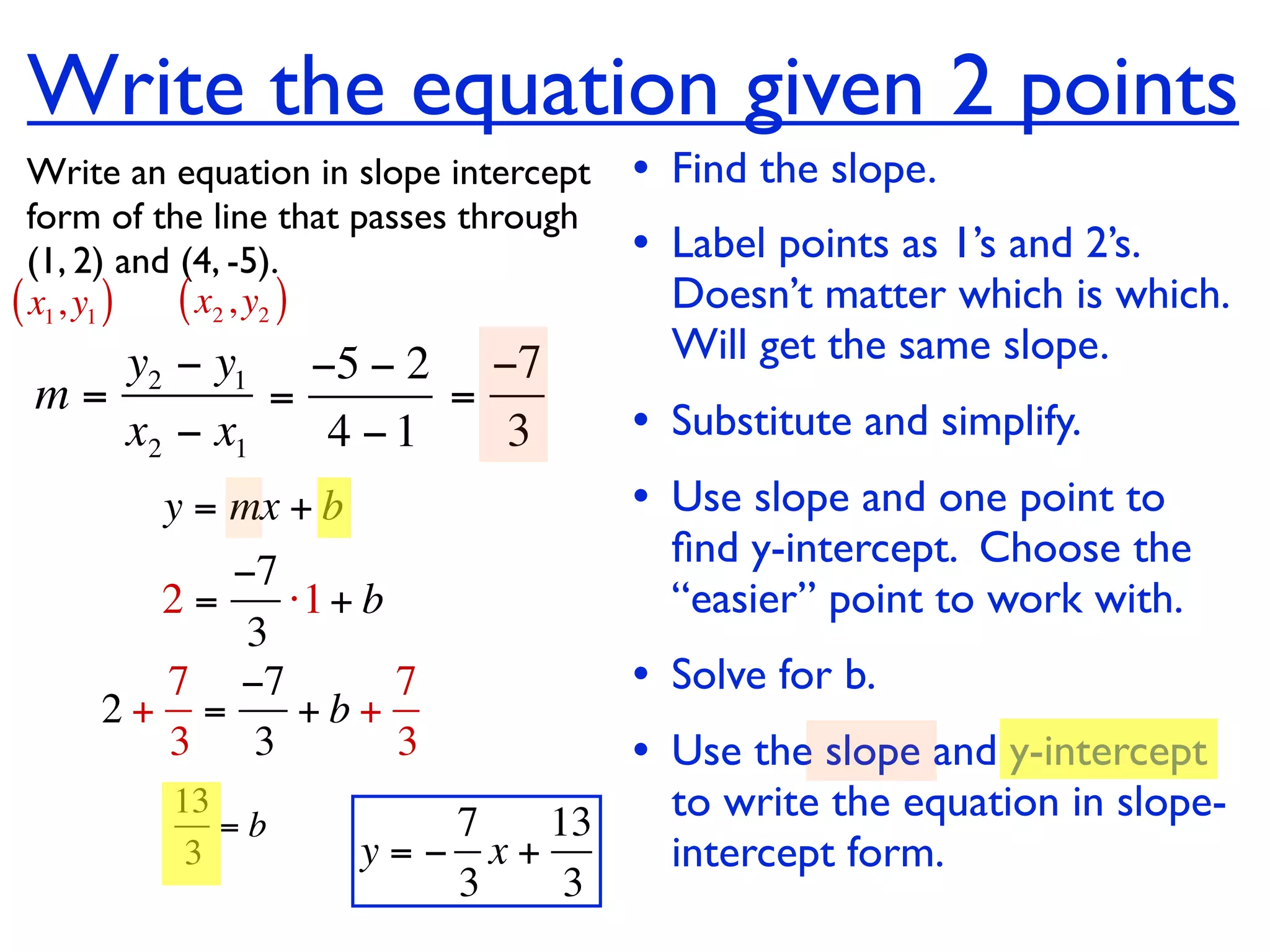
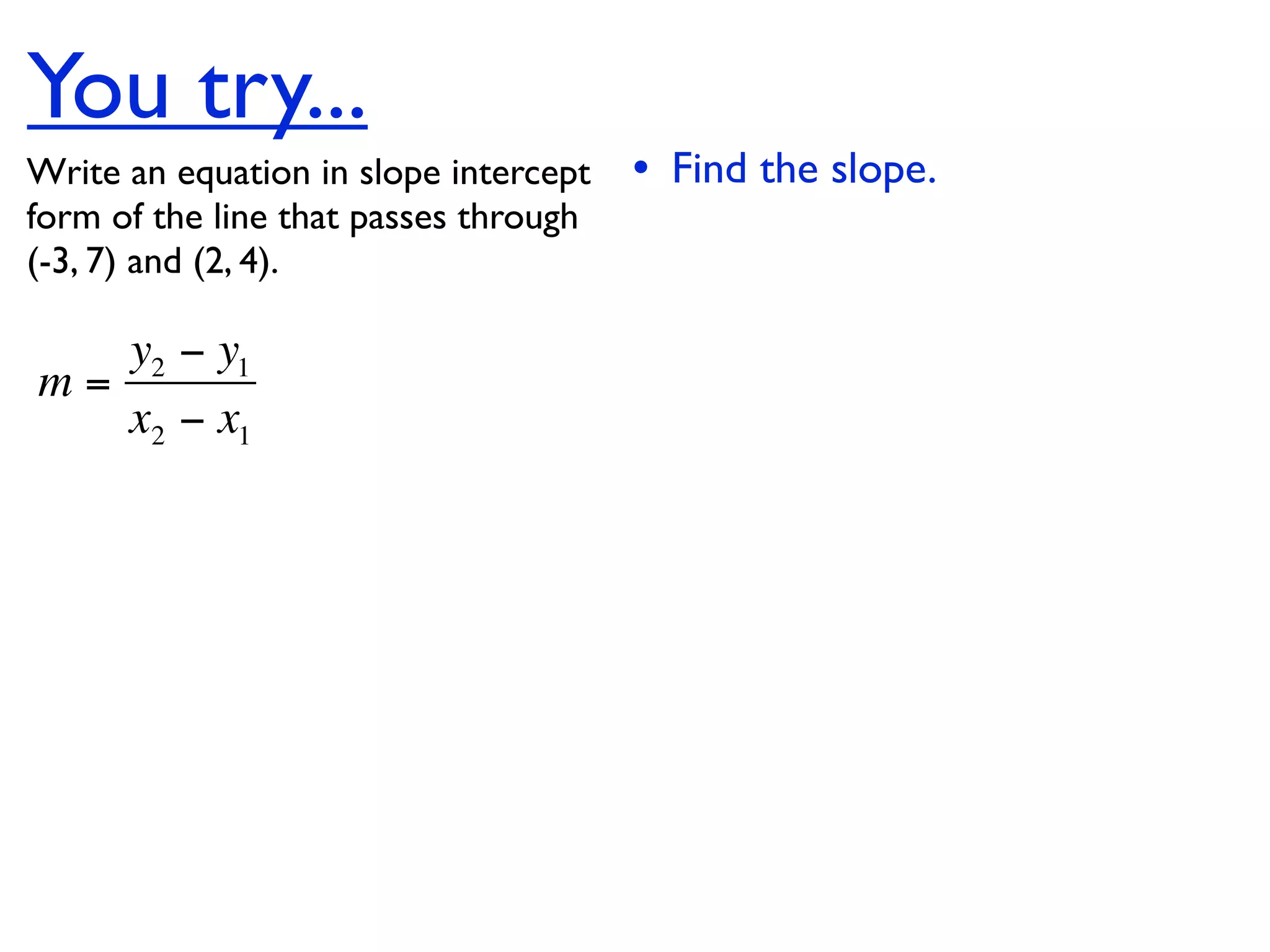
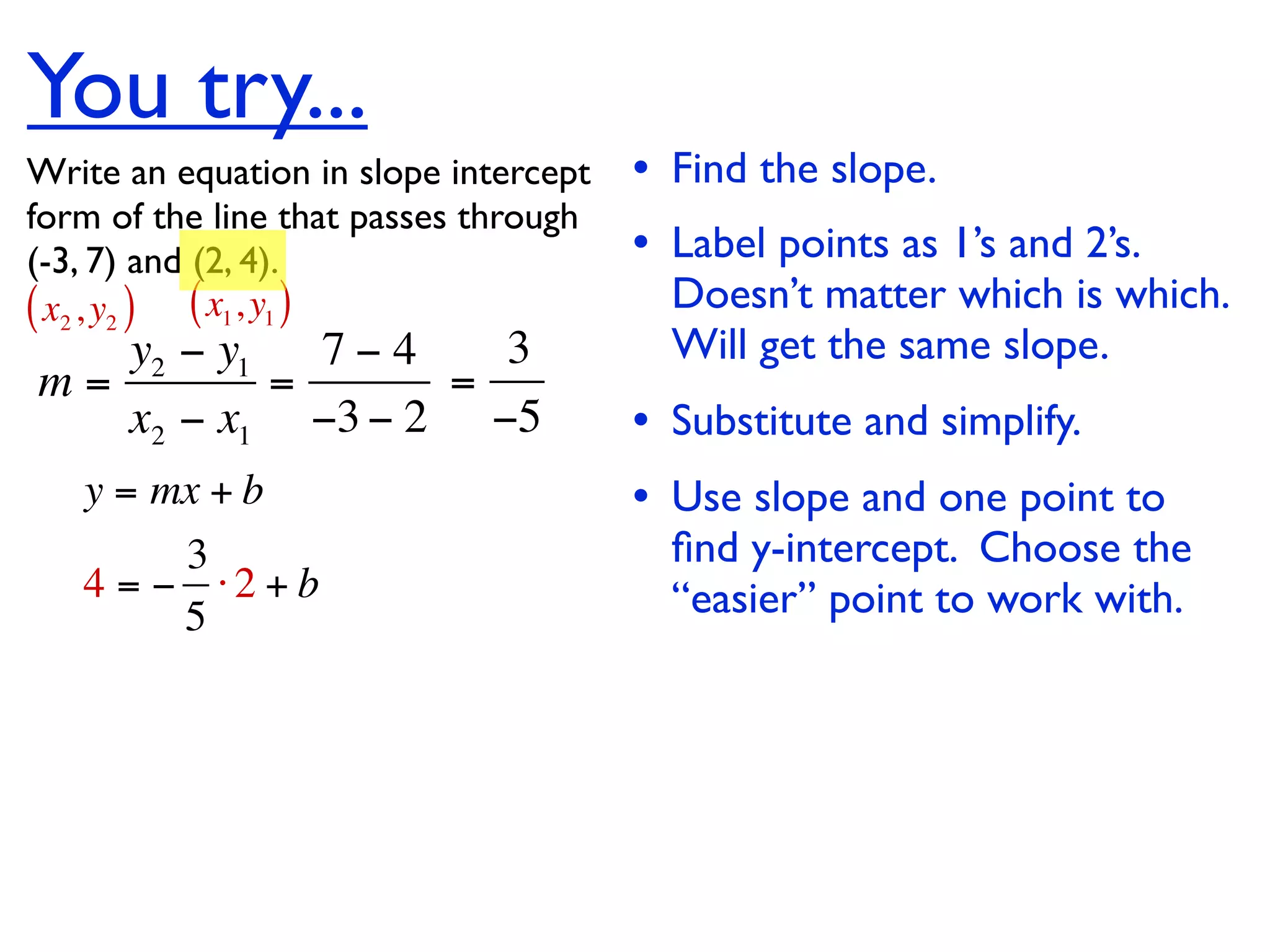
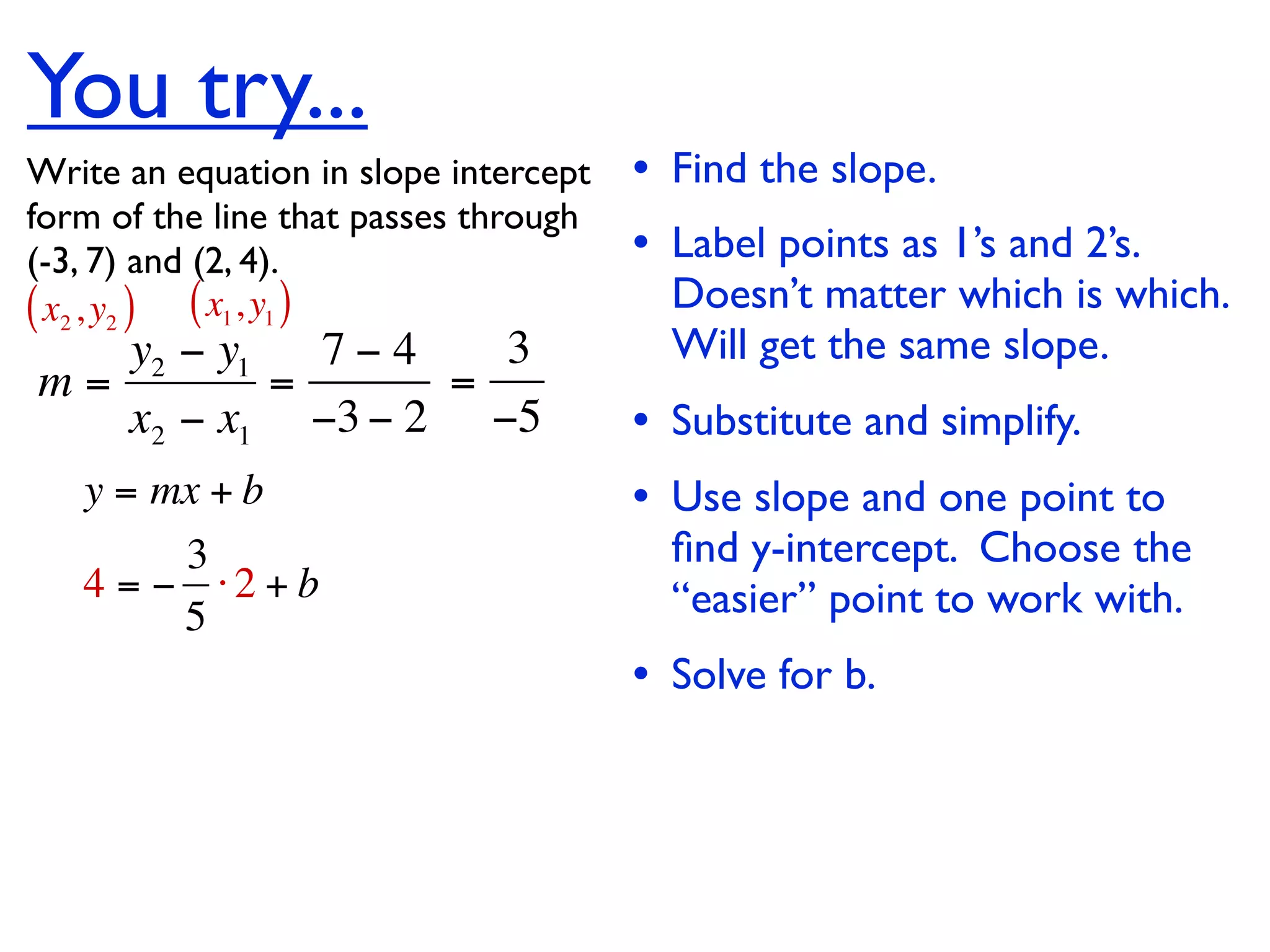
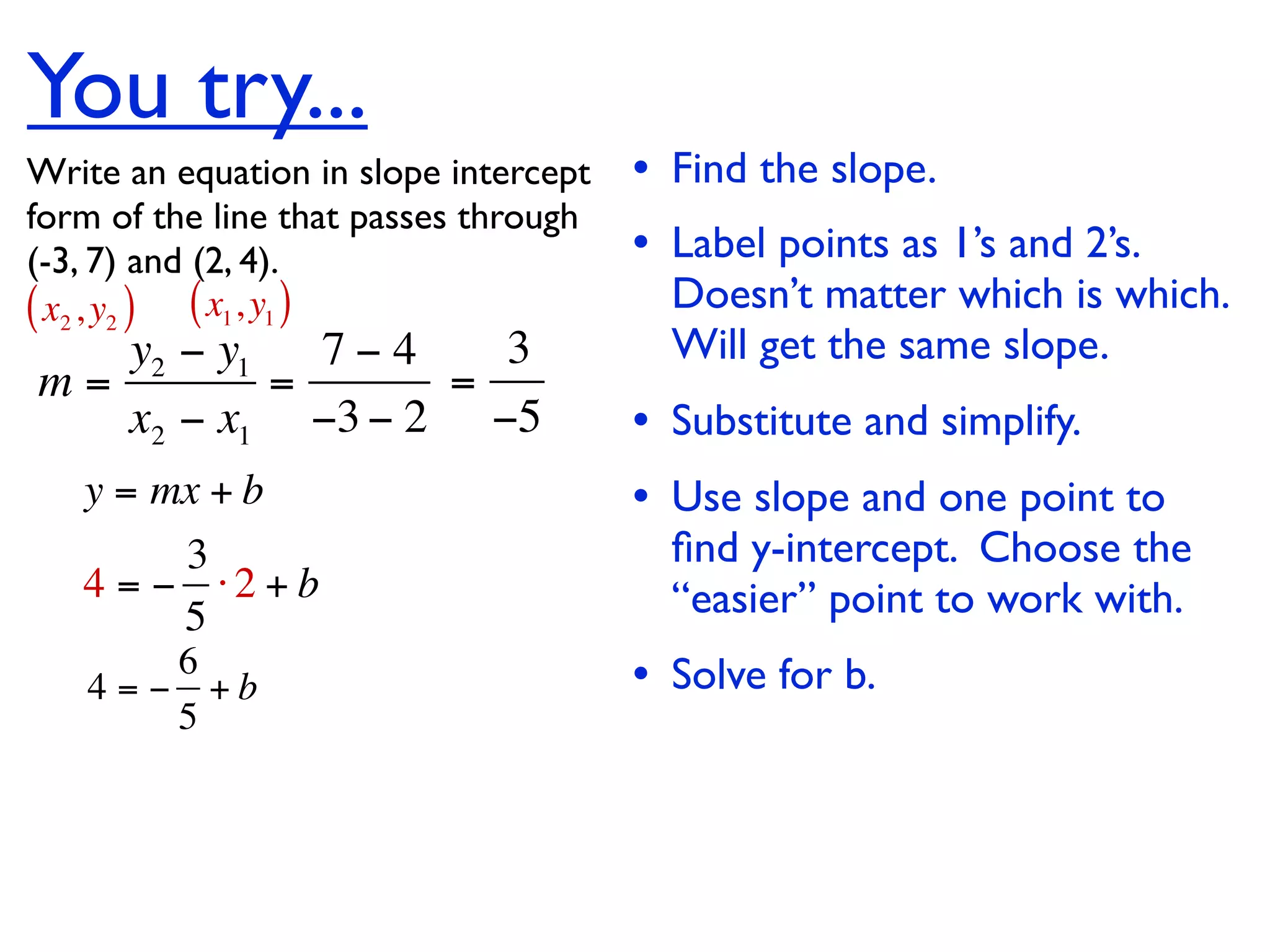
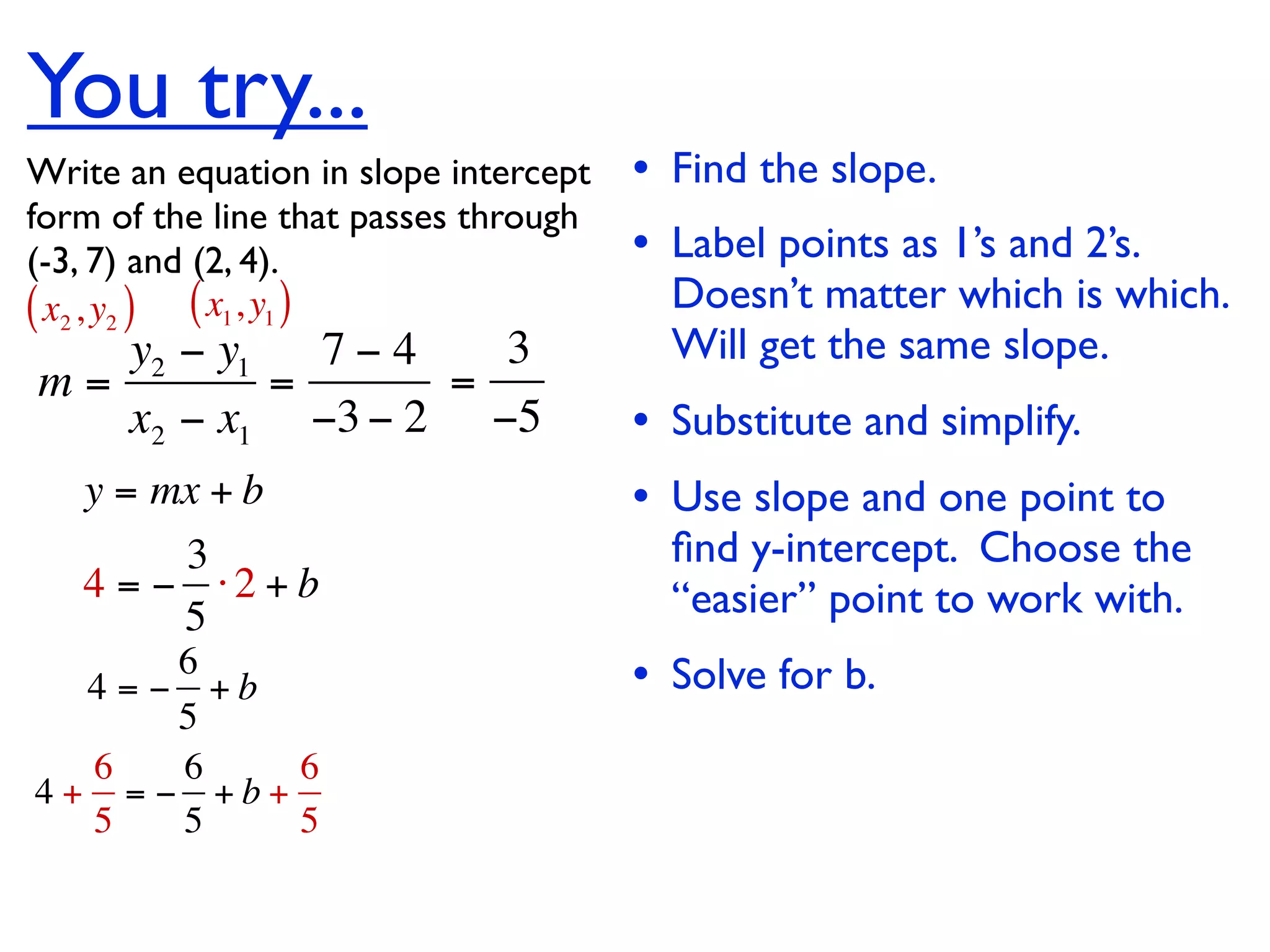
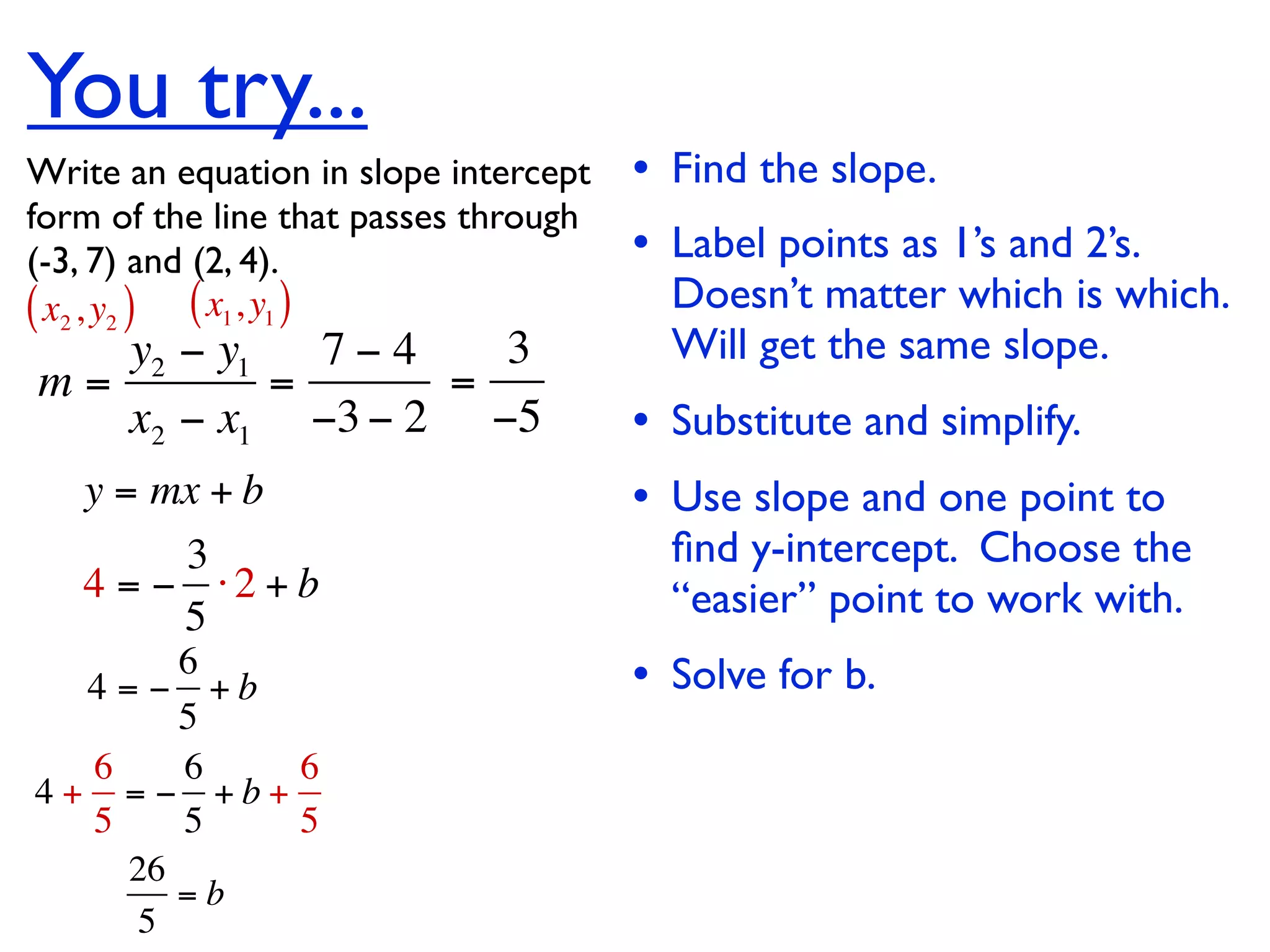
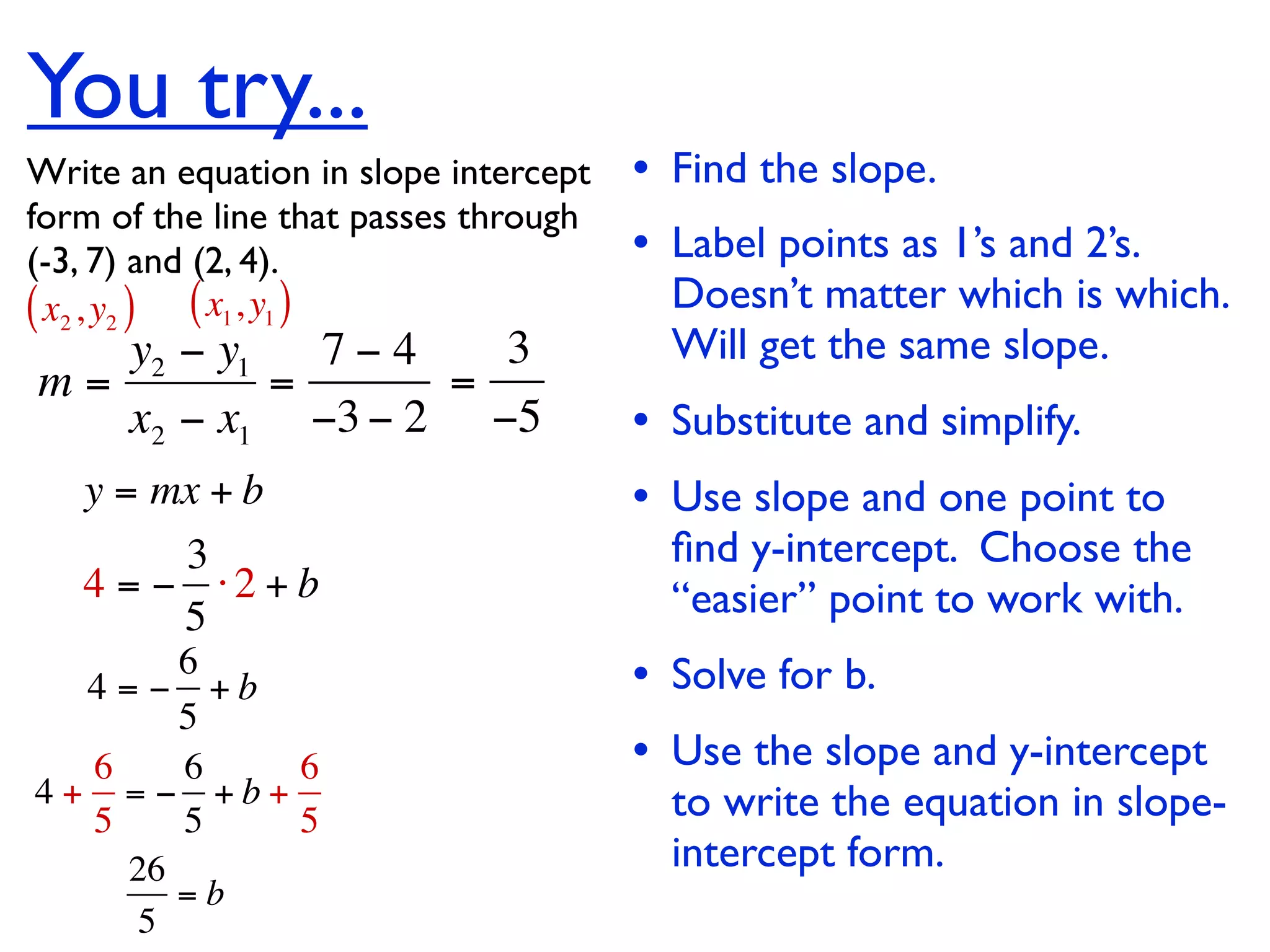
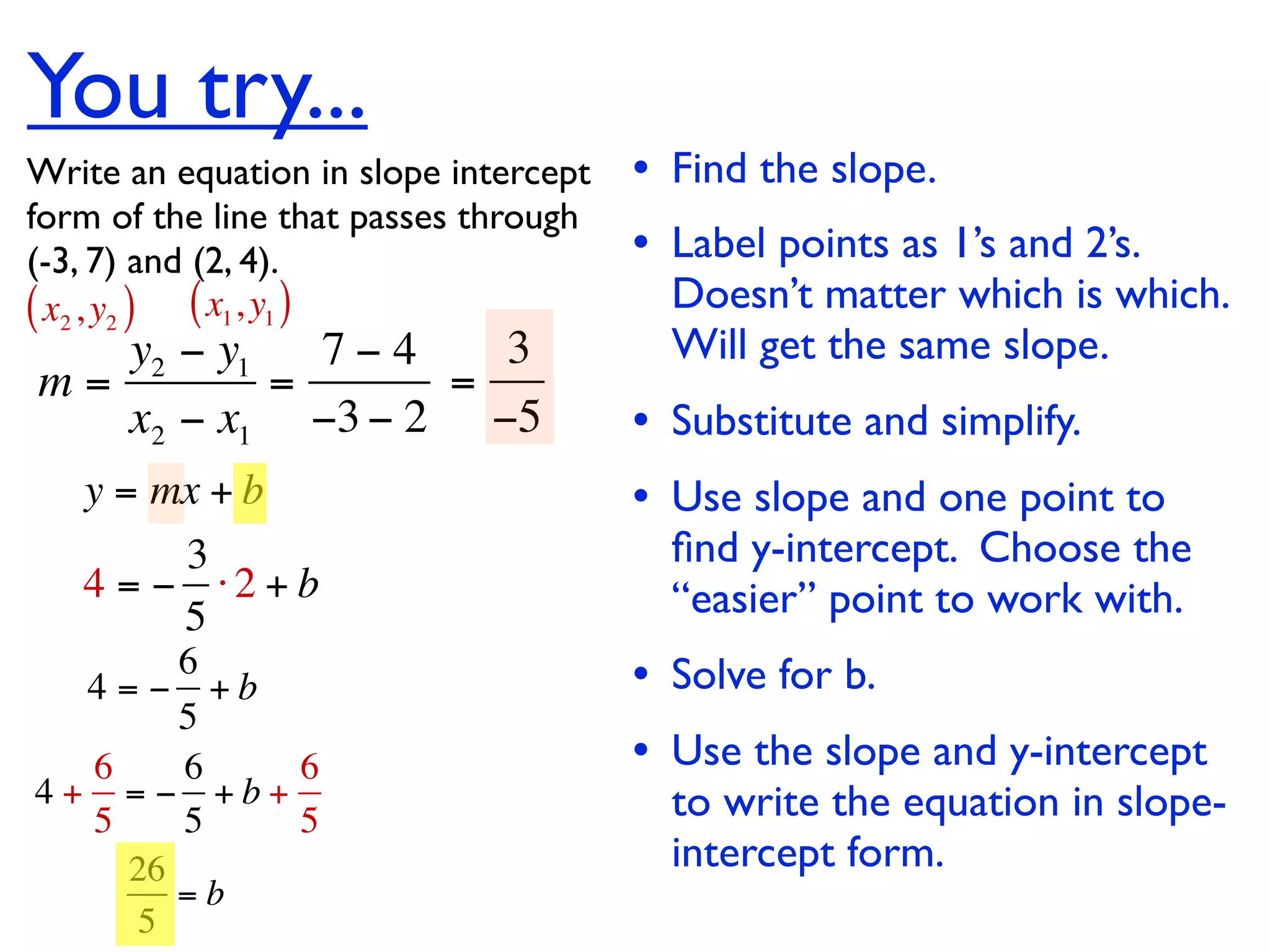
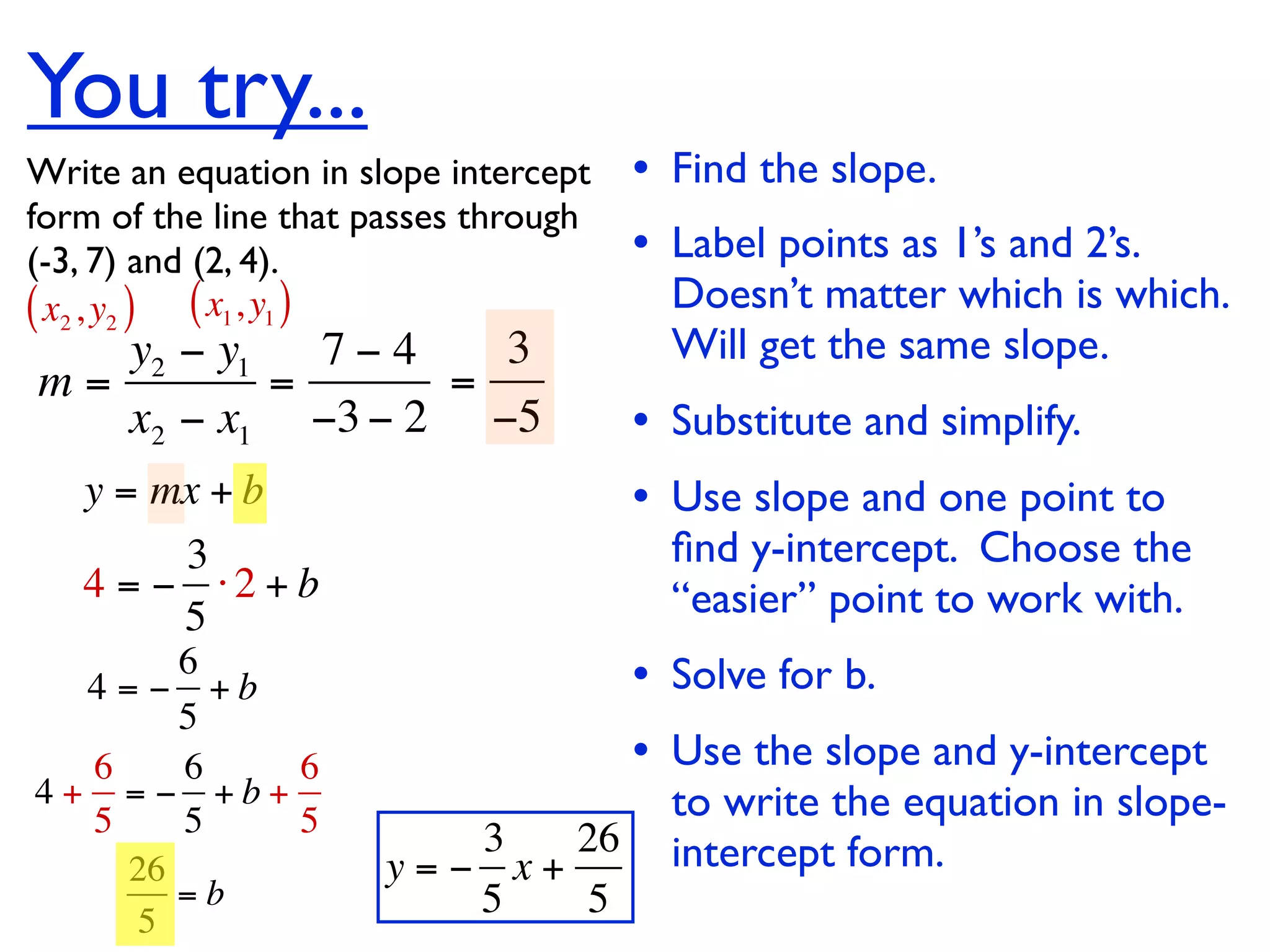
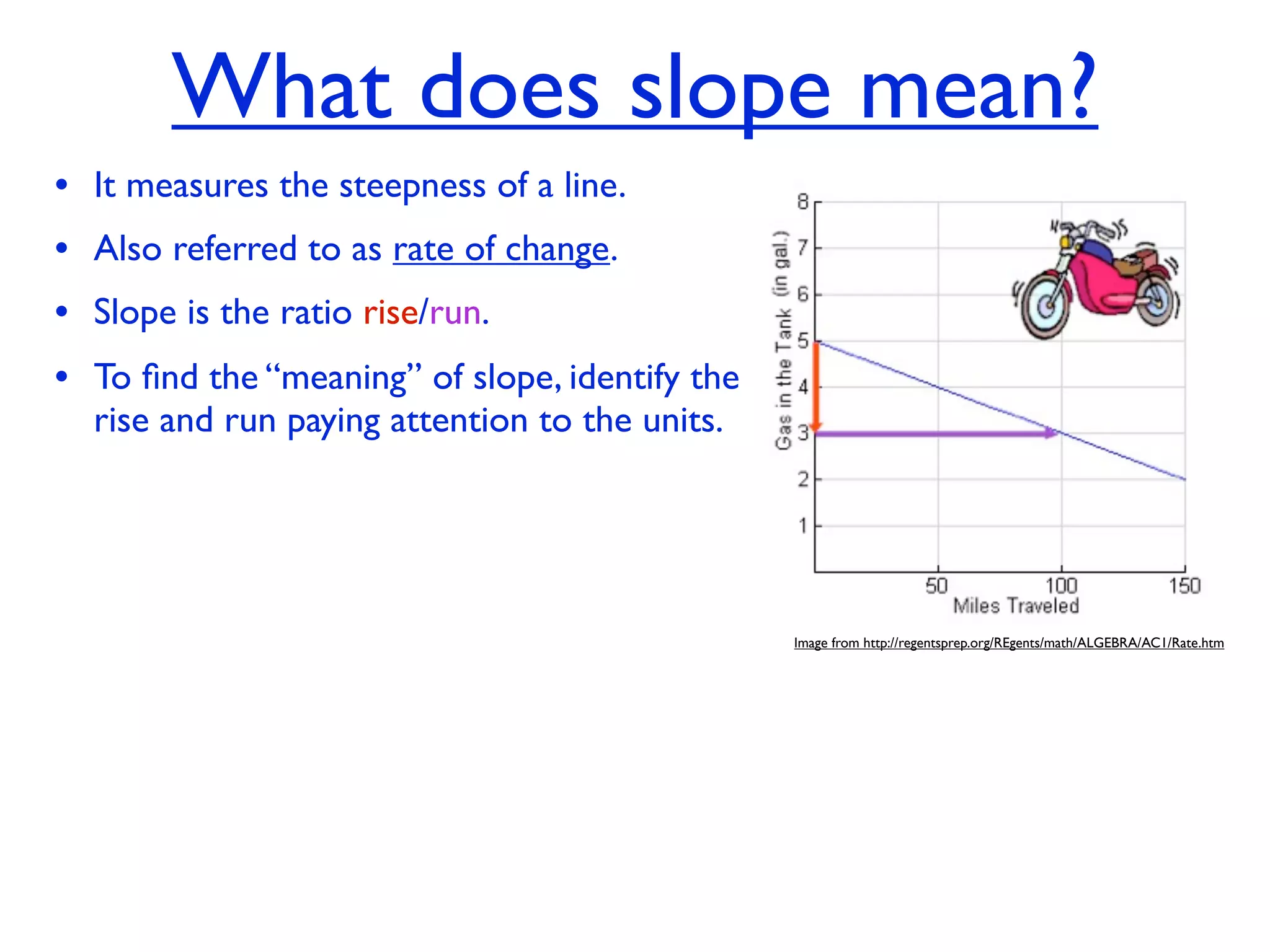
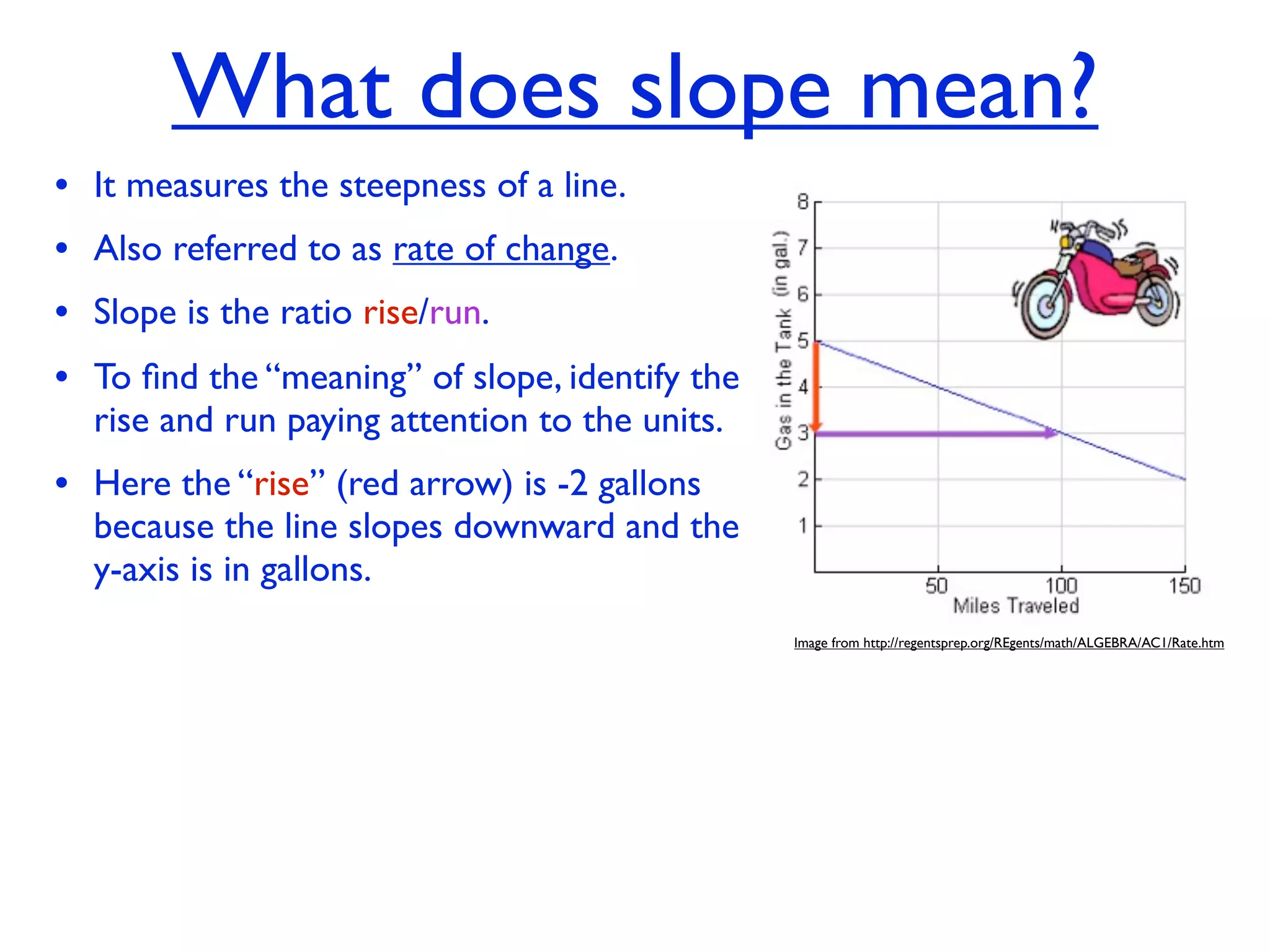
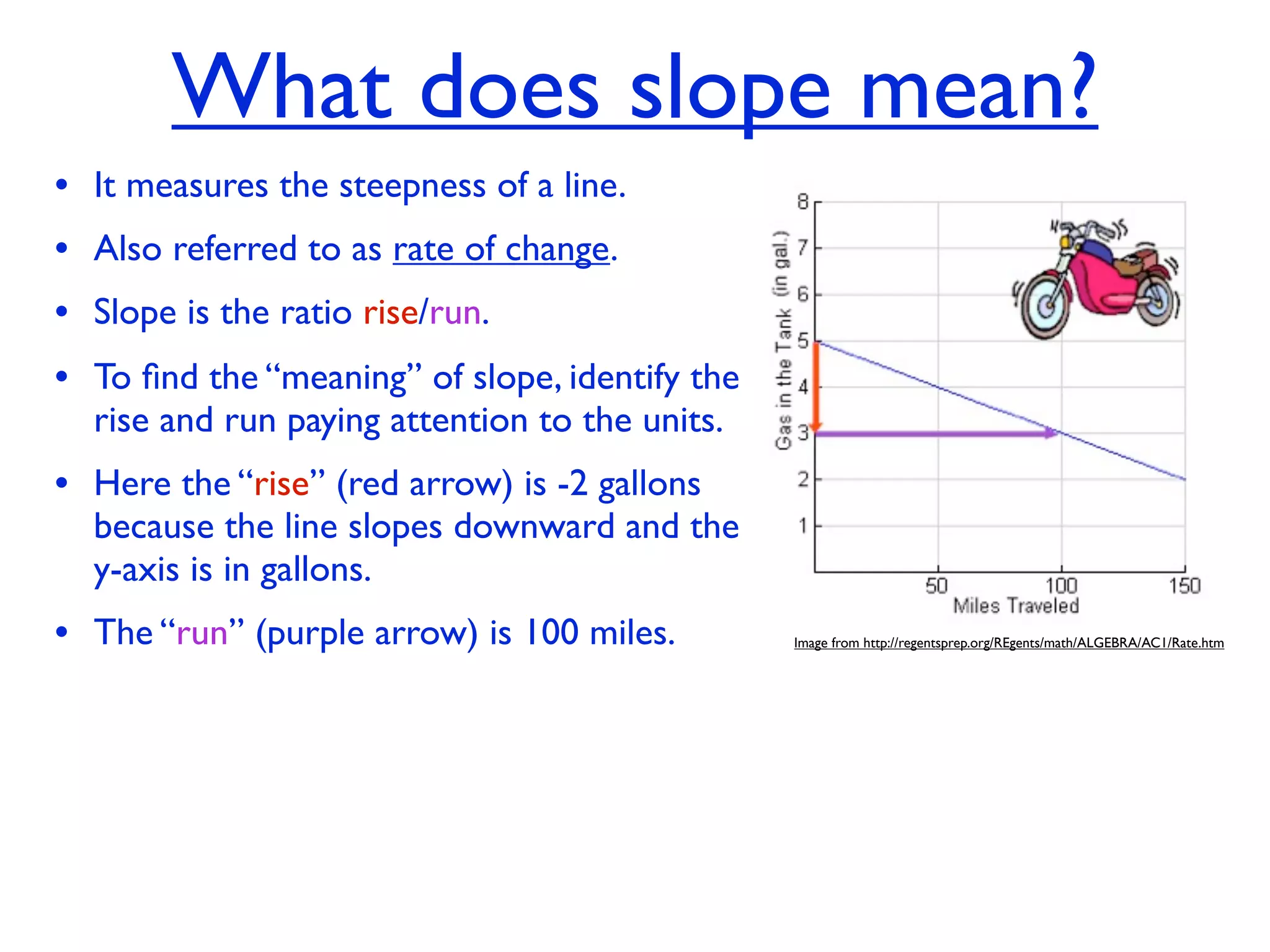
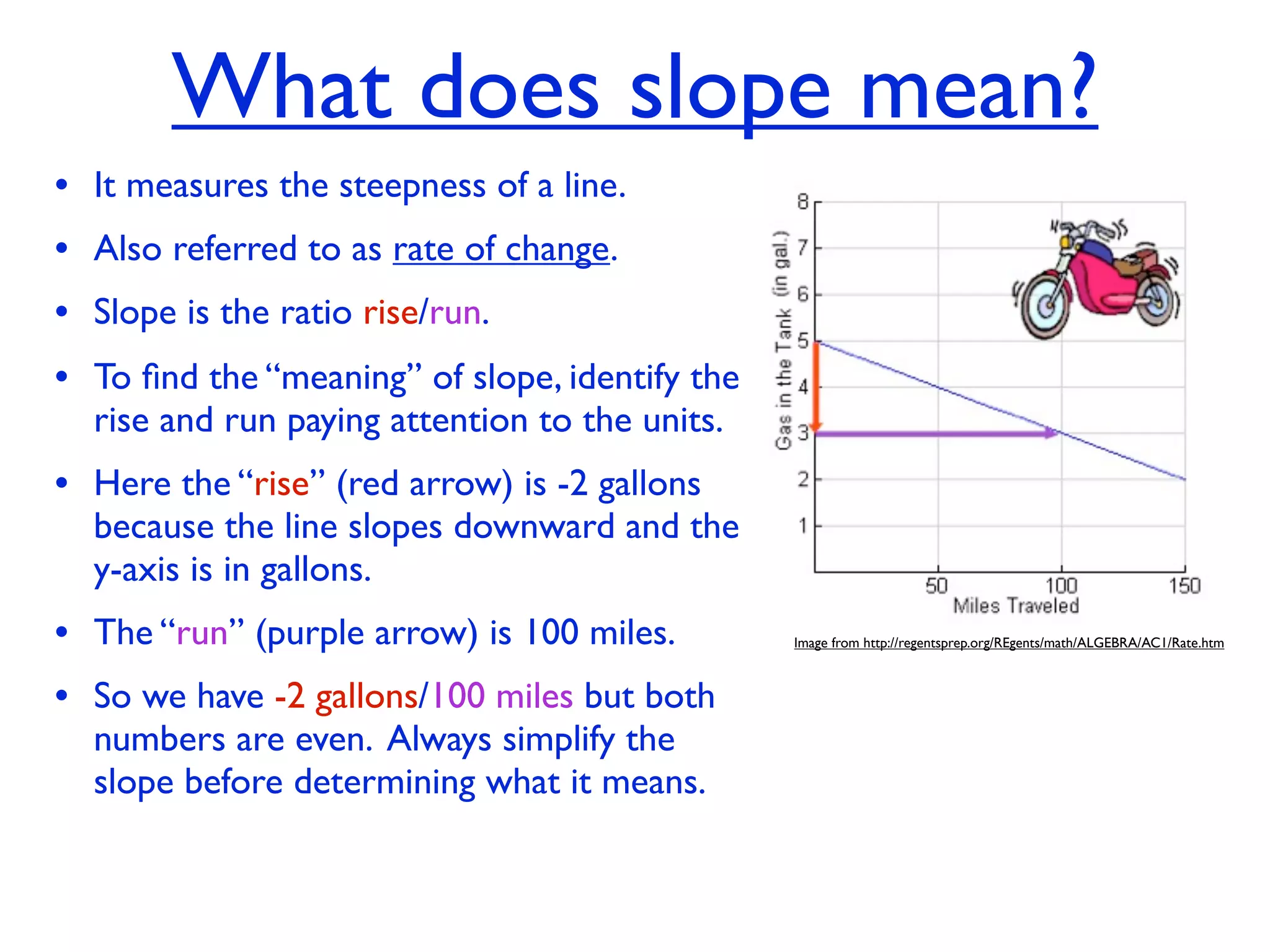
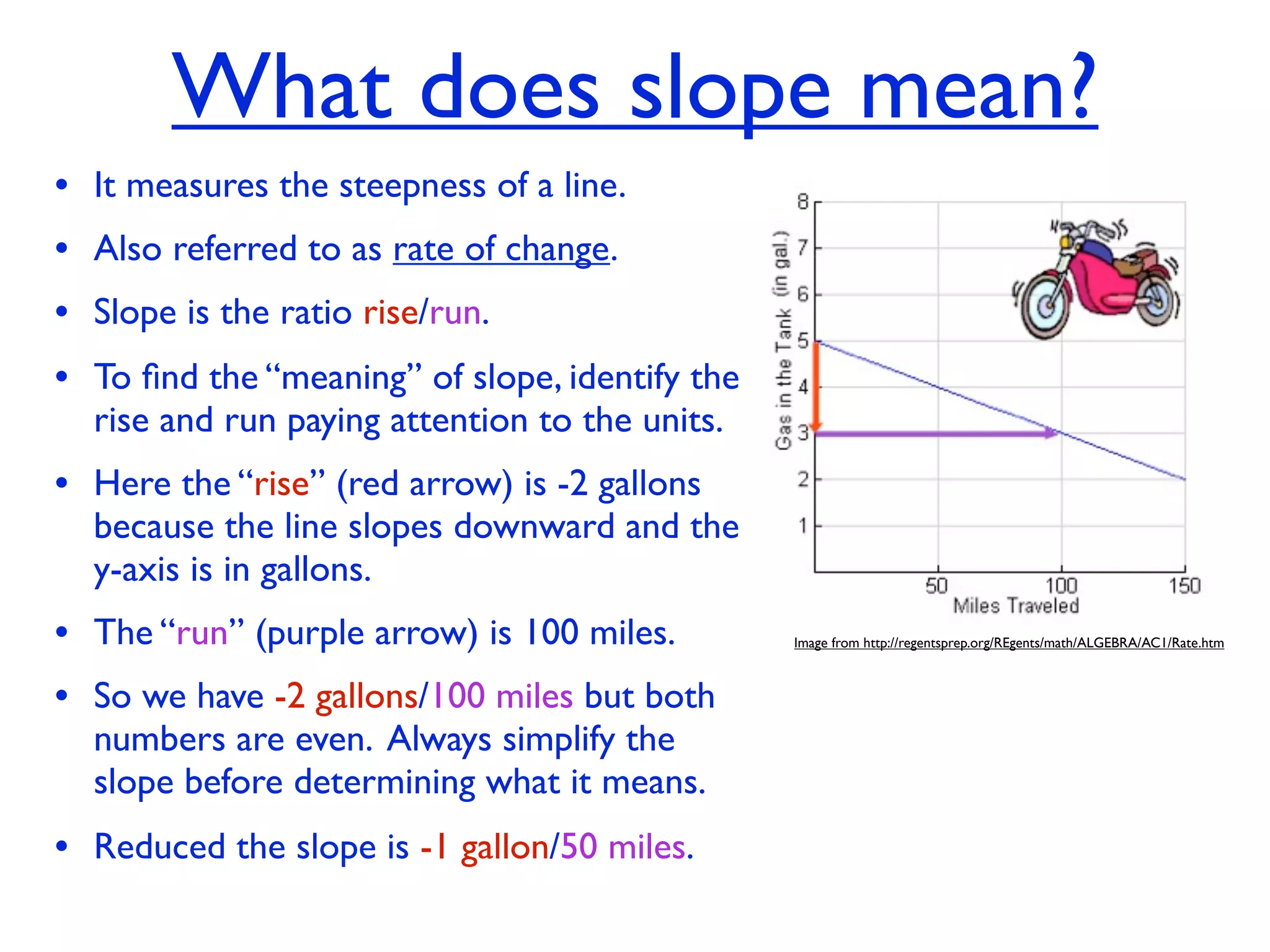
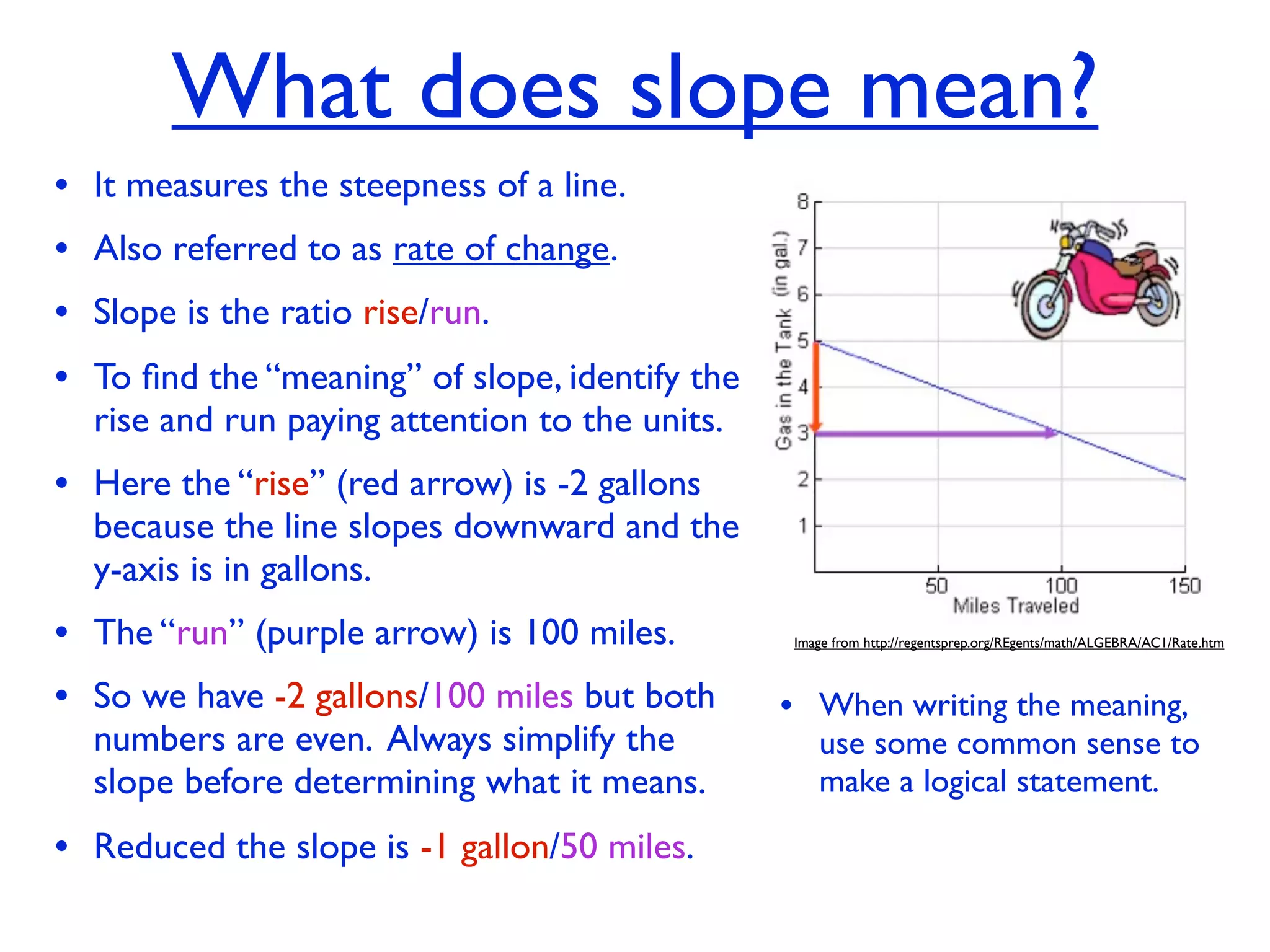
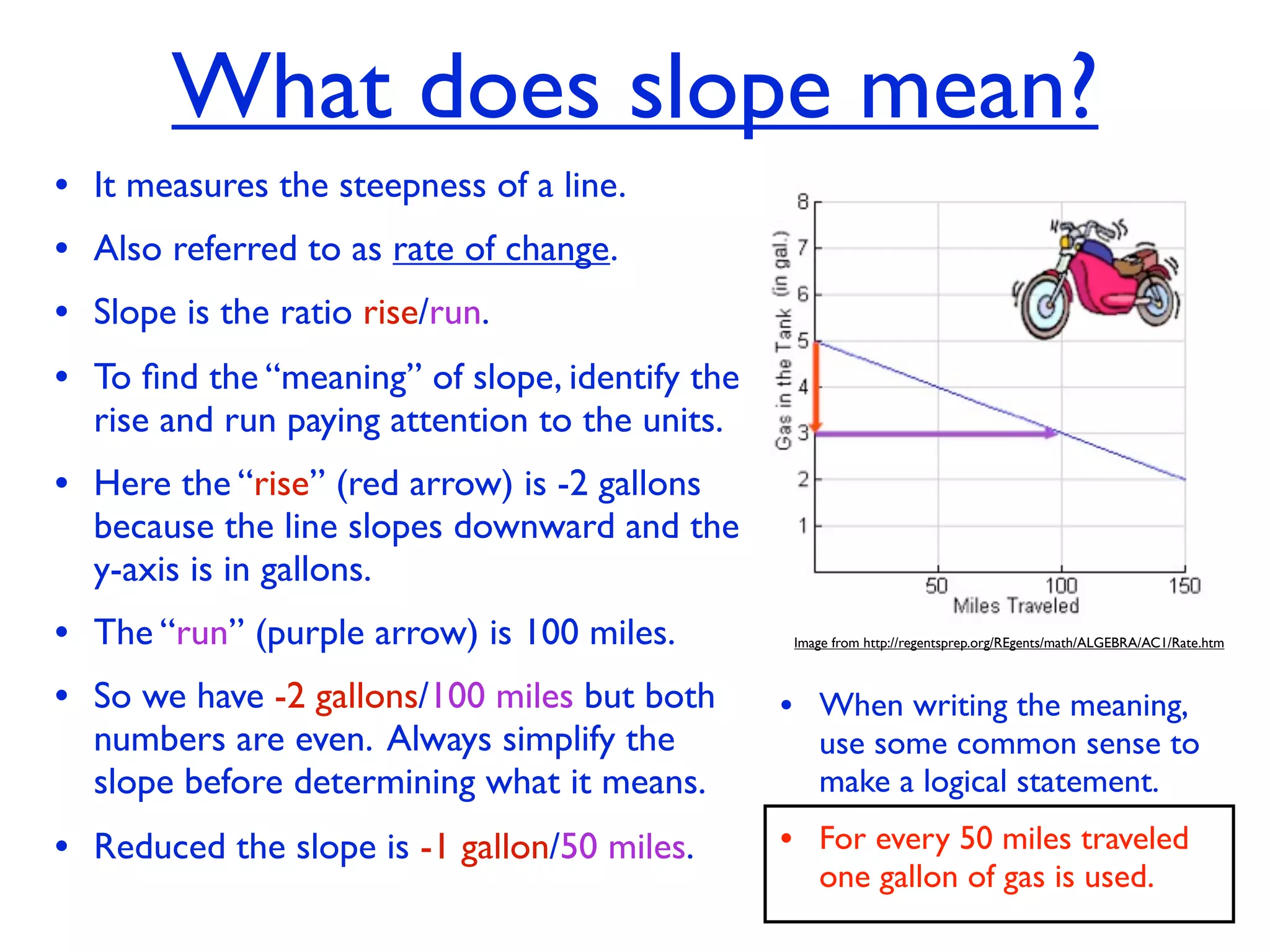
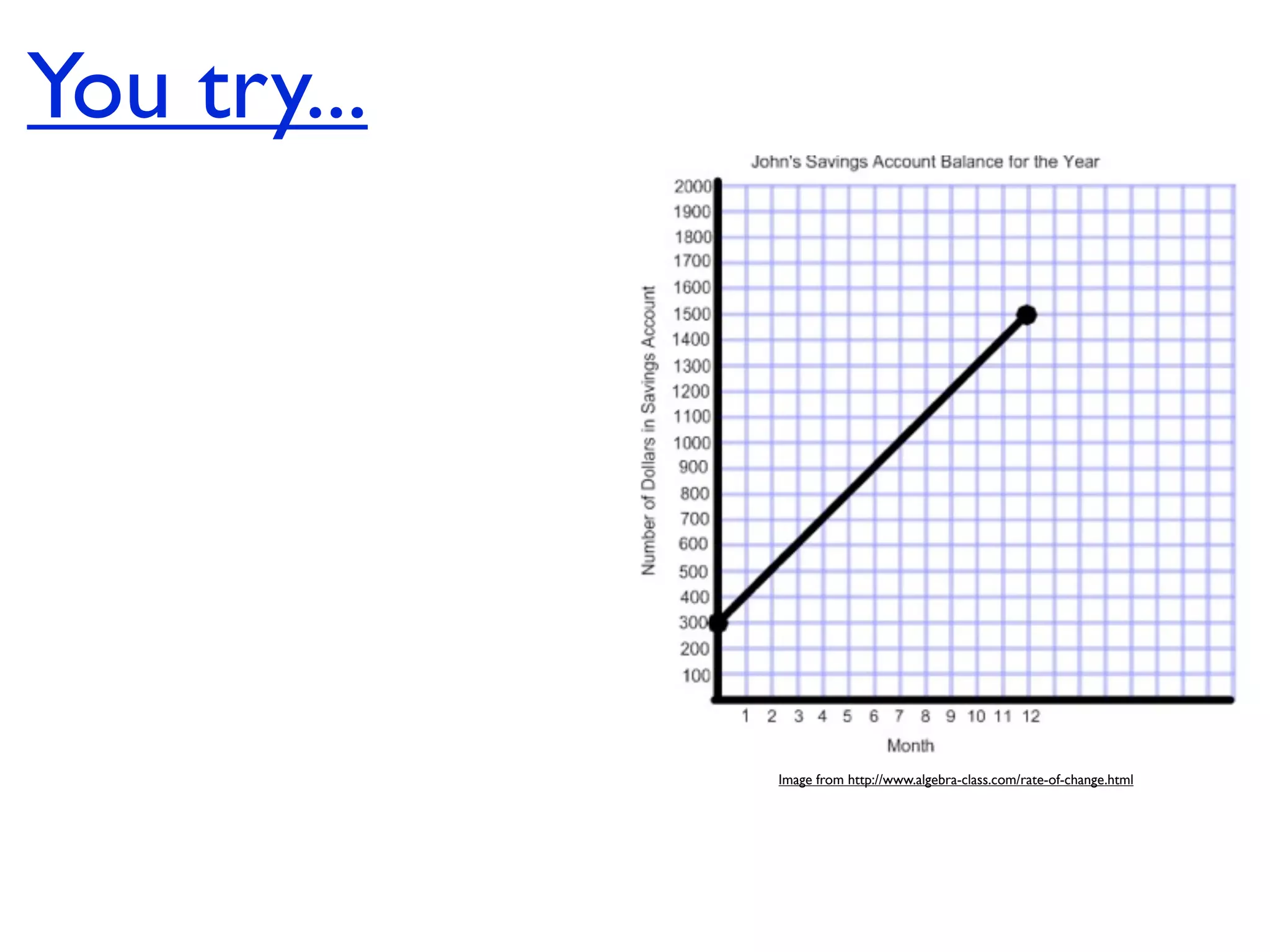
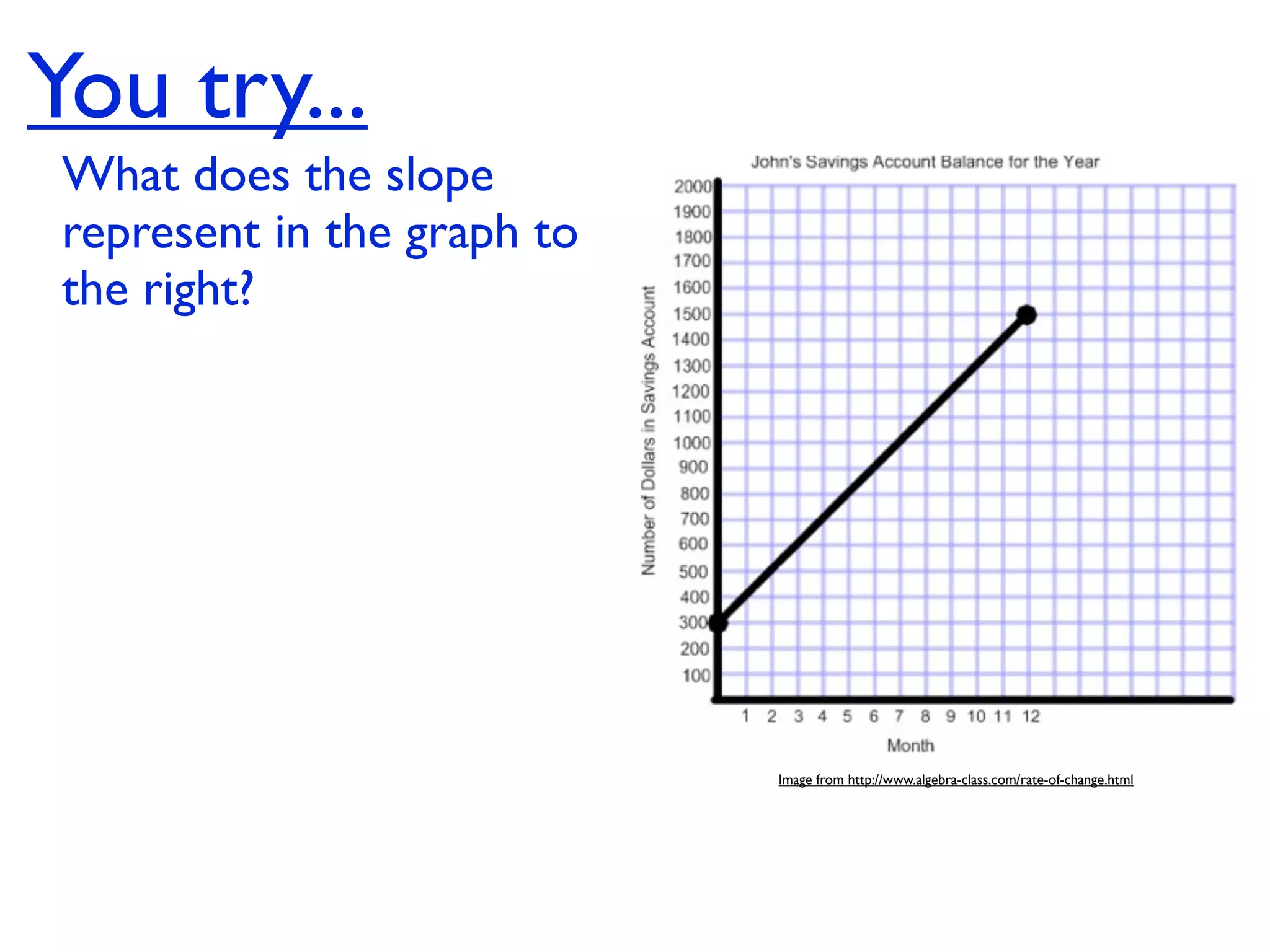
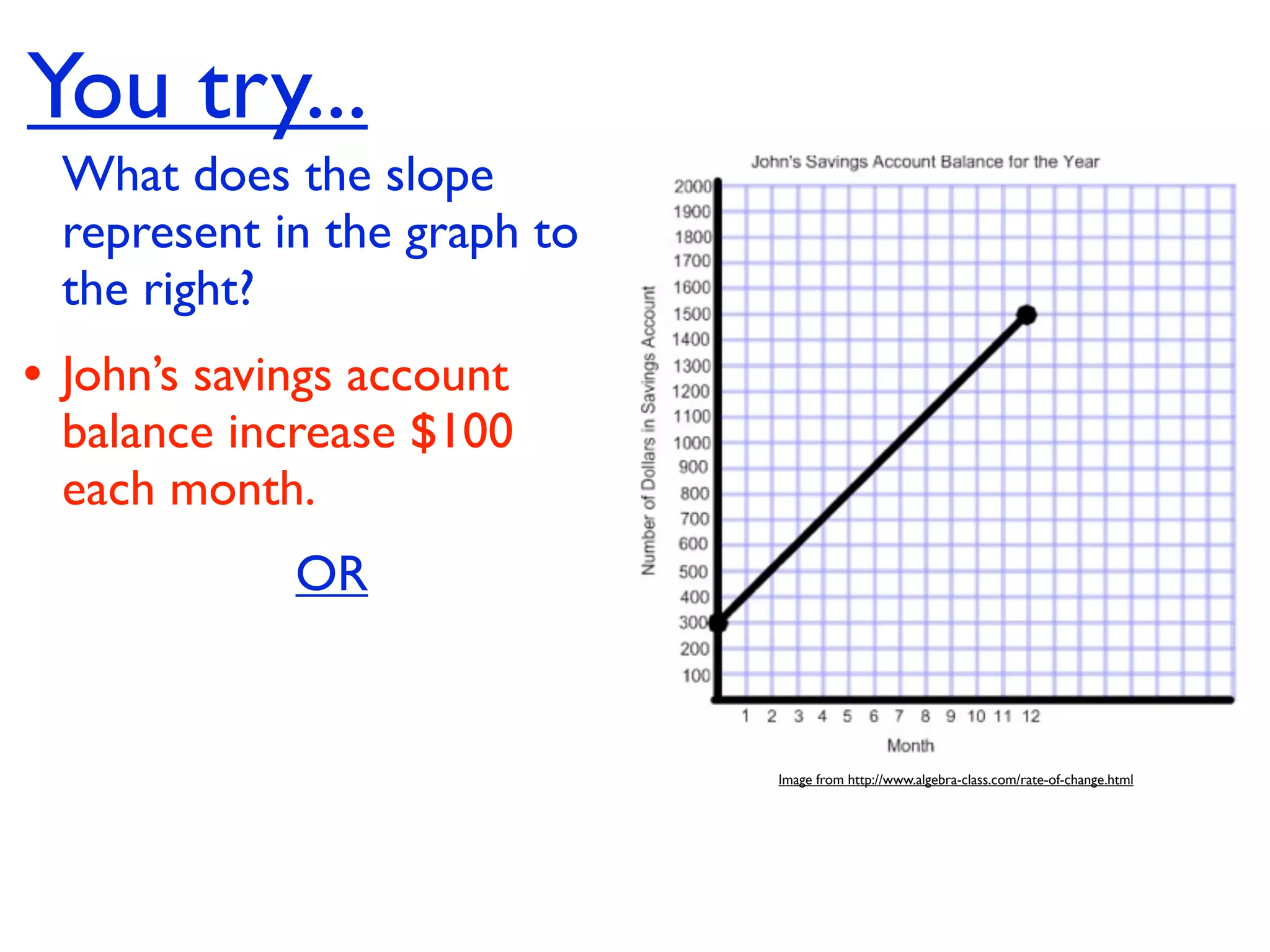
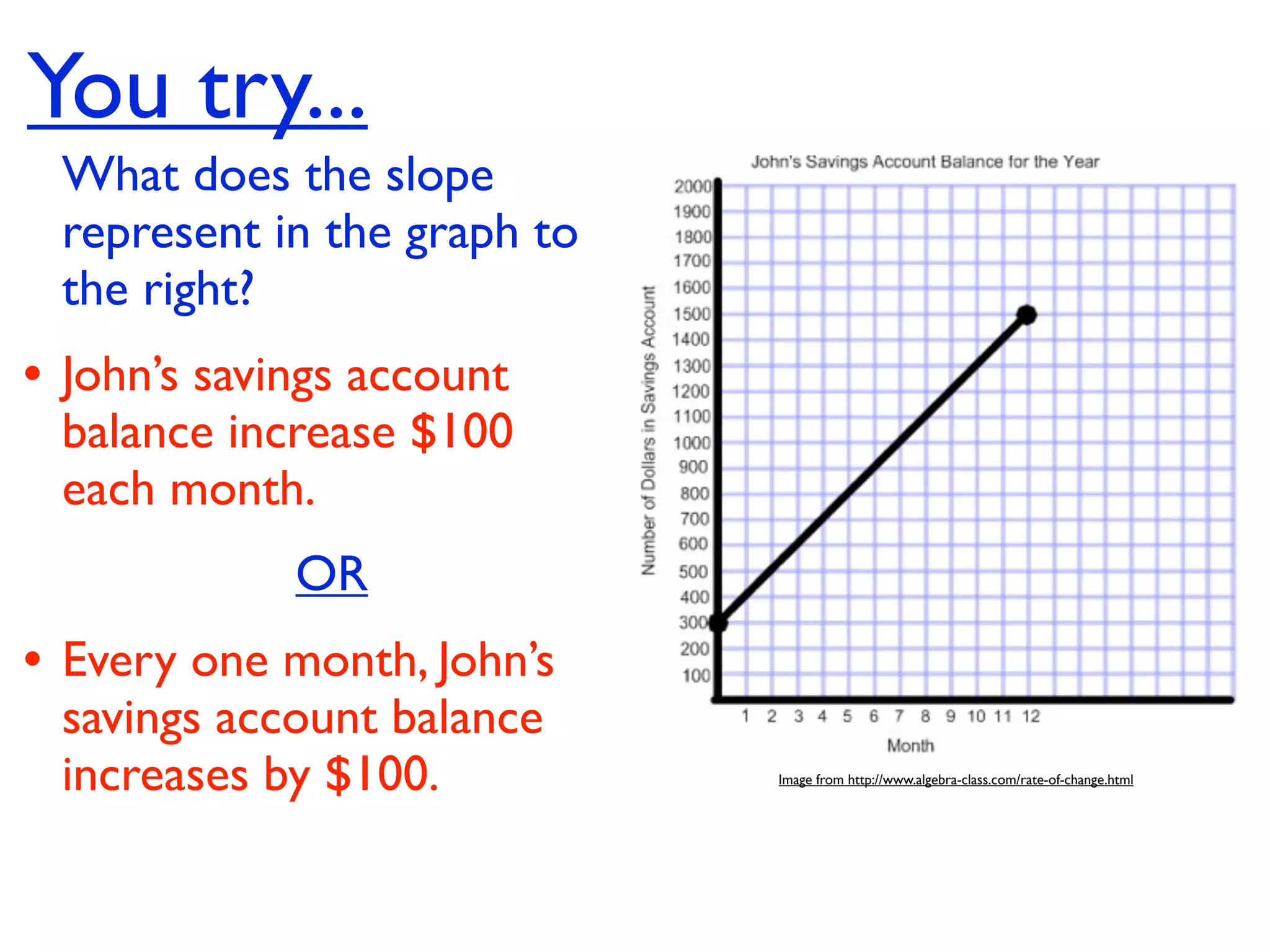
This document discusses direct variation, which is a linear equation that passes through the origin. It defines direct variation as y=kx, where k is the constant of variation. It provides examples of graphs that do and do not represent direct variations. It also shows step-by-step processes for finding the direct variation equation from two points, and for solving a direct variation problem when given a point and asked to find the corresponding y-value for a different x-value.