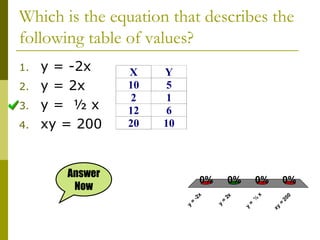
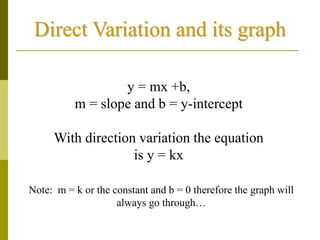
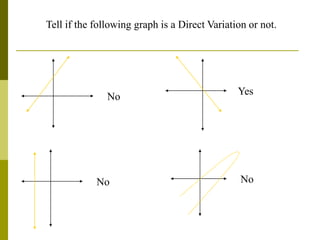
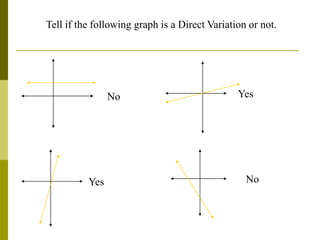
1. Direct variation is a relationship between two quantities where one quantity varies as the other changes in proportion. It can be represented by the equation y = kx, where k is the constant of variation.
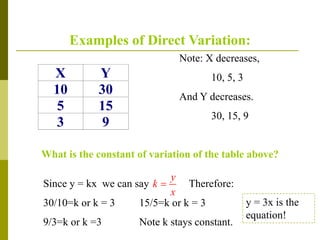
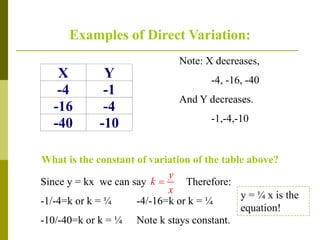
2. Examples show that as x increases or decreases, y also increases or decreases proportionally, maintaining a constant ratio (k). The constant k can be determined from the ratios of corresponding x and y values.
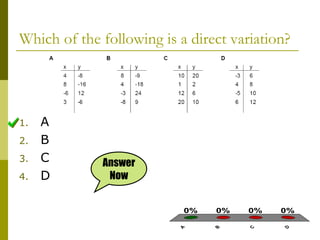
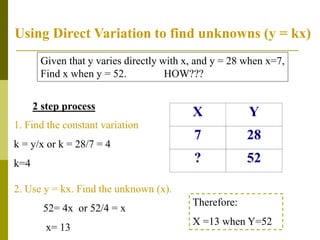
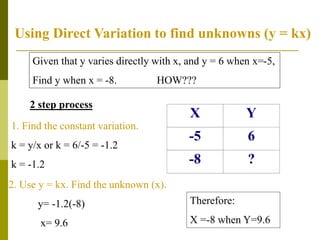
3. Direct variation problems can be solved using a two step process: 1) determine the constant k, and 2) use the direct variation equation y = kx to find the unknown value.