The document discusses direct variation, which is a relationship where two quantities vary proportionally such that their ratio remains constant. The key points are:
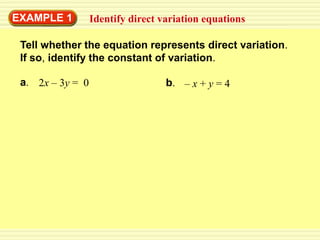
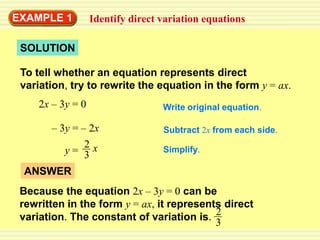
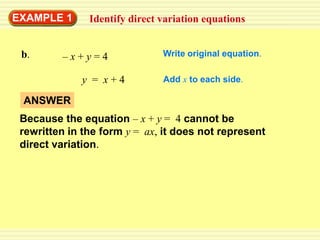
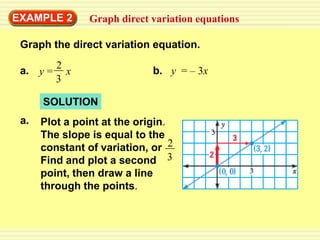
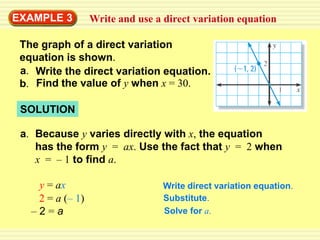
1) A direct variation relationship can be expressed as y = ax, where a is the constant of variation.
2) For a relationship to be direct variation, the equation must be able to be rewritten in the form y = ax.
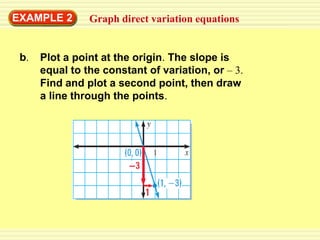
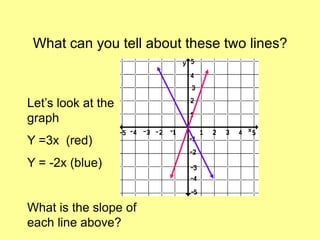
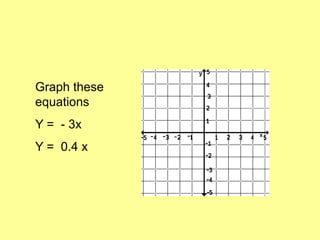
3) A direct variation equation will result in a line passing through the origin when graphed.