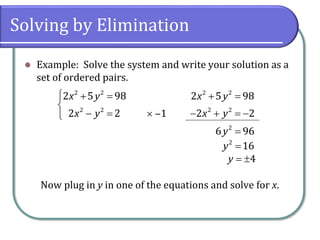
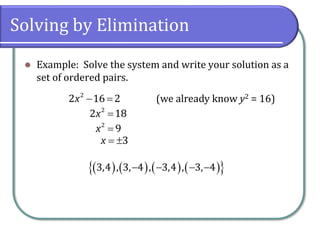
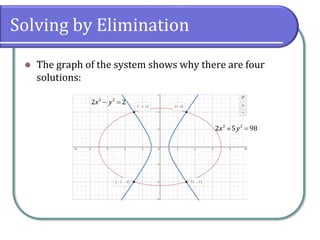
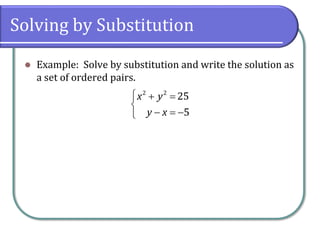
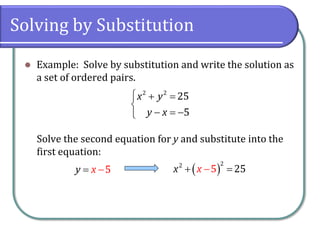
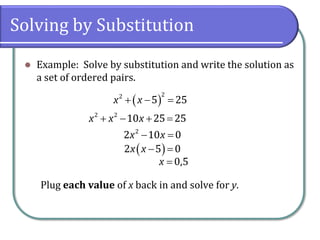
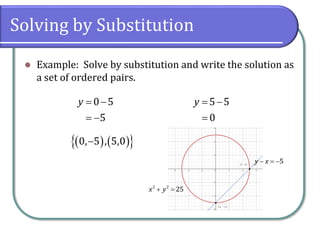
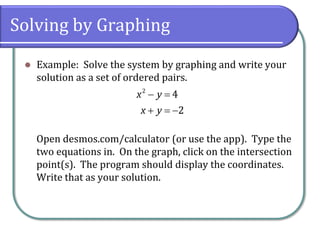
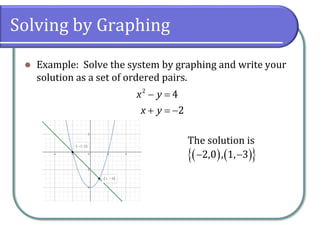
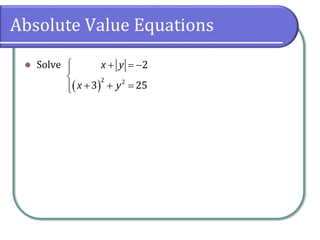
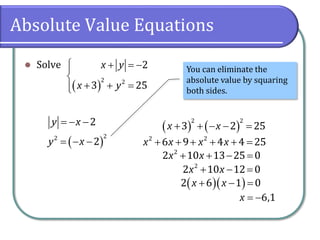
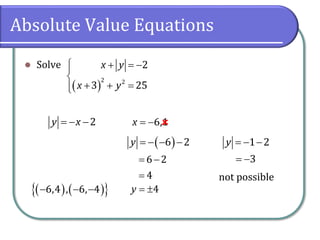
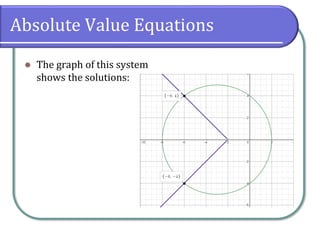
This document discusses methods for solving nonlinear systems of equations, including elimination, substitution, and graphing. It provides examples of solving systems by each method and writing the solutions as ordered pairs. Nonlinear systems contain at least one equation that is not linear. Elimination transforms equations so variables can be eliminated. Substitution solves one equation for a variable and substitutes into the other equations. Graphing can also show the intersection points that are the solutions. The document emphasizes being able to use any solving method and explains solutions may be irrational numbers. It concludes with assigning practice problems from the textbook.