Embed presentation
Downloaded 20 times


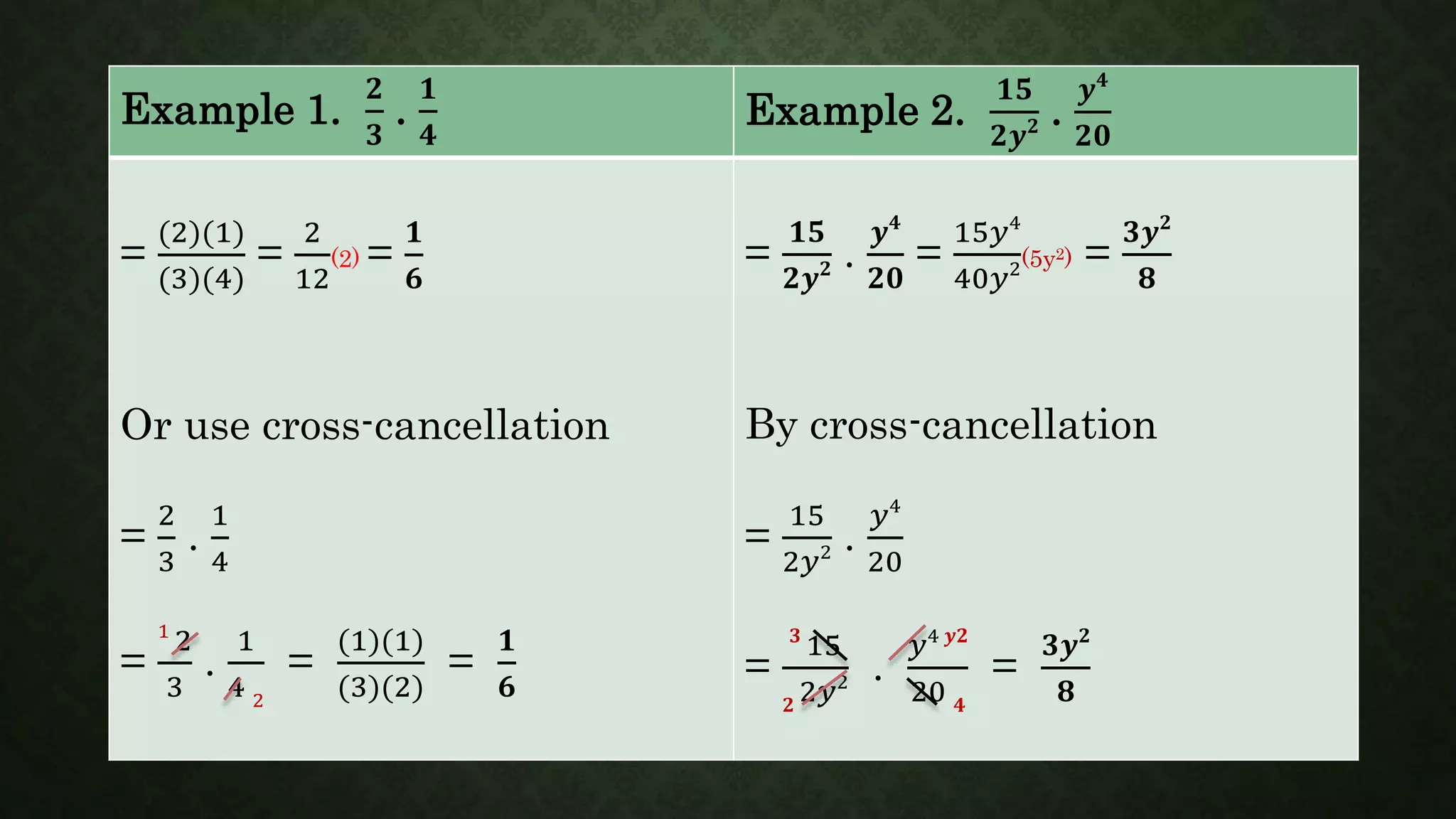

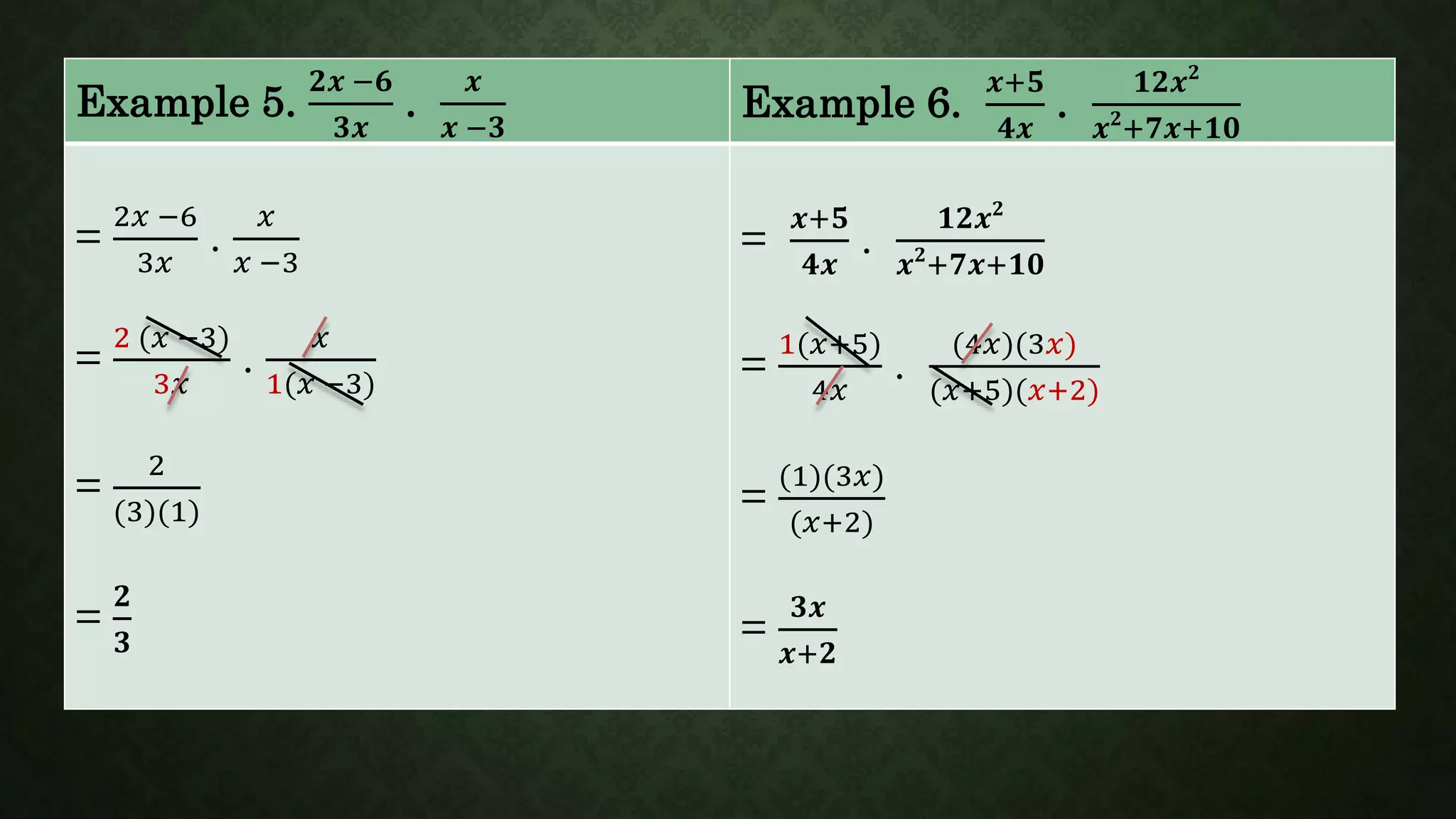

In multiplying rational expressions, we multiply the numerators and denominators, then express the product in its lowest term. This involves: - Multiplying the numerators and denominators of each rational expression - Using cross-cancellation to express the product in lowest terms - Examples are provided to demonstrate multiplying rational expressions and expressing the product in lowest terms through cross-cancellation.





