The document discusses different types of variations:
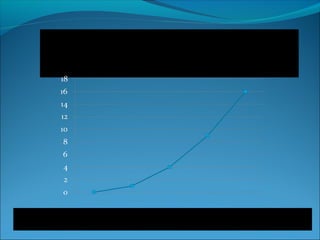
1) Direct variation results in a straight line graph, while direct square variation results in a parabolic graph.
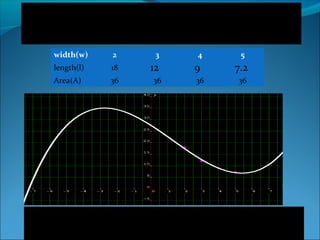
2) Inverse variation means that as one variable increases, the other decreases, maintaining a constant product. The graph of an inverse variation is a hyperbola.
3) Examples show inverse variations between variables like pressure and volume of a gas, or jobs completed and number of workers.
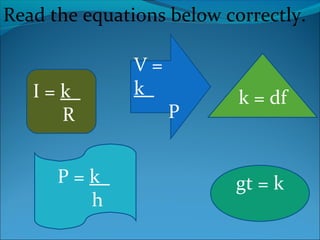
4) Quiz questions test understanding of direct, inverse, and their equation representations.