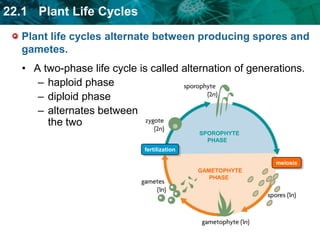
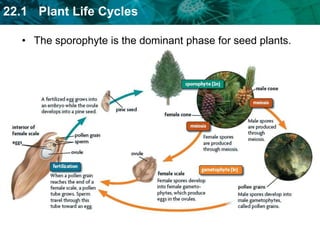
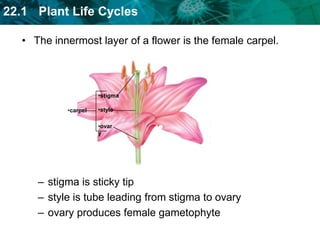
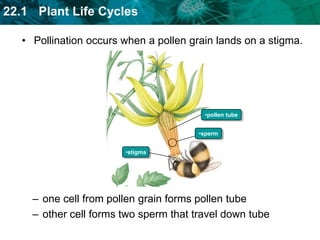
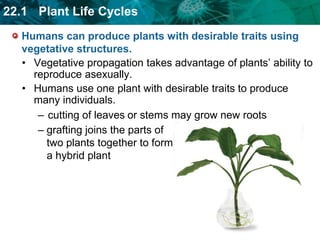
1. Plant life cycles alternate between a sporophyte phase and gametophyte phase through the process of meiosis and fertilization.
2. The sporophyte phase produces spores via meiosis while the gametophyte phase produces gametes via mitosis which can fuse during fertilization.
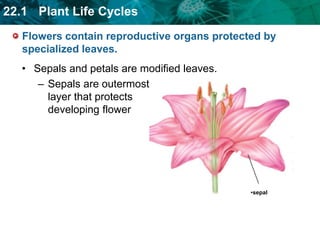
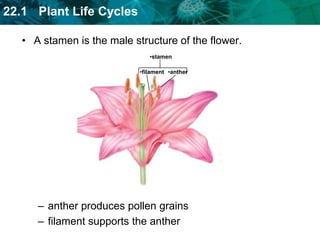
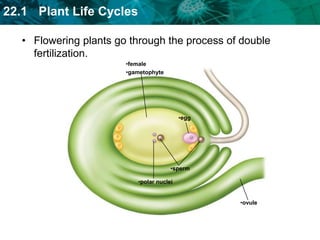
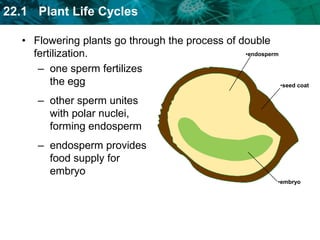
3. Flowering plants undergo a double fertilization process within flowers where one sperm cell fertilizes the egg to form the embryo while another sperm cell fuses with polar nuclei to form endosperm.