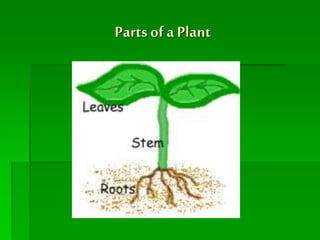
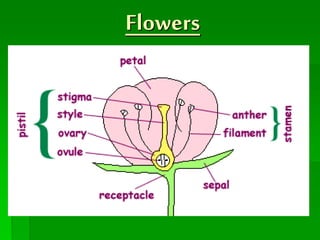
Roots take in water and minerals from the soil and anchor the plant. Stems transport water and nutrients between the roots and leaves using xylem and phloem. Leaves use photosynthesis to produce food for the plant by converting carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight into glucose. Flowers are important for reproduction by making seeds through fertilization to attract pollinators like bees and birds. Plants have adapted features like thorns, spikes, poisonous leaves, colorful flowers and fruits, wind-pollinated pollen, and dormancy to protect themselves, reproduce, and survive in different climates and locations.