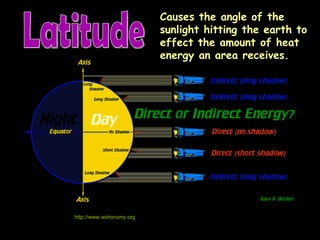
The climate of an area is determined by temperature and precipitation. Several factors influence temperature and precipitation differences around the world, including latitude, altitude, ocean currents, prevailing winds, and mountain ranges. Closer proximity to the equator means more direct sunlight and higher temperatures, while latitude also determines the angle of incoming sunlight. Altitude and proximity to ocean currents transporting warm or cold water also impact regional climates. Prevailing winds can influence precipitation levels depending on their moisture content, and mountain ranges often create rain shadows on their leeward sides where precipitation is lower.