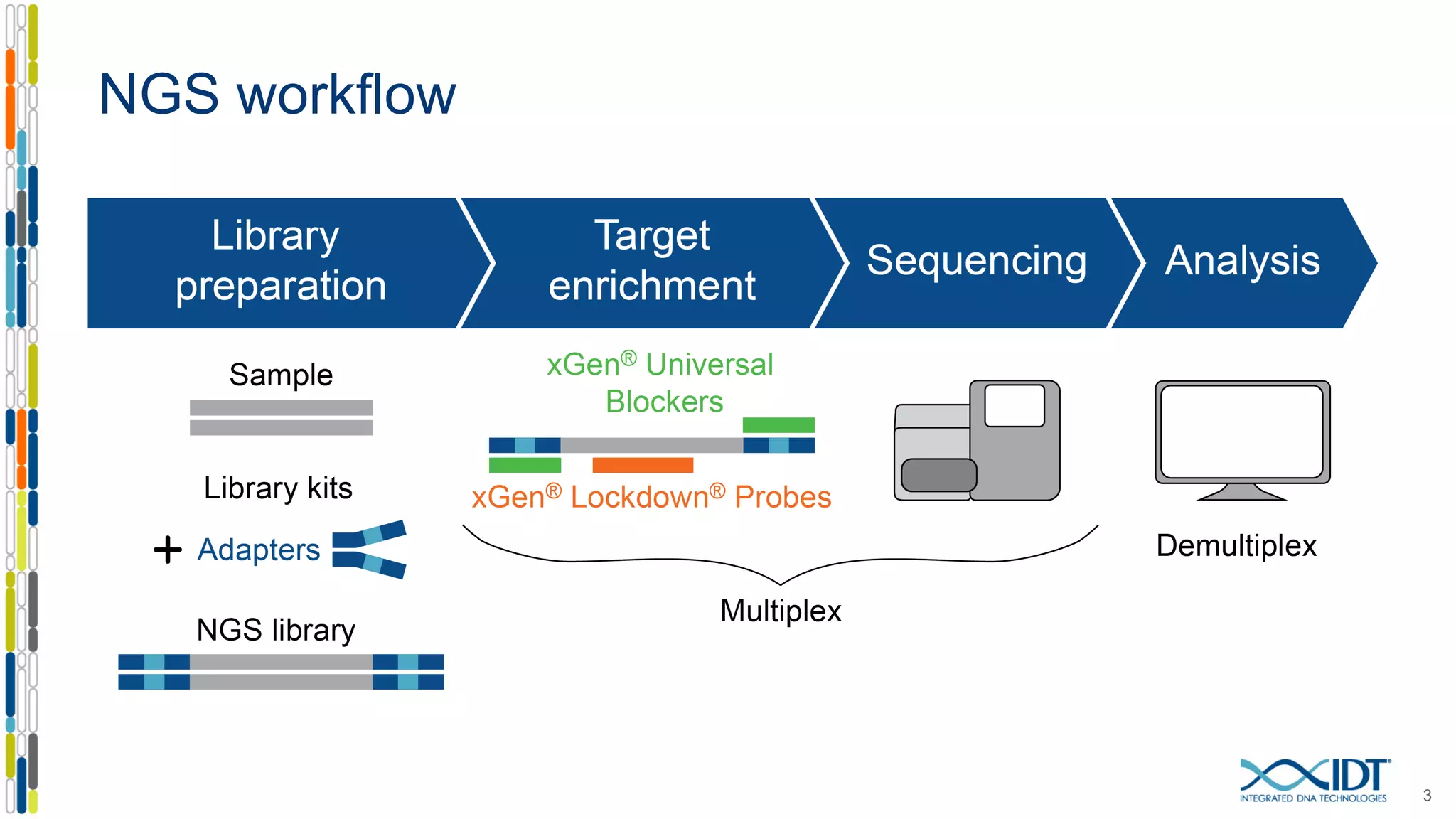
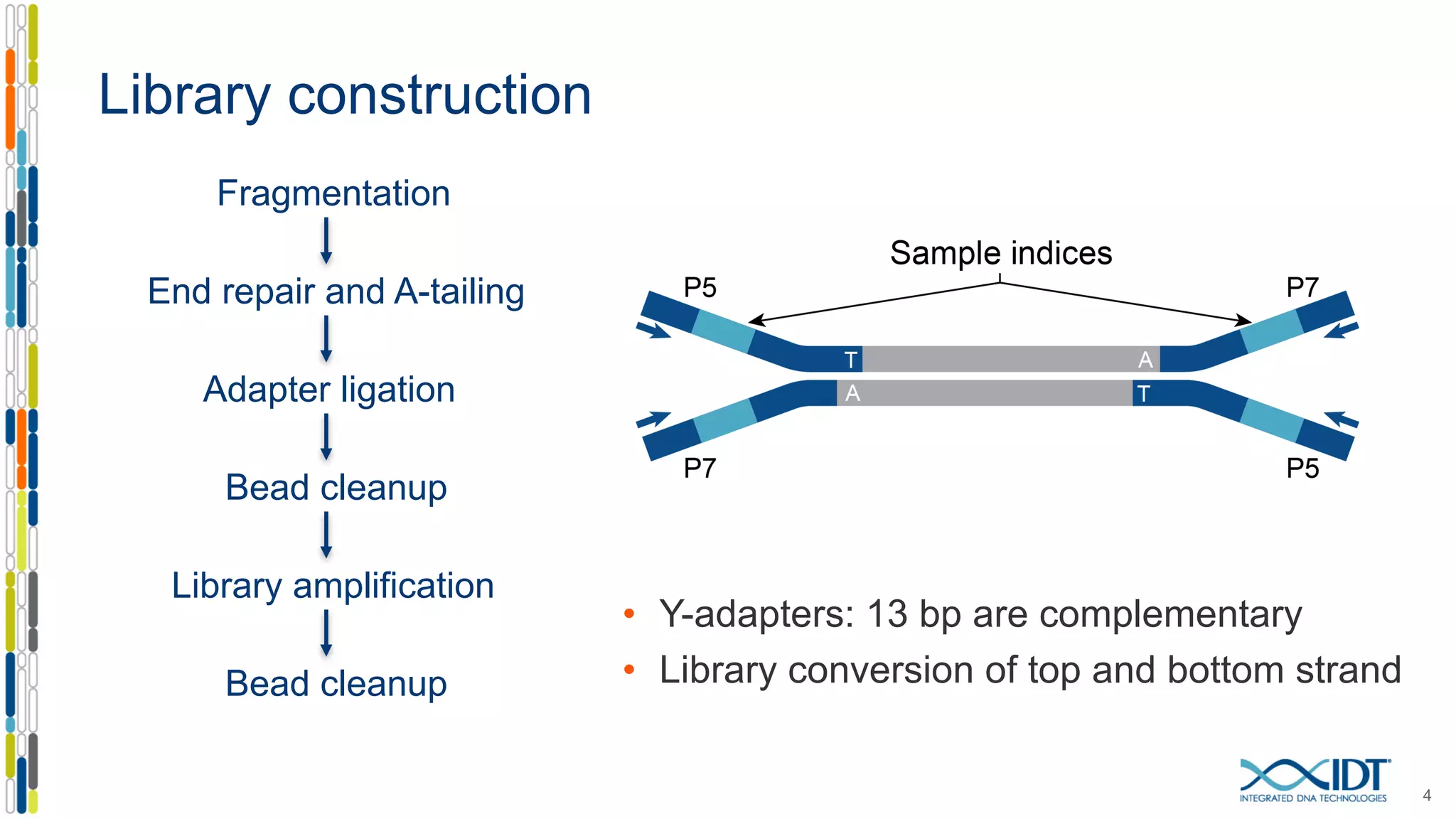
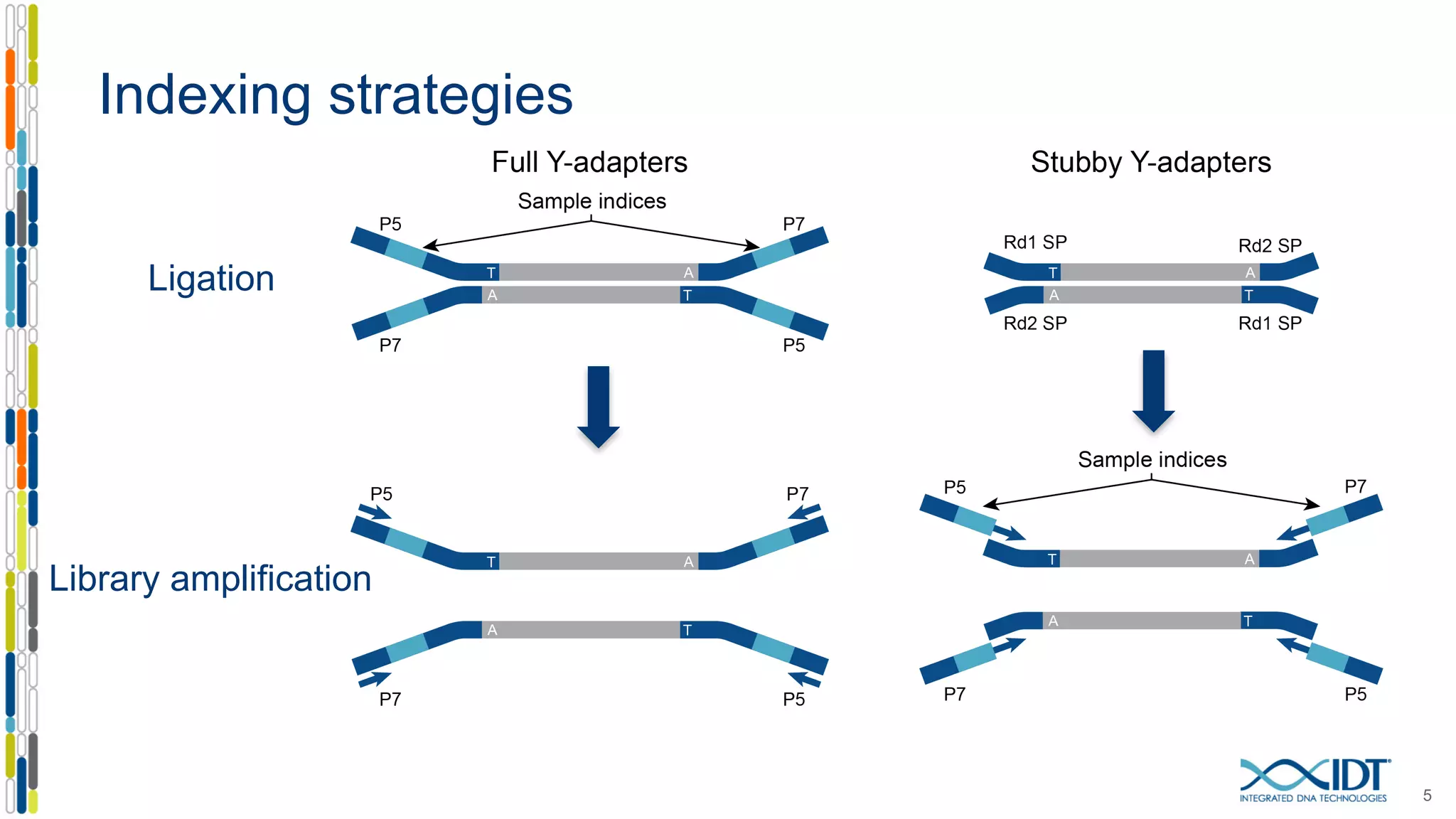
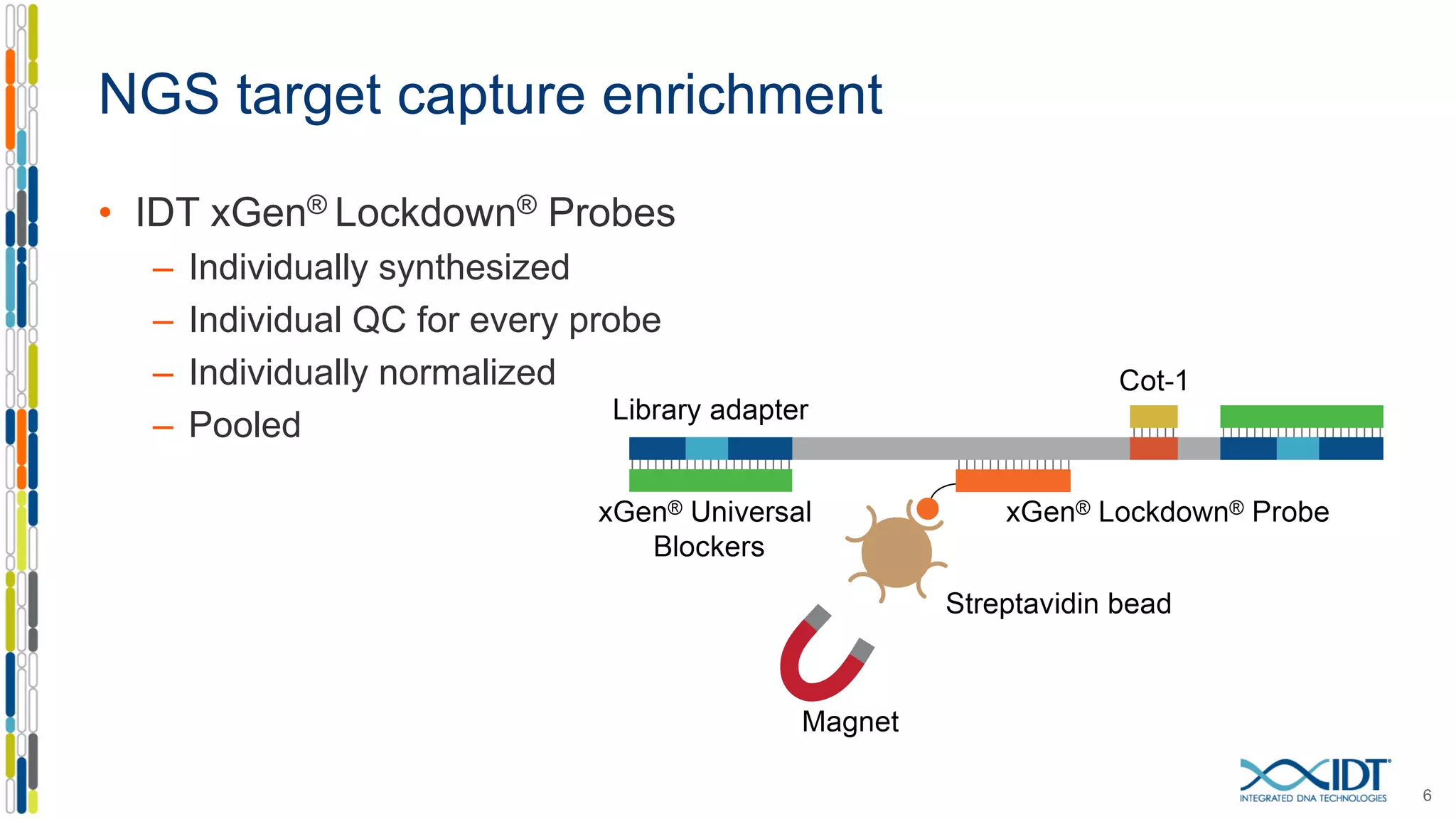
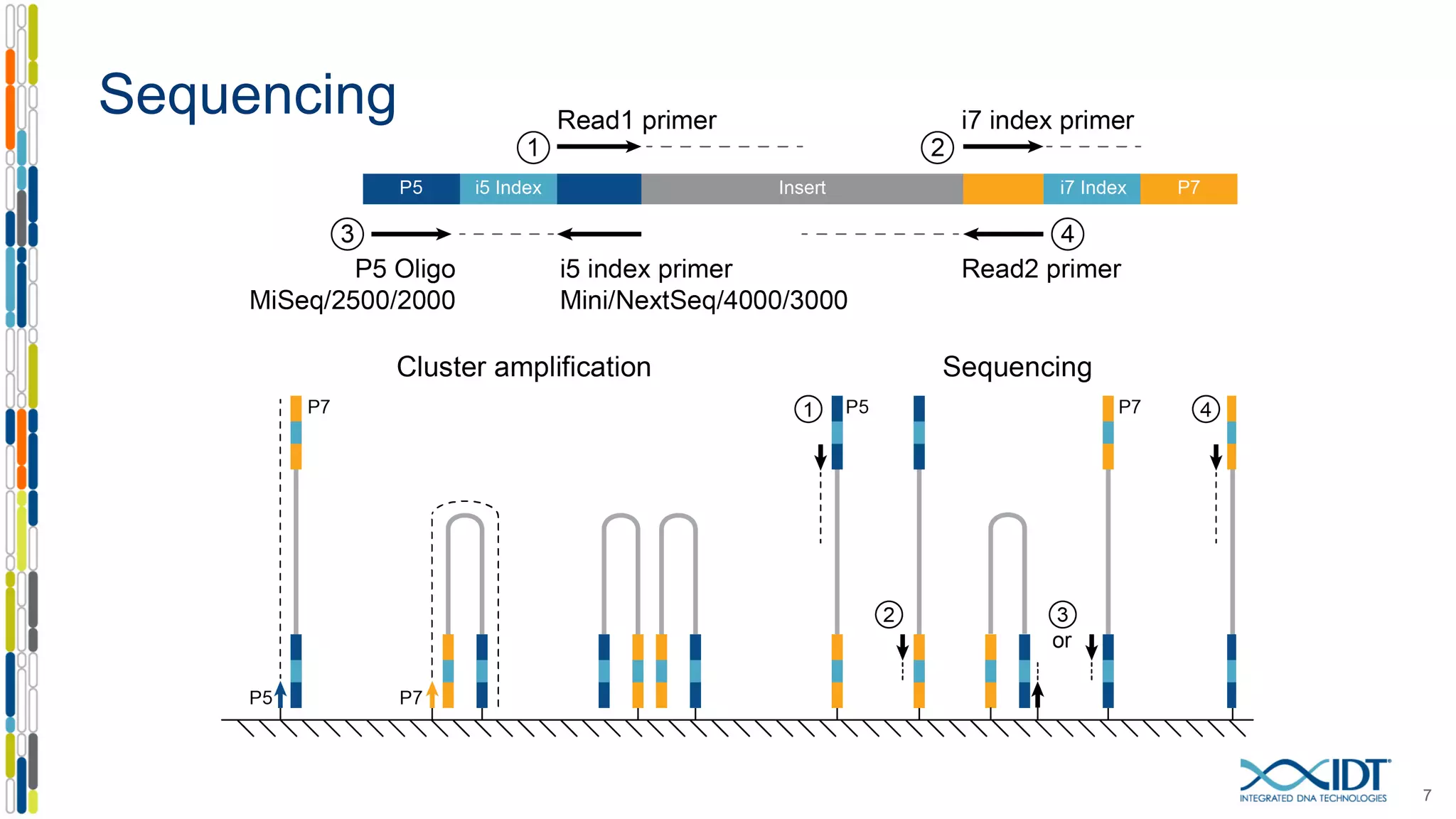
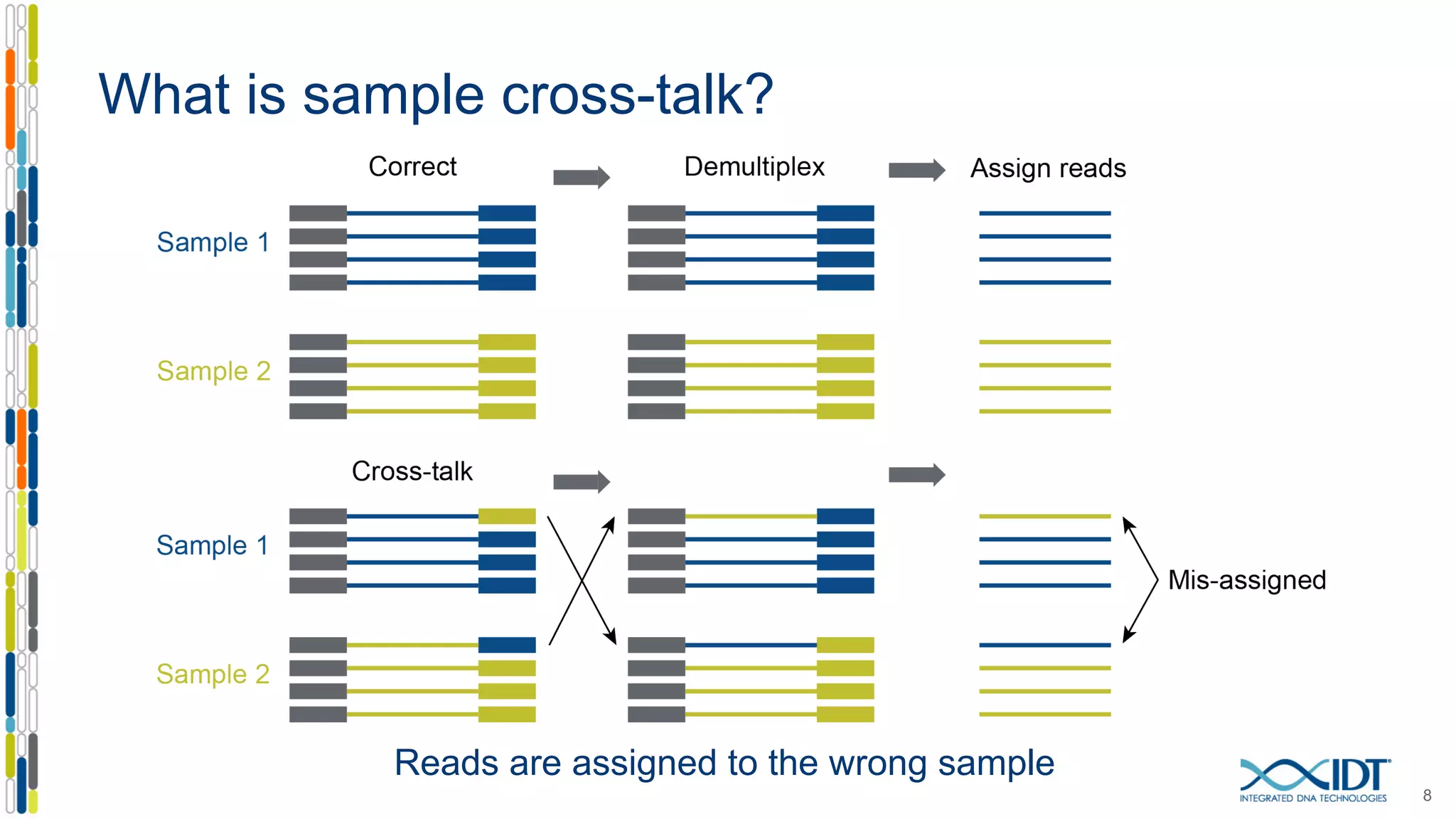
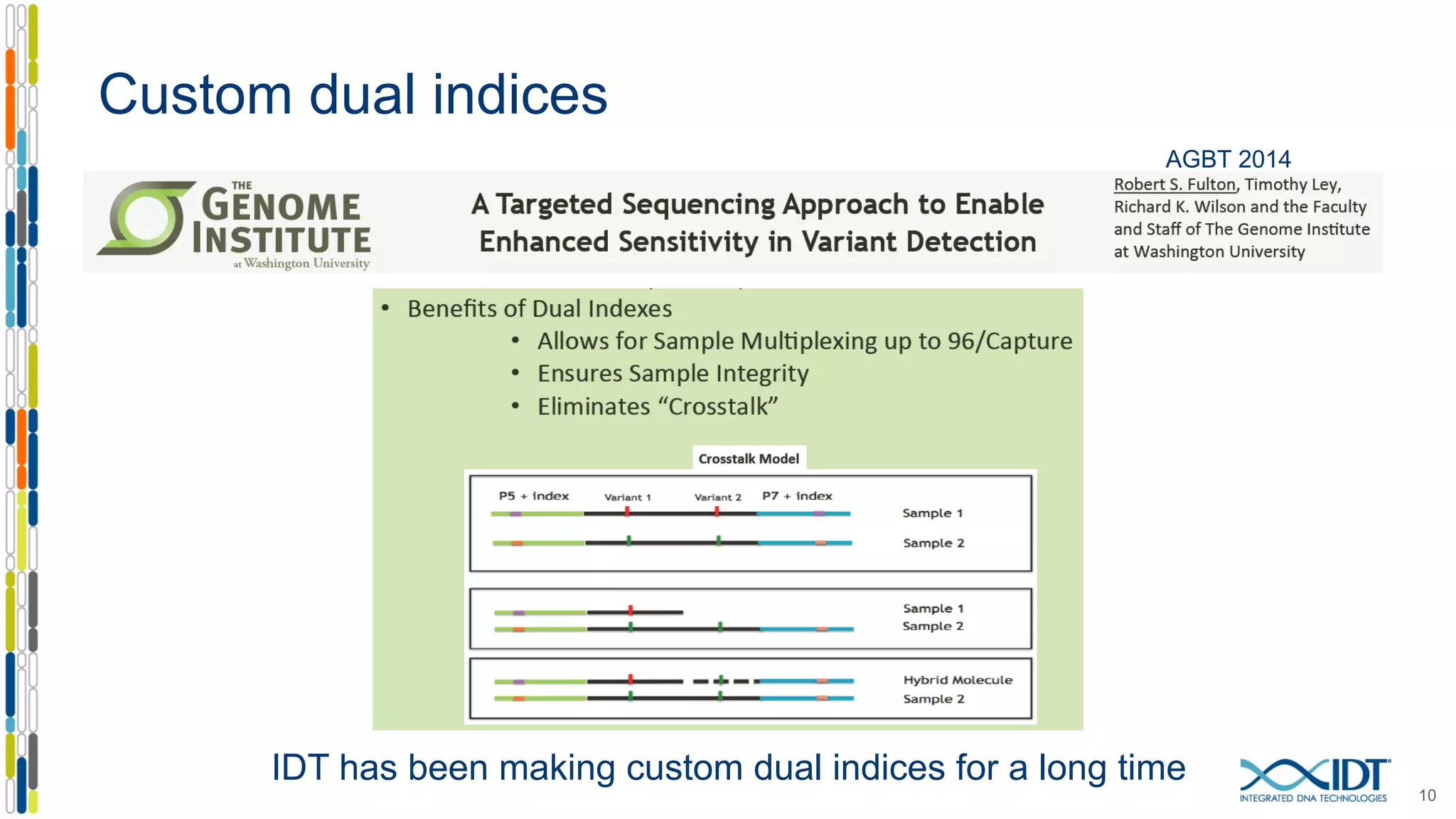
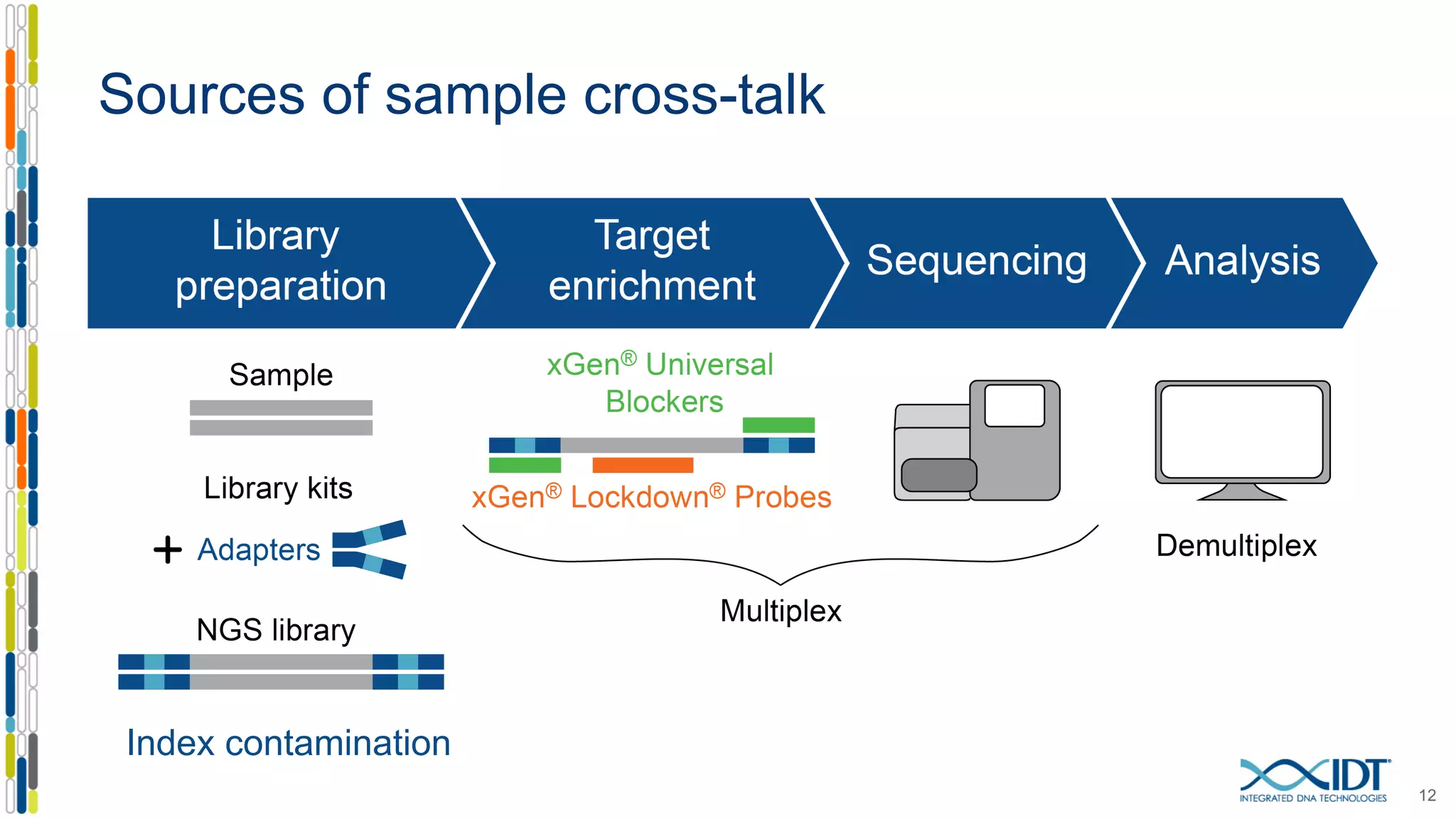
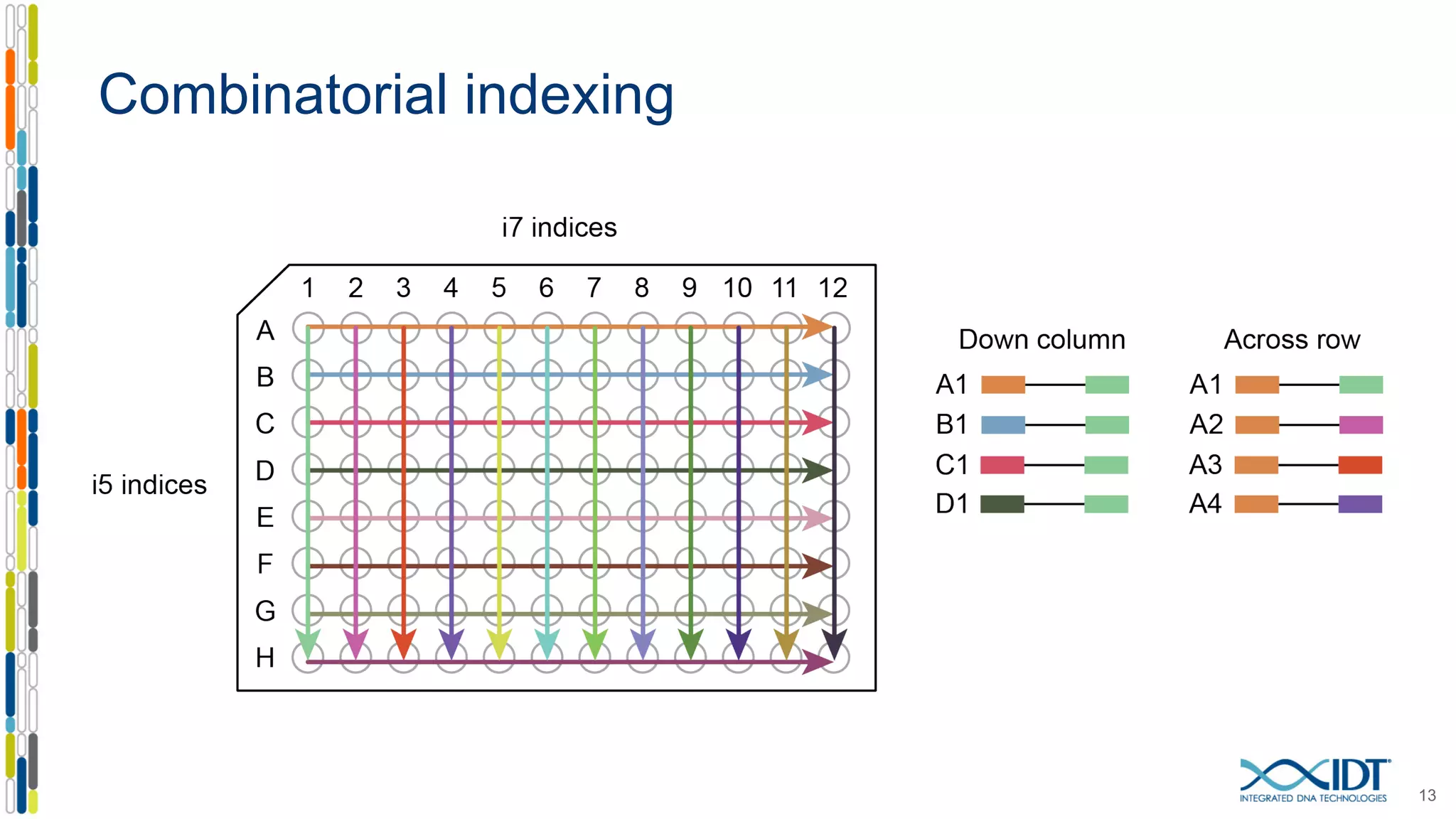
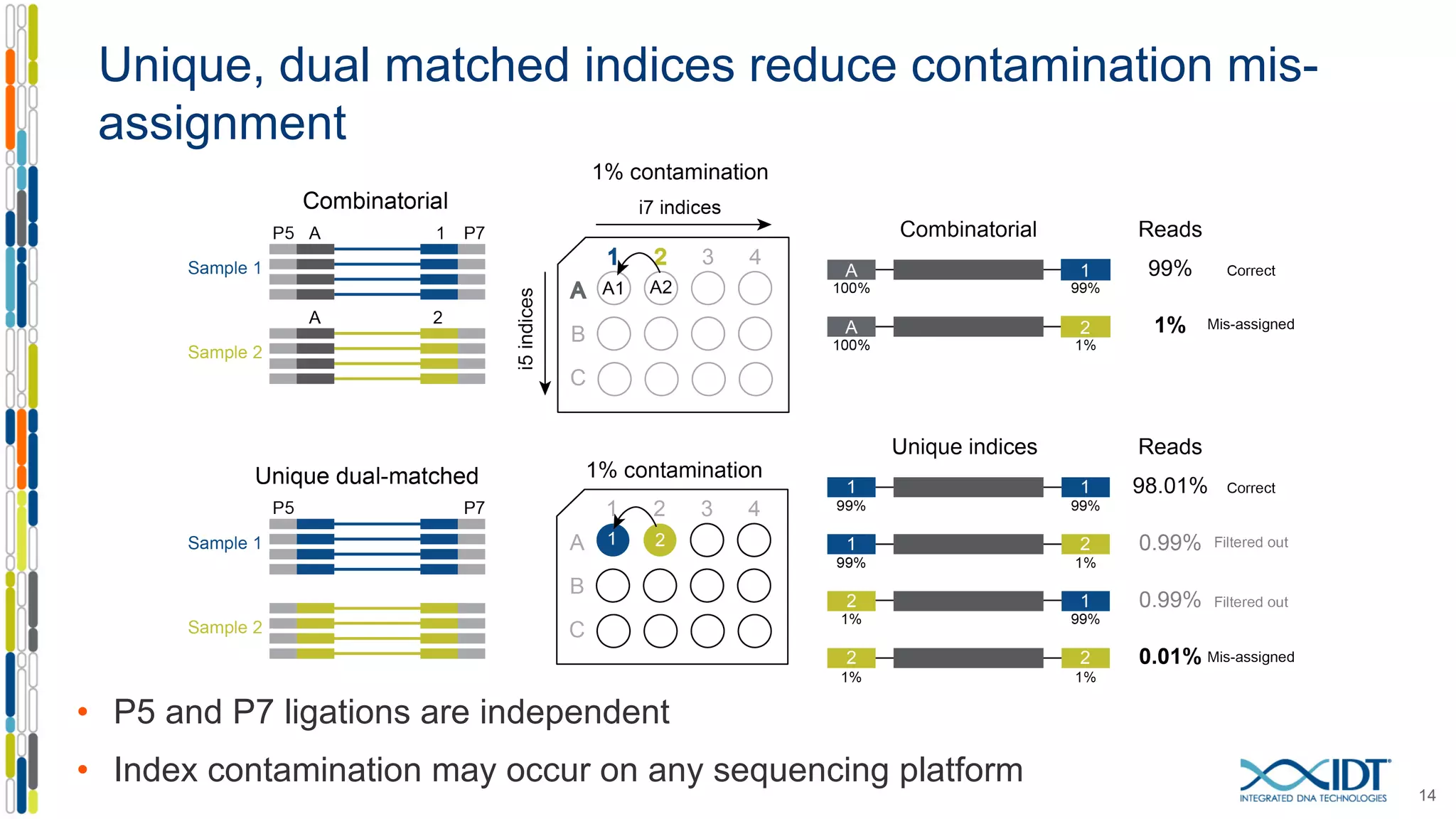
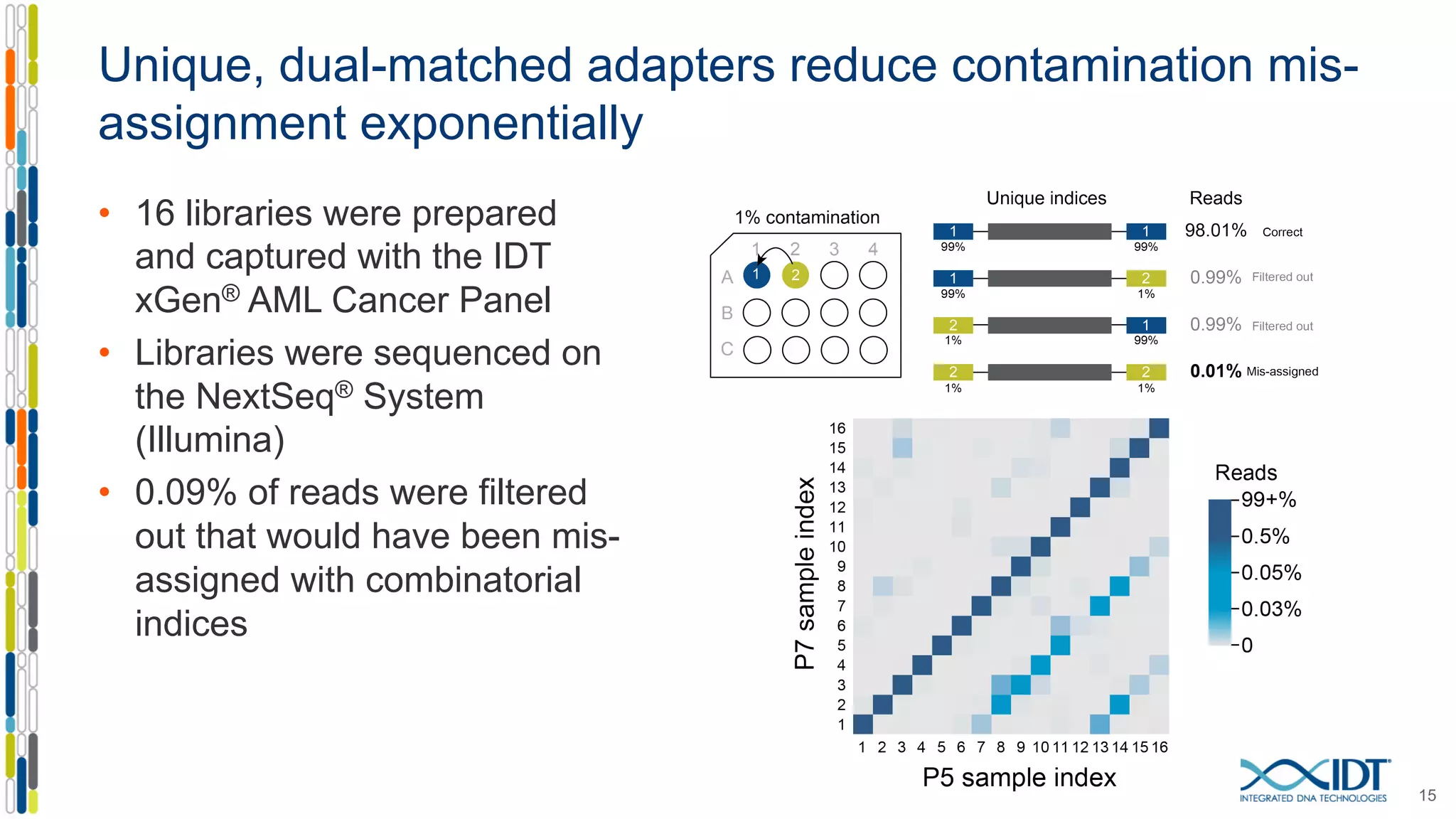
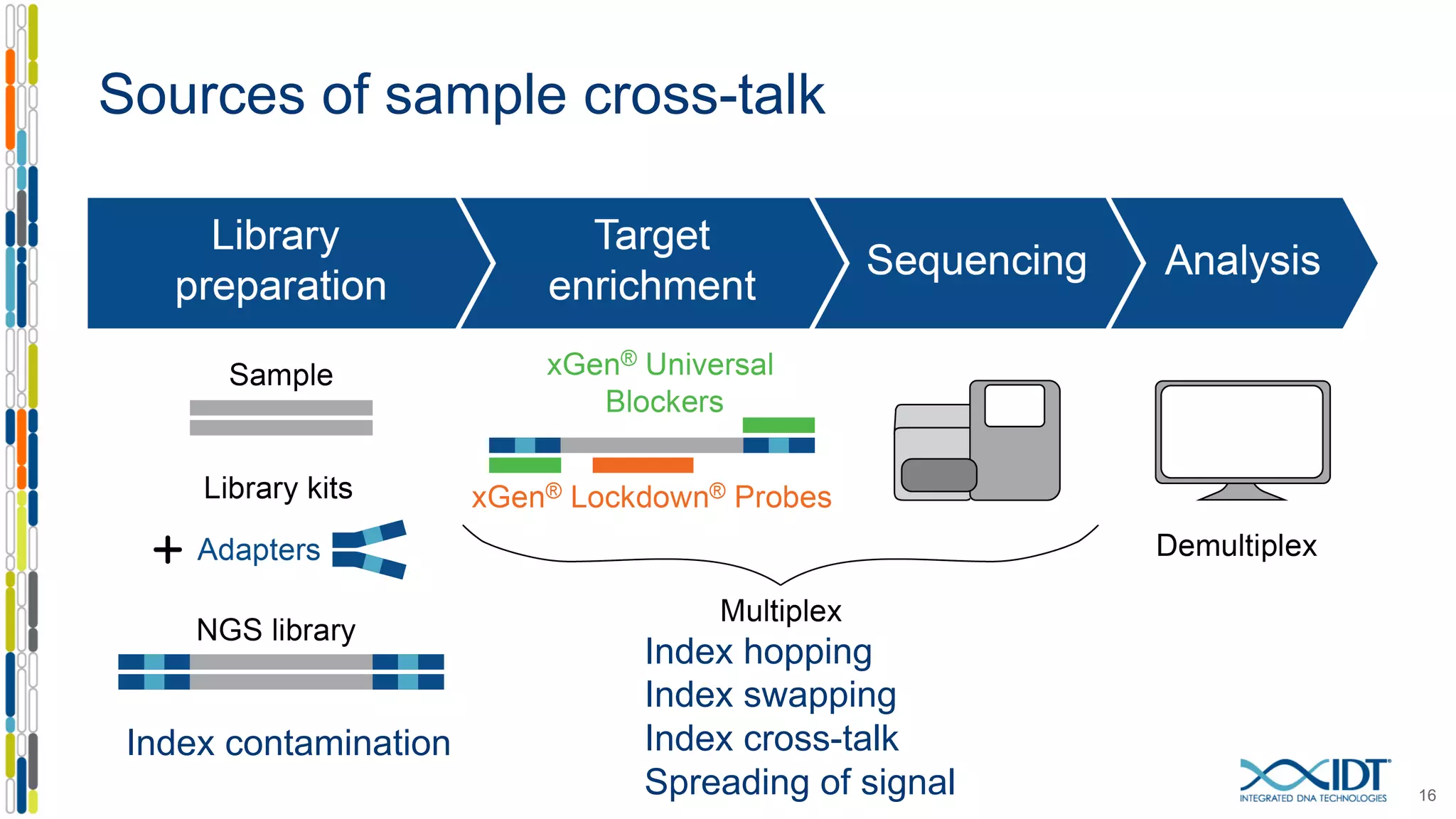
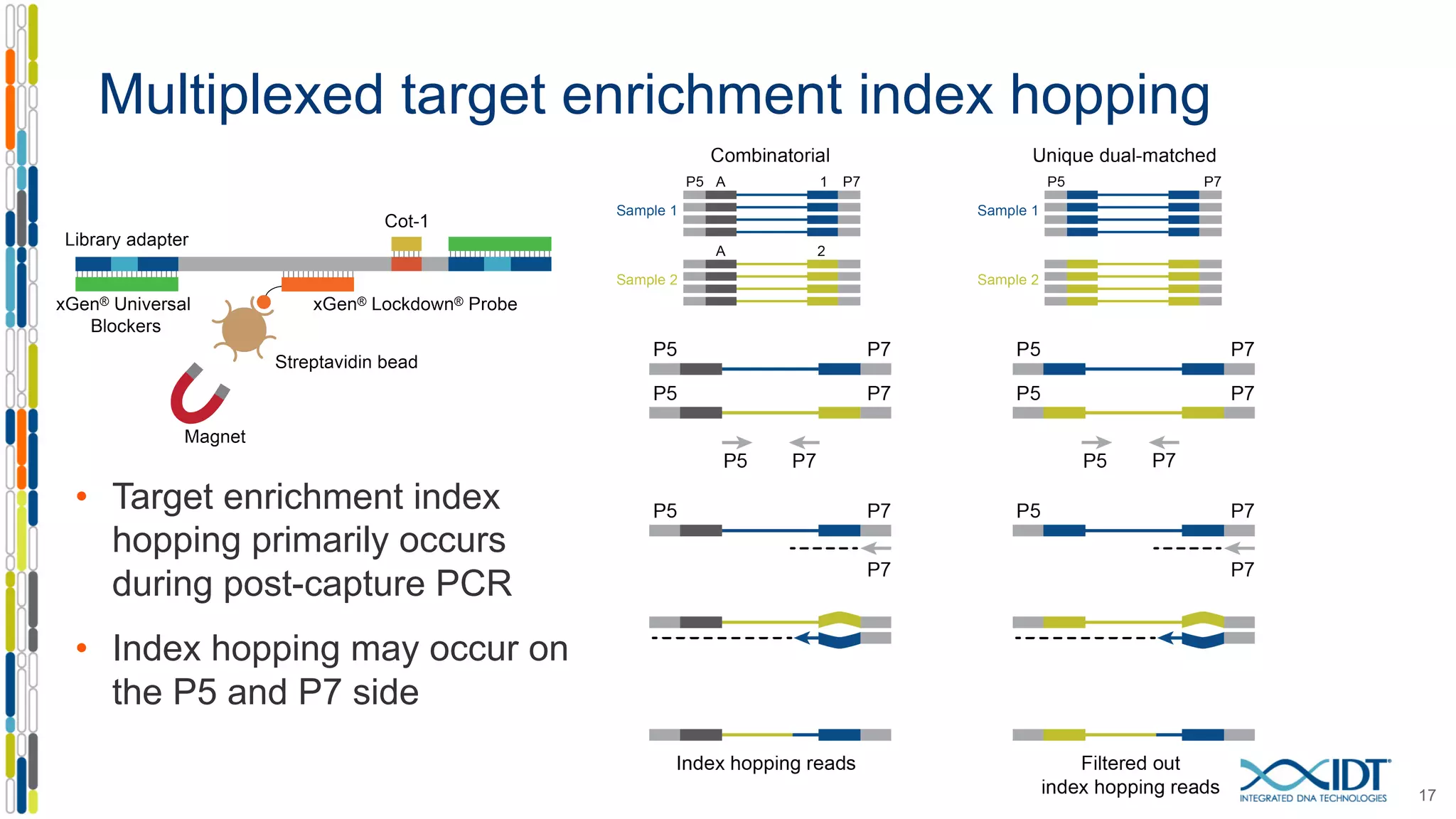
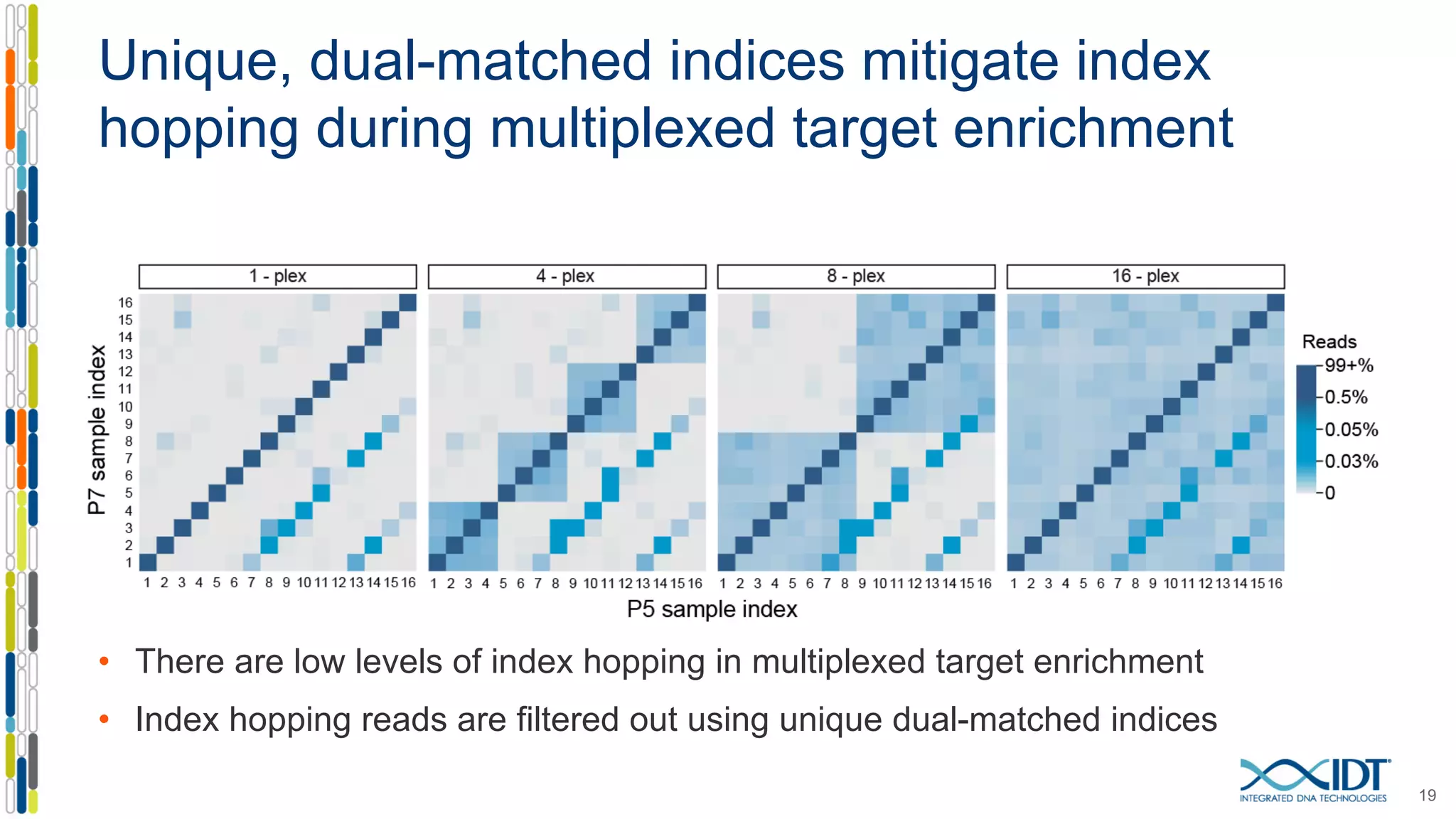
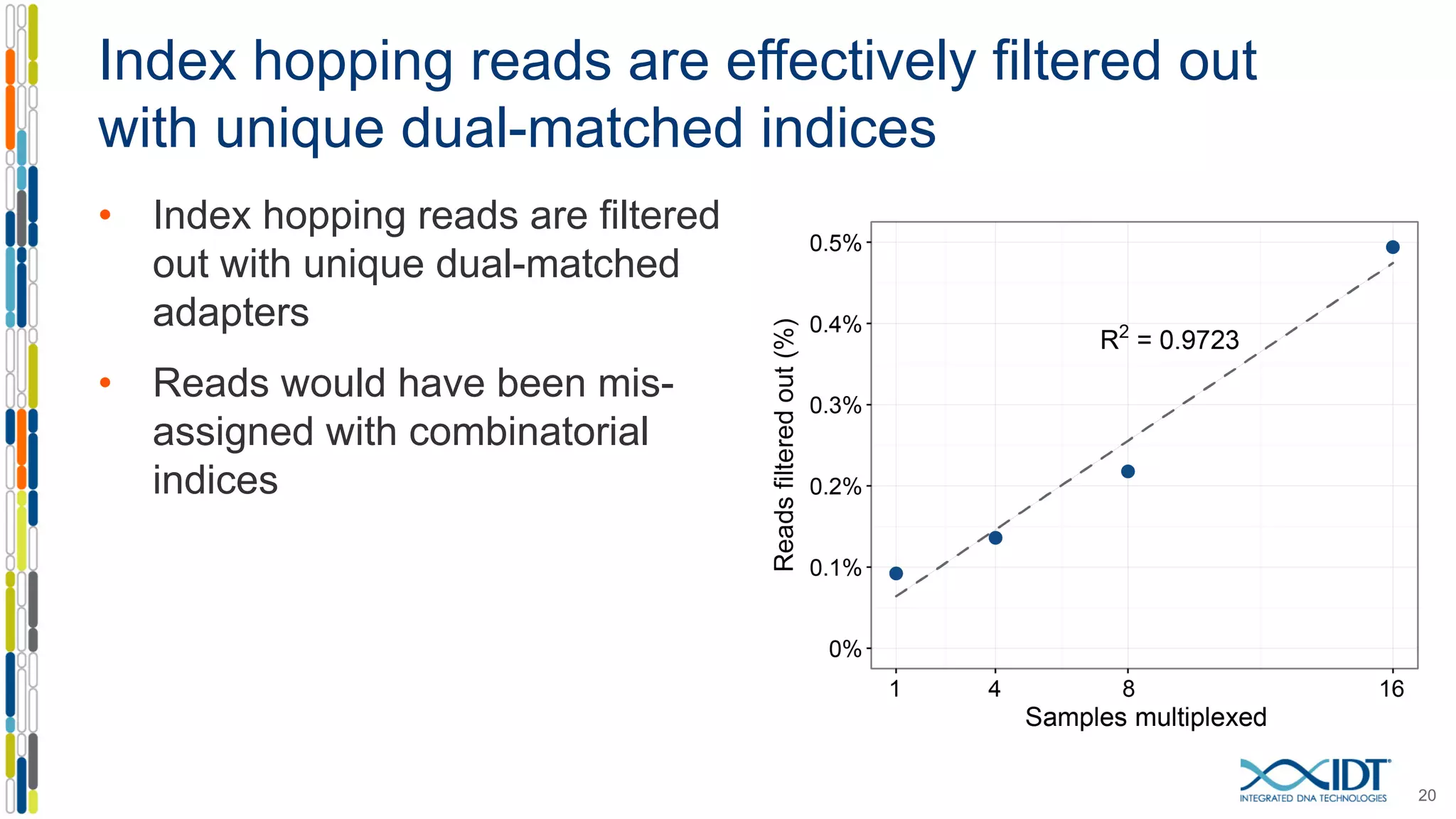
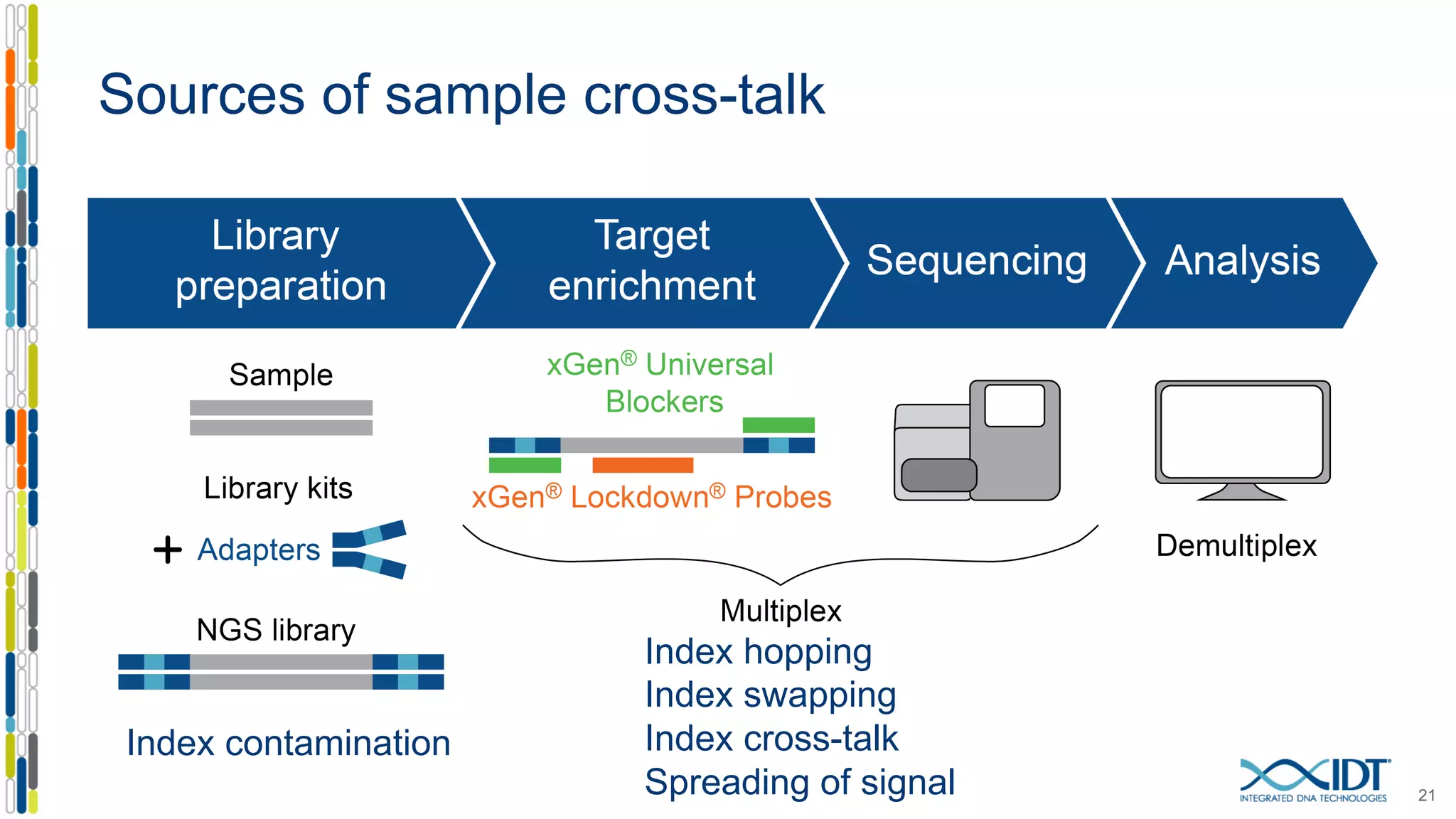
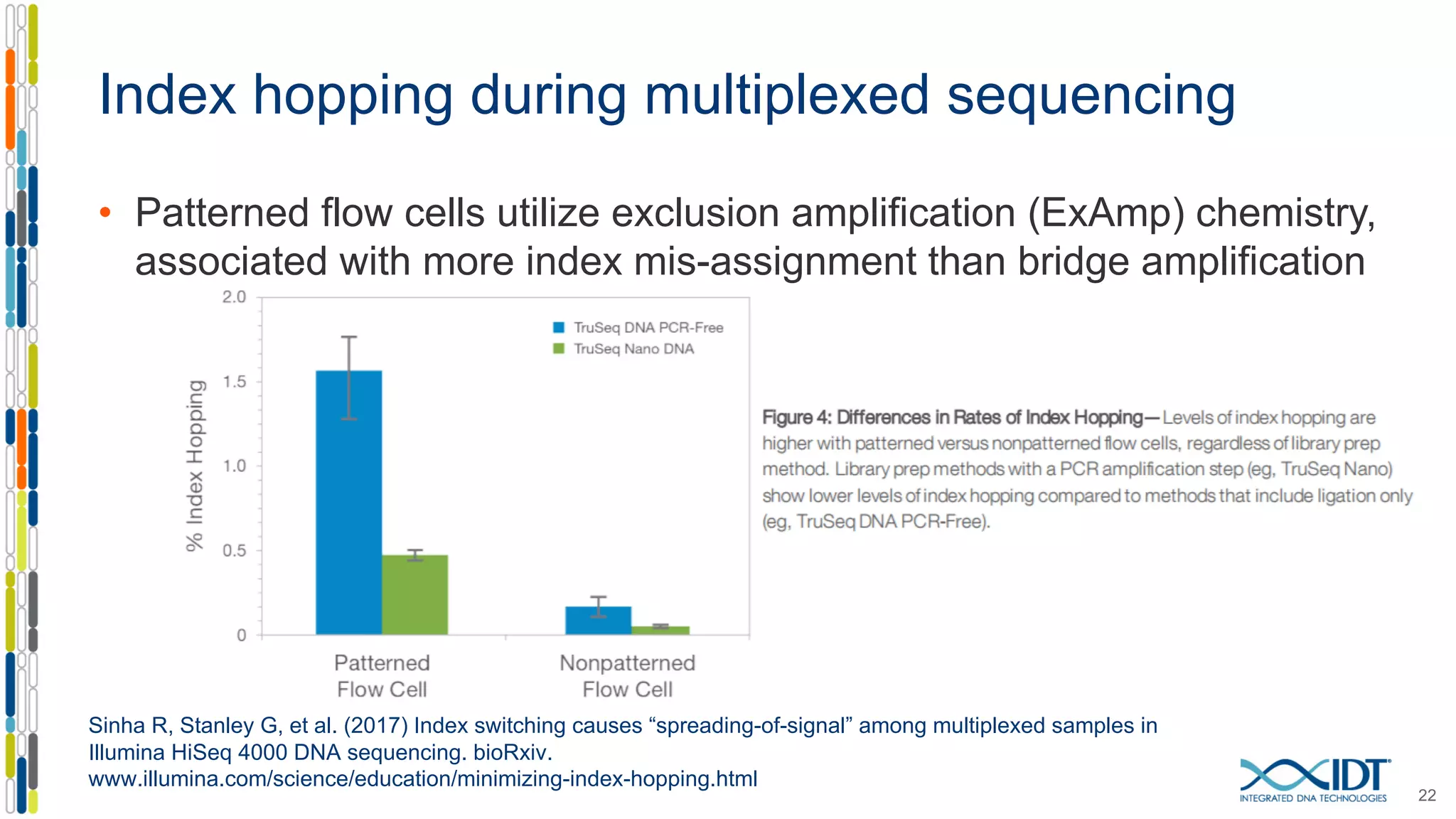
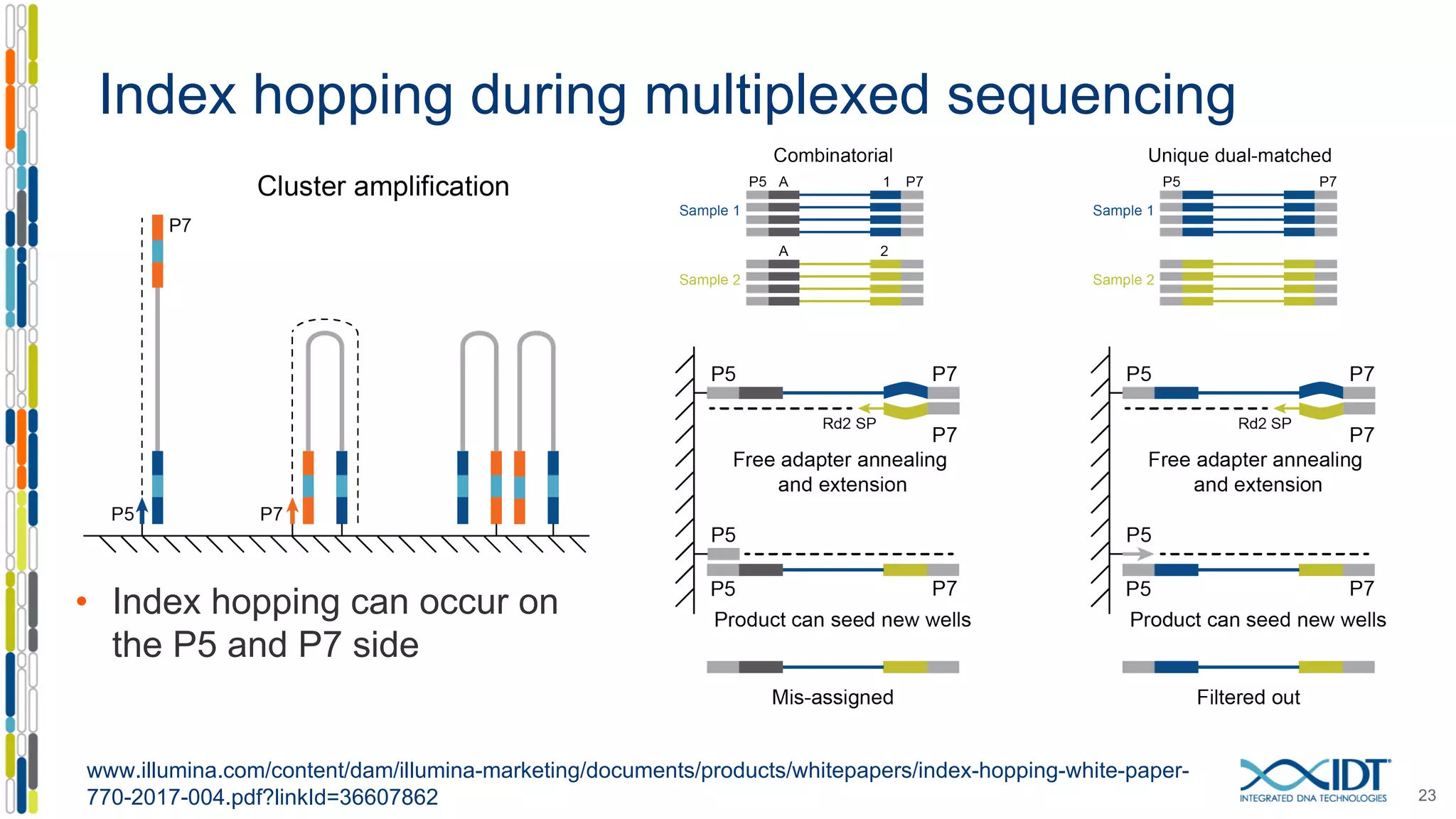
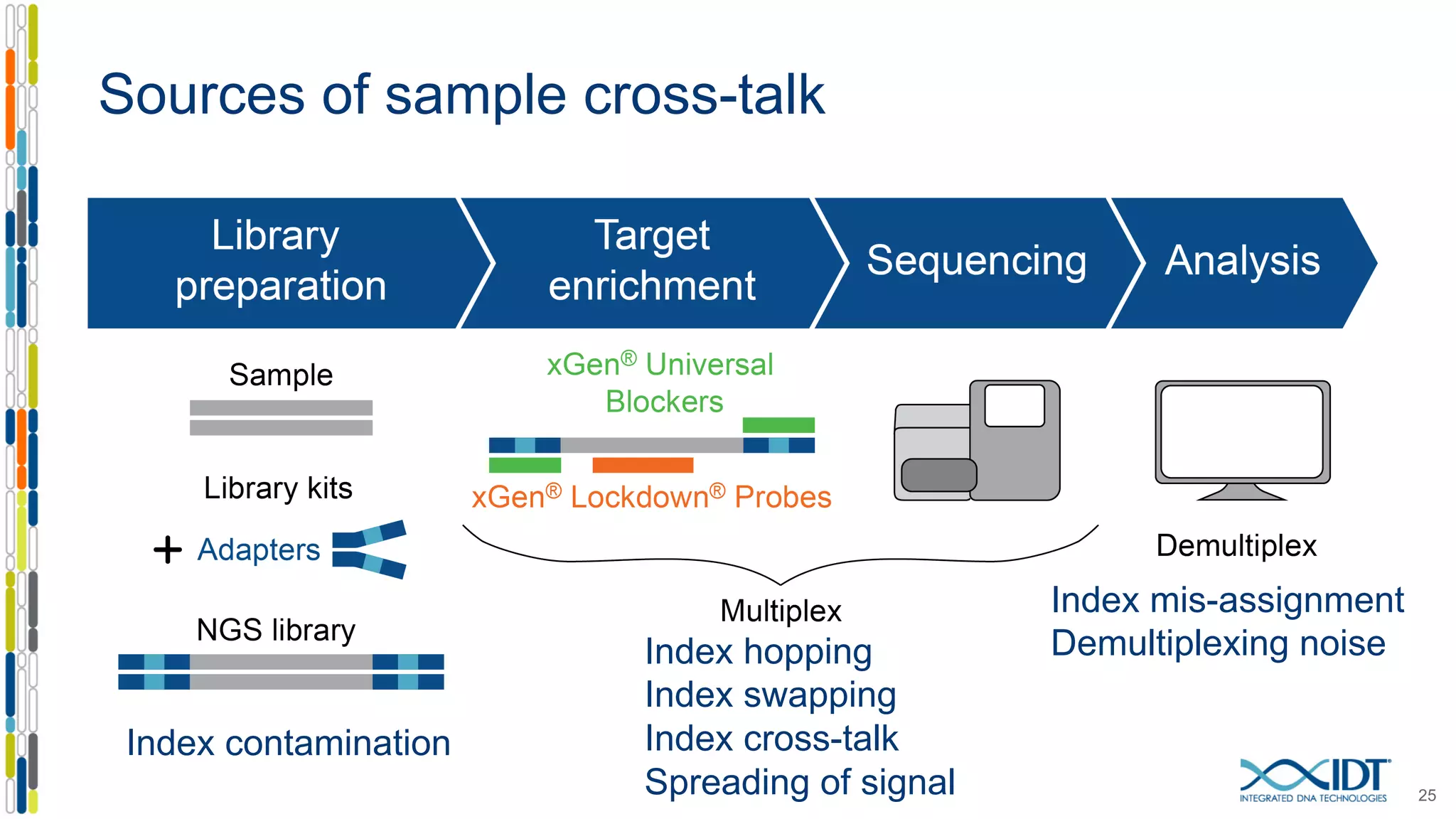
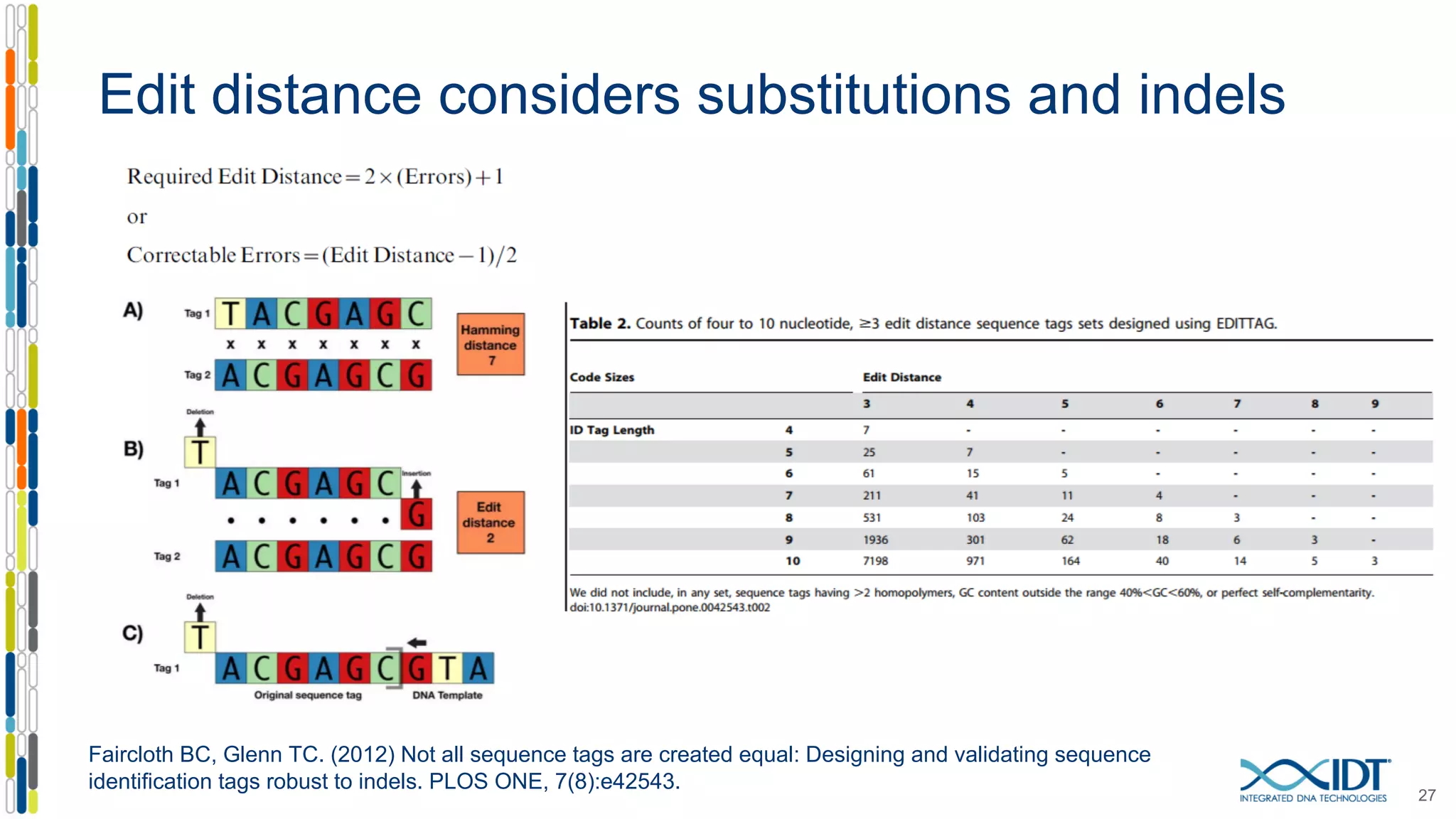
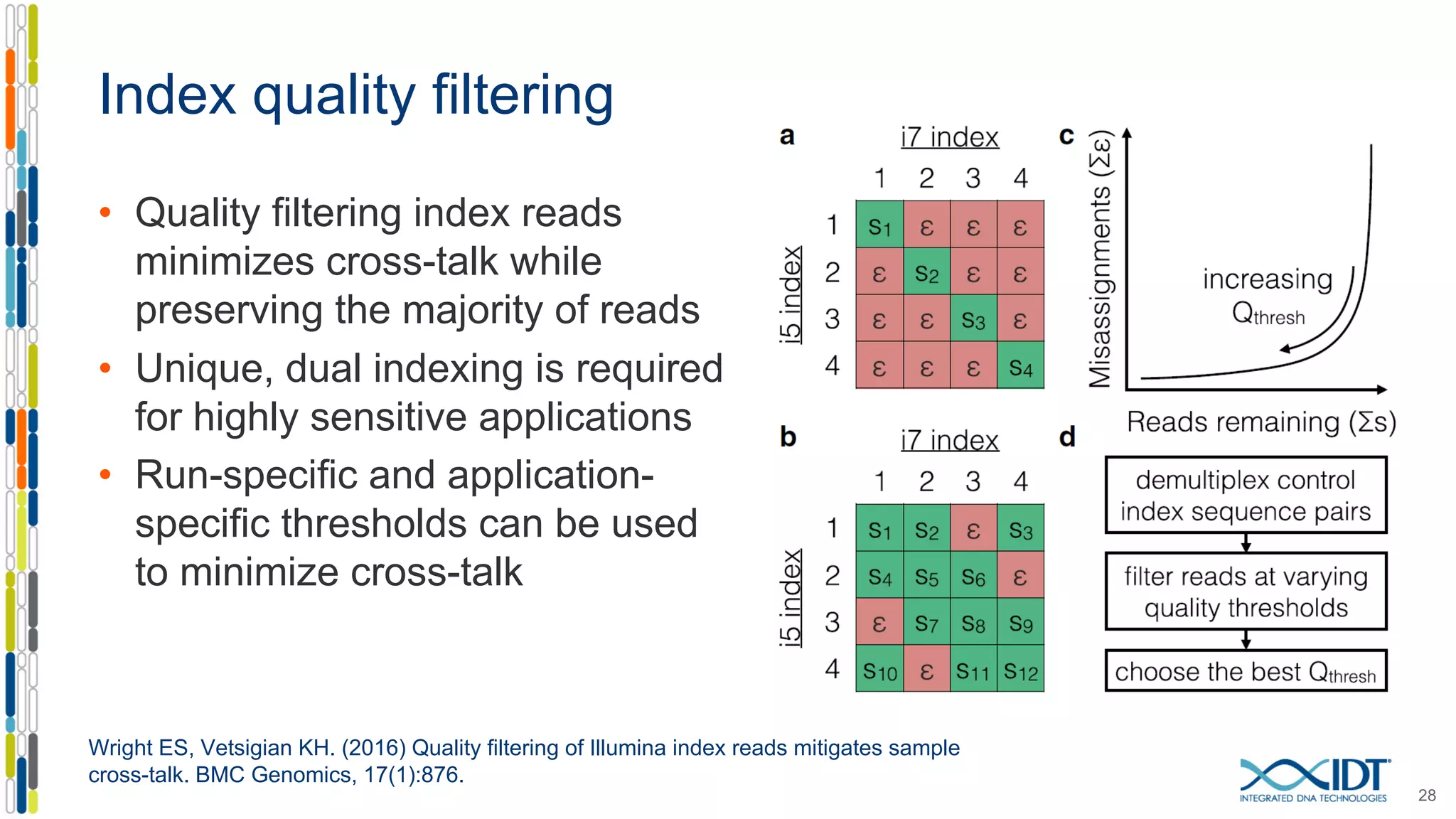
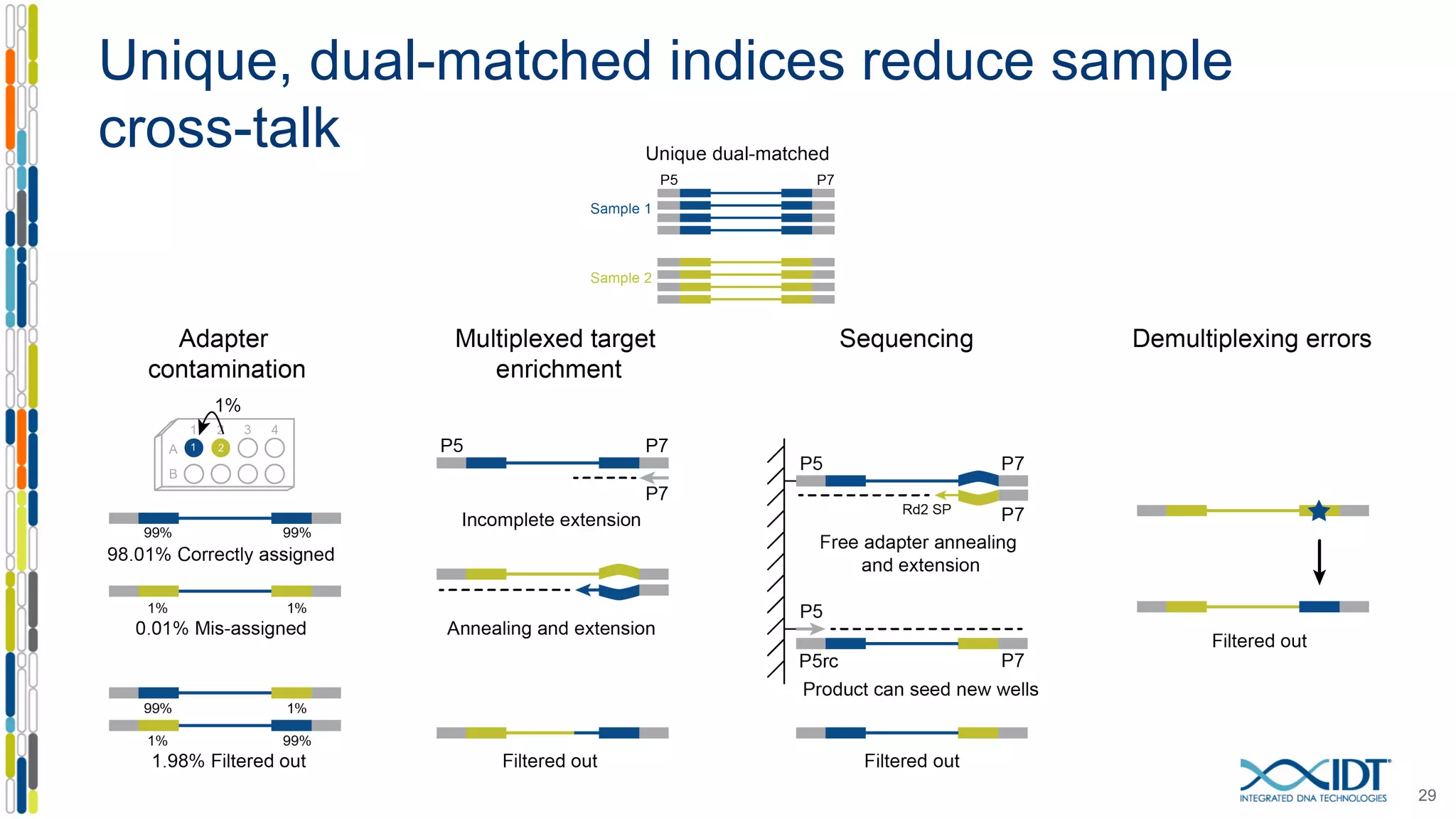
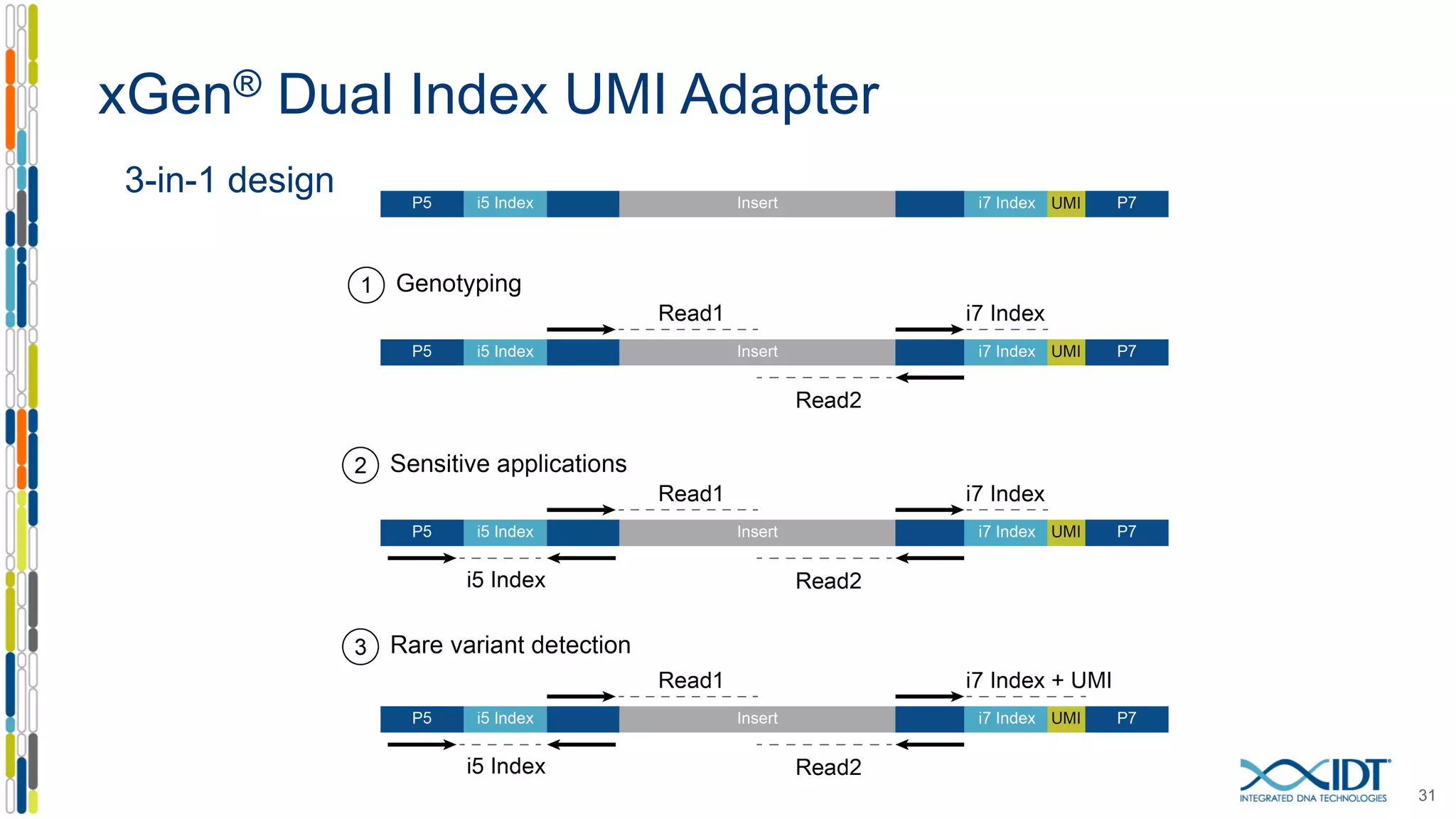
The document discusses methods to mitigate sample cross-talk in next-generation sequencing (NGS) using unique, dual-matched adapters. It identifies sources of cross-talk such as index hopping and contamination, and highlights the importance of custom dual indices for accurate sample assignment in multiplexed applications. Recommendations for reducing mis-assignment and improving read accuracy in sequencing workflows are also provided.