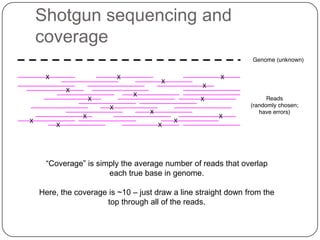
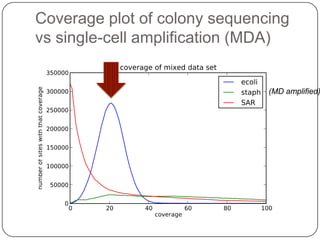
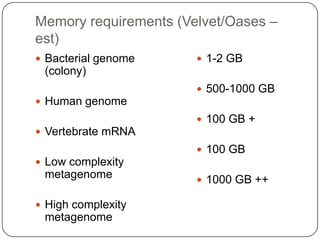
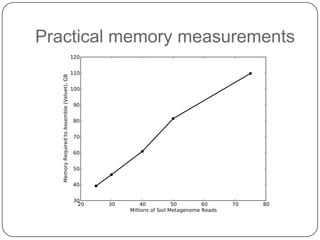
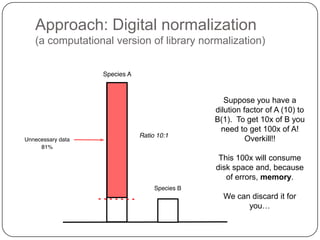
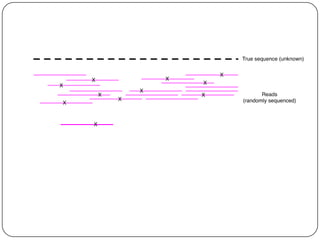
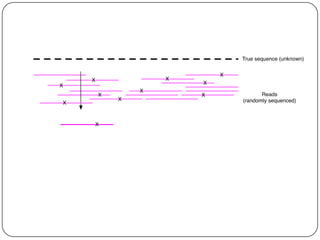
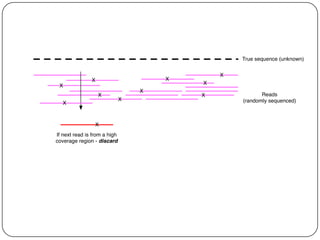
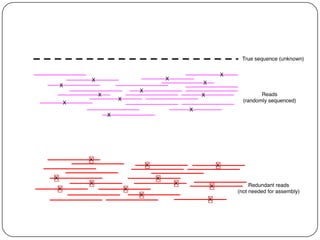
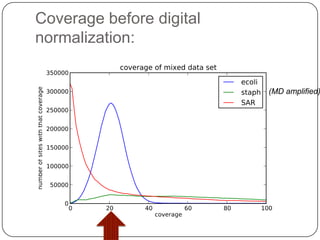
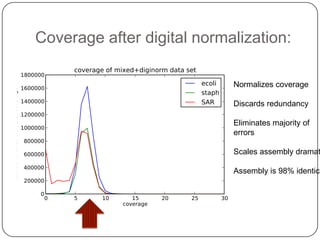
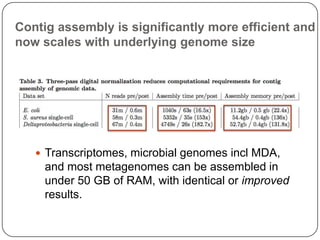
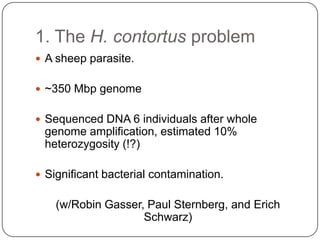
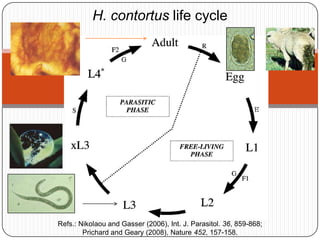
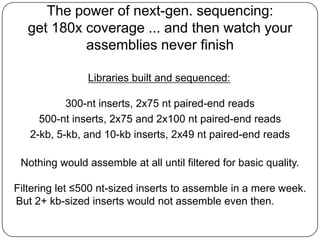
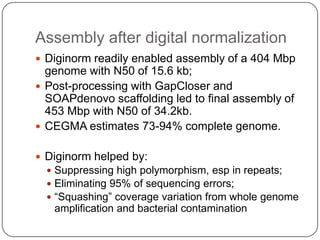
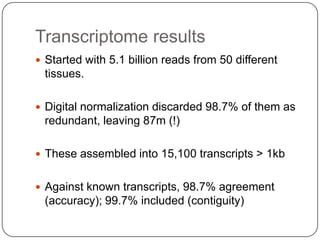
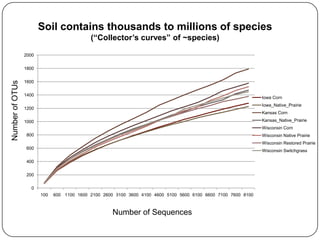
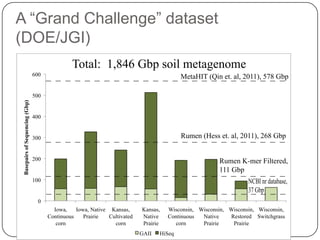
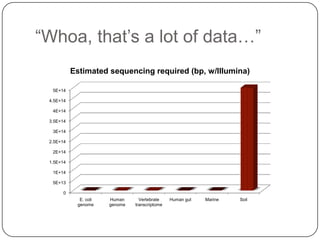
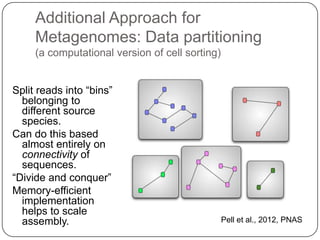
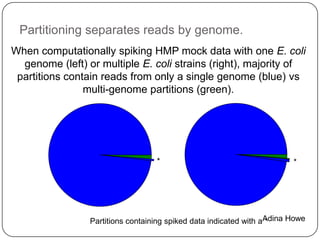
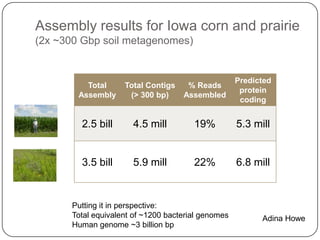
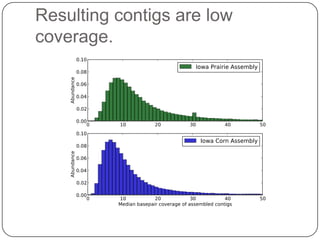
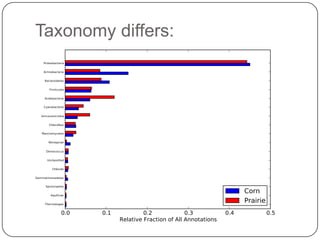
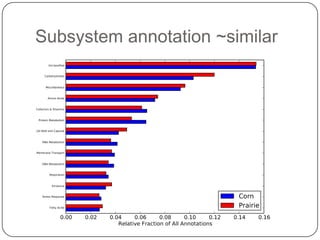
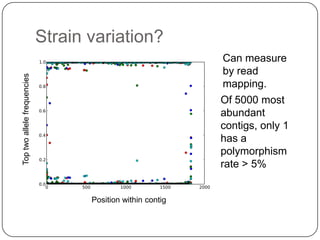
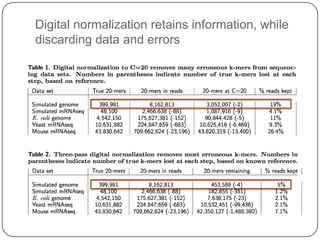
This document discusses improved techniques for de novo genome, transcriptome, and metagenome assembly using digital normalization. Digital normalization is a computational technique that discards redundant sequencing reads, smoothing coverage and eliminating most errors. This allows assemblies to scale efficiently with genome size. Examples presented include assembling the parasitic nematode H. contortus genome and the lamprey transcriptome. Digital normalization also enabled assembly of large soil metagenomes that were previously intractable.