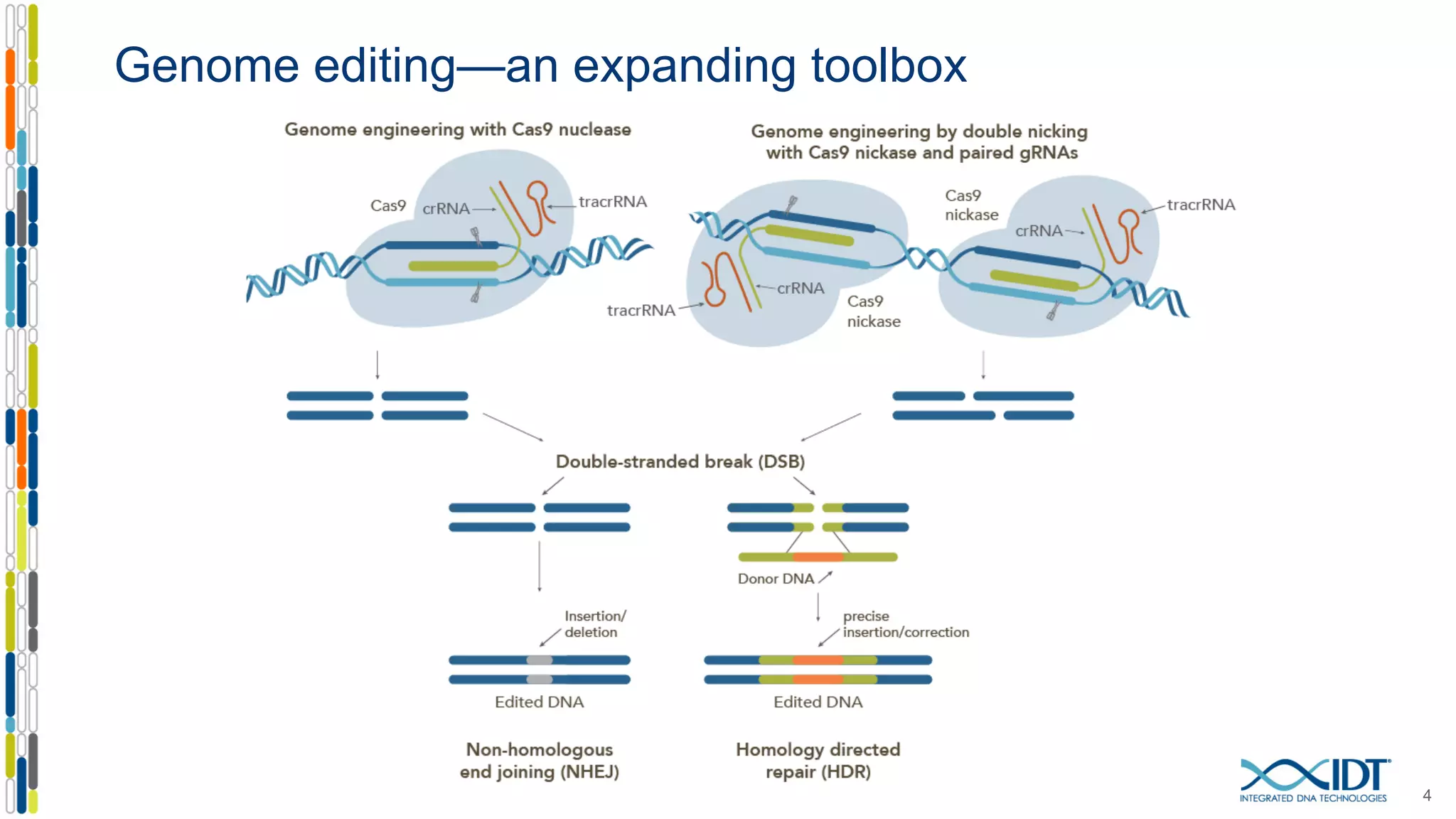
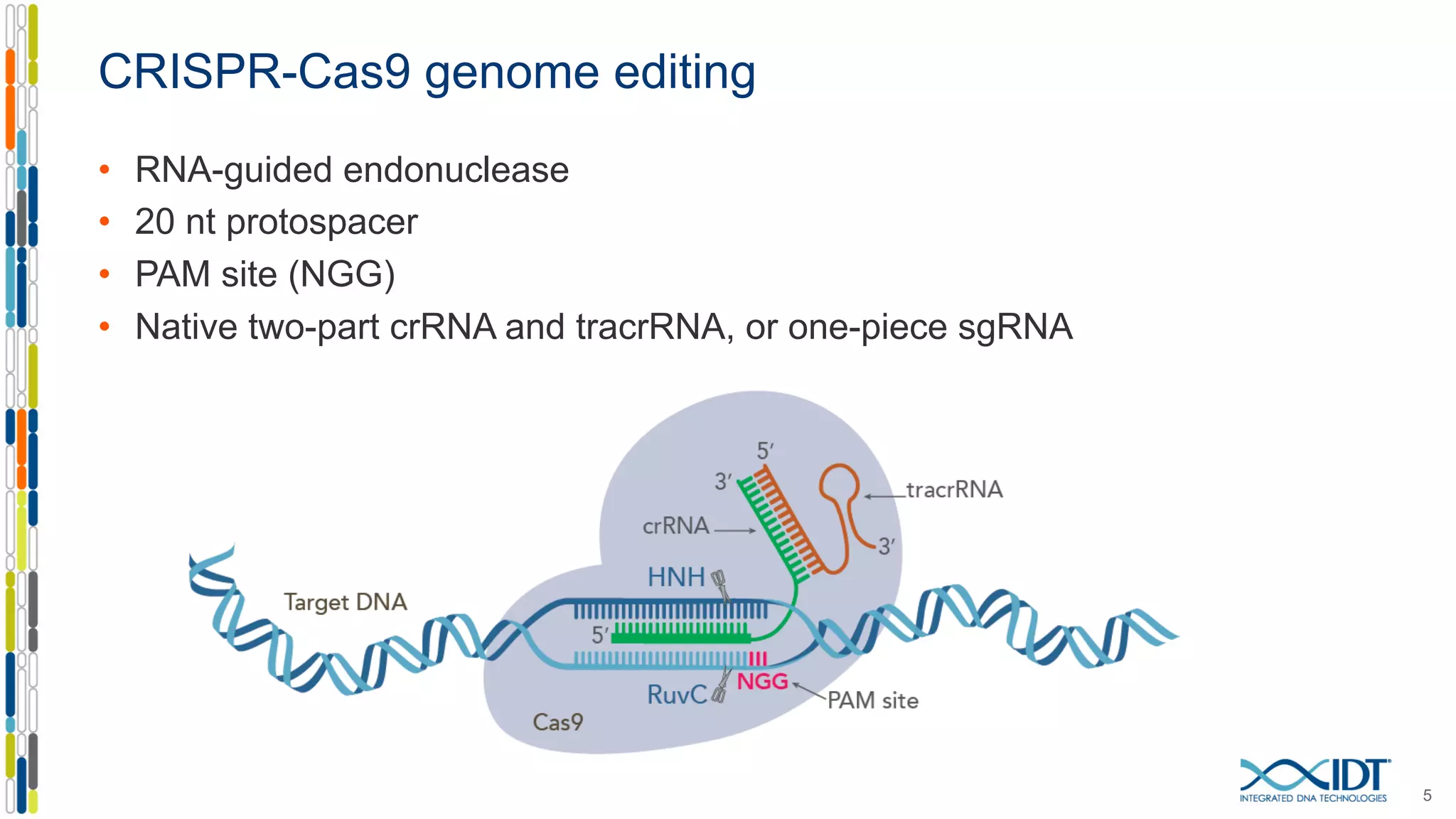
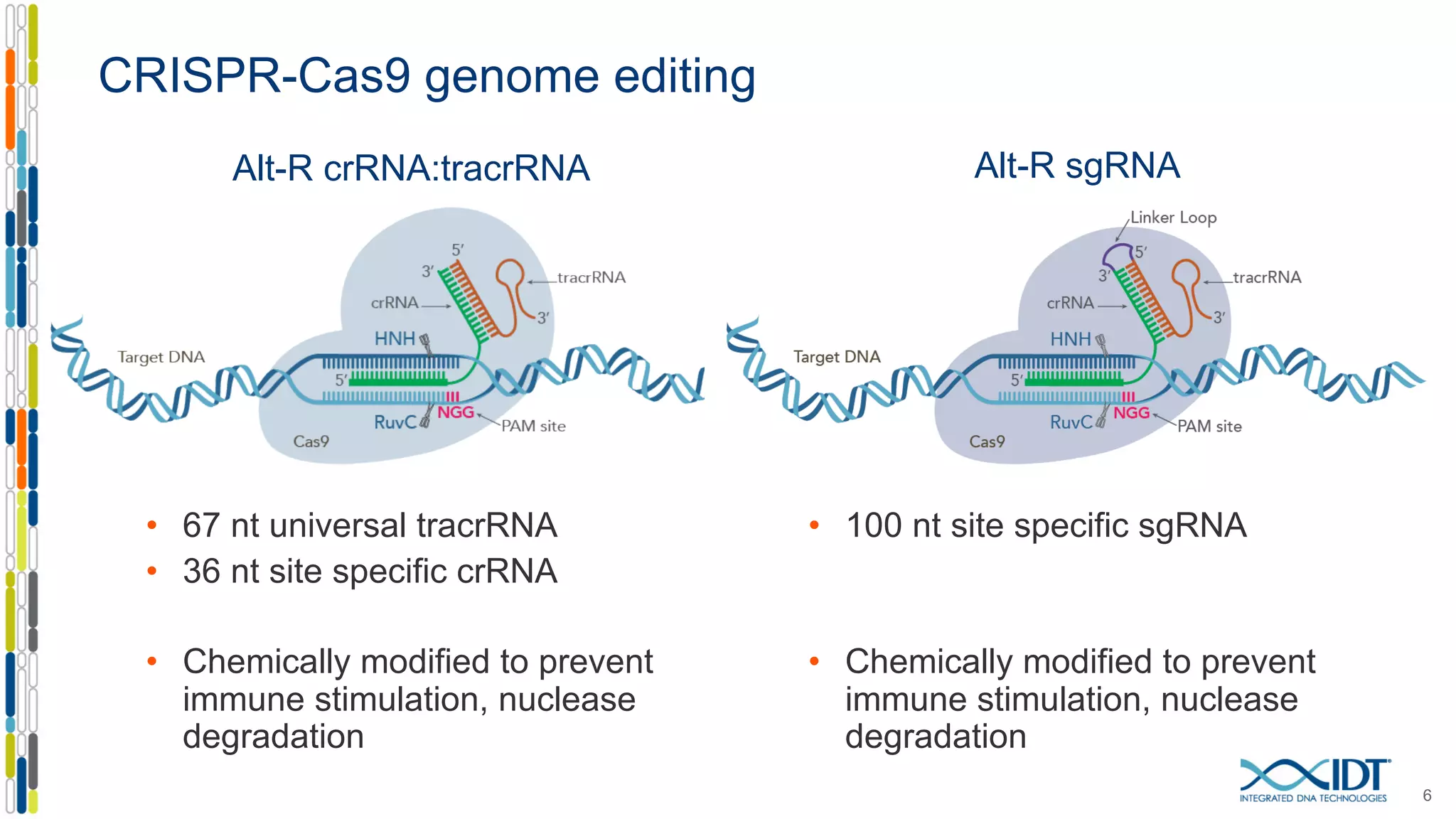
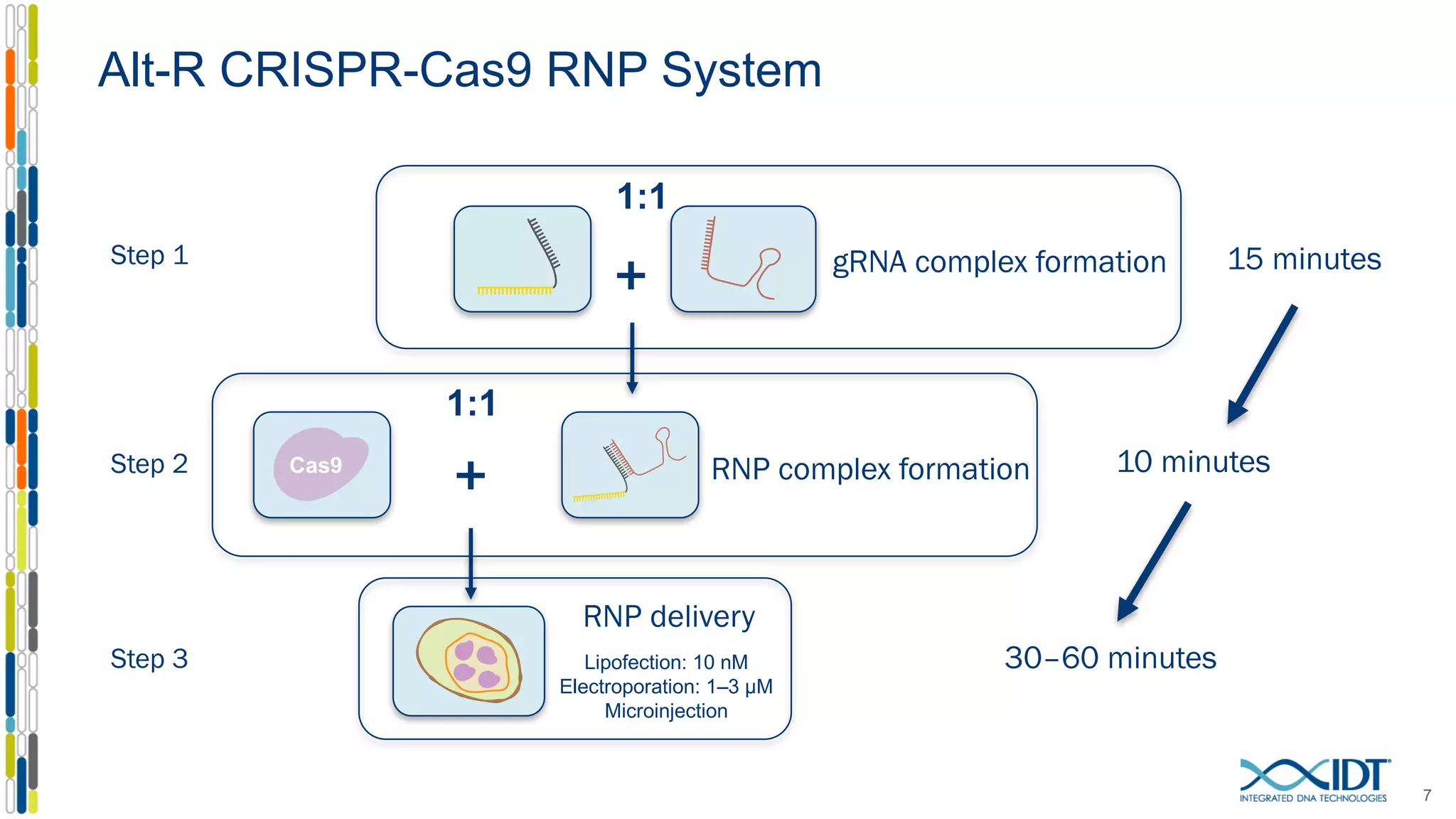
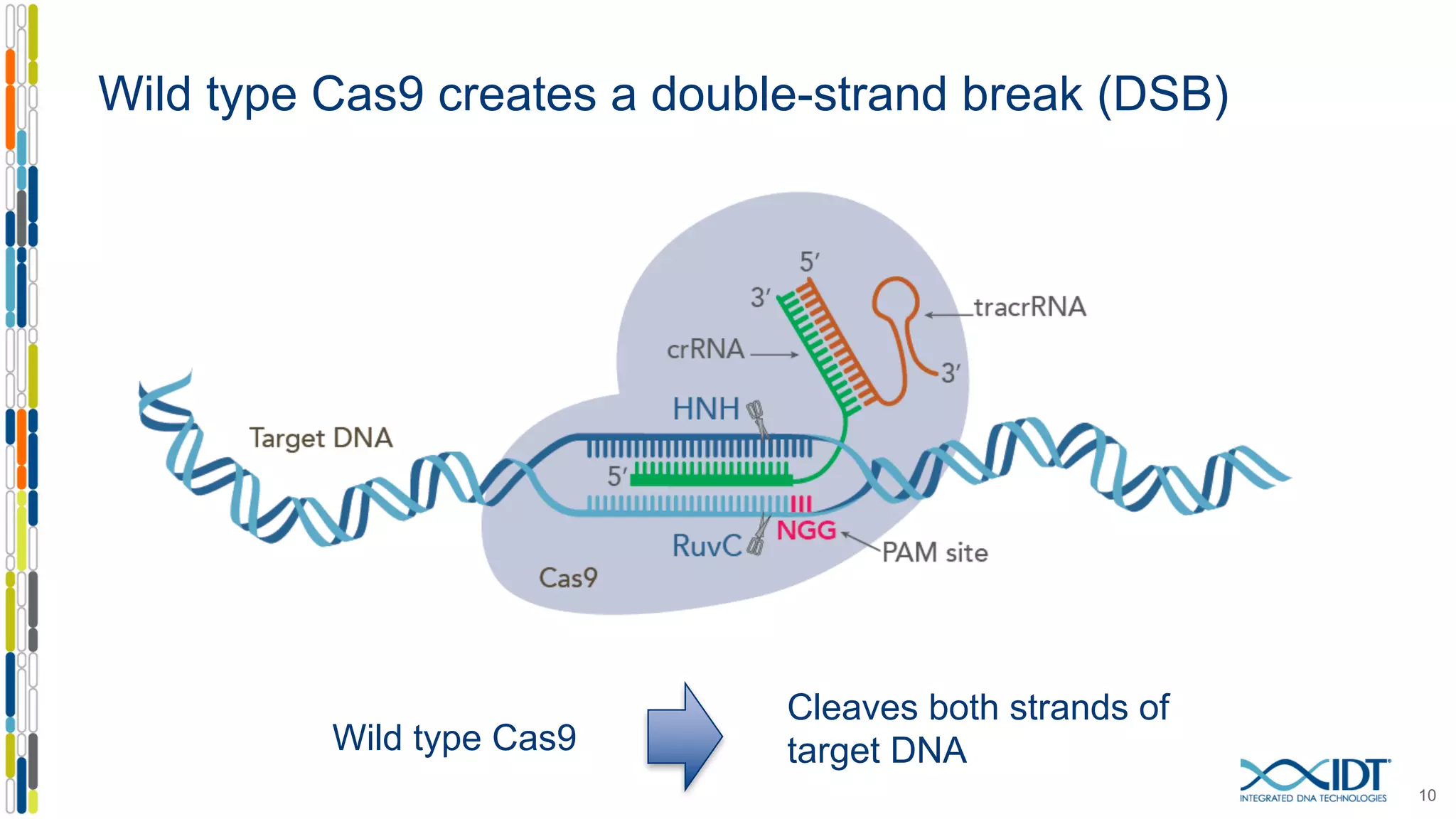
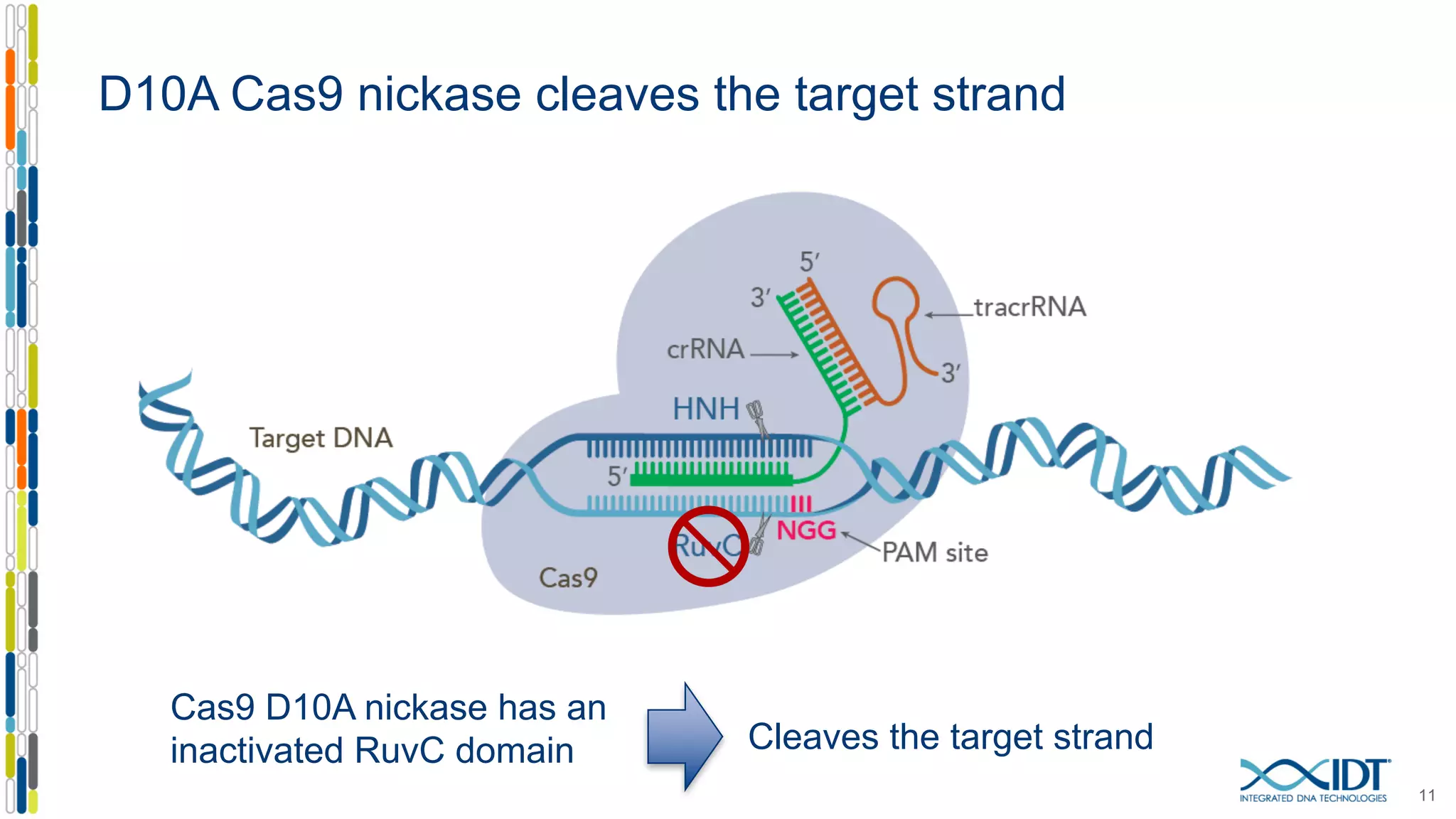
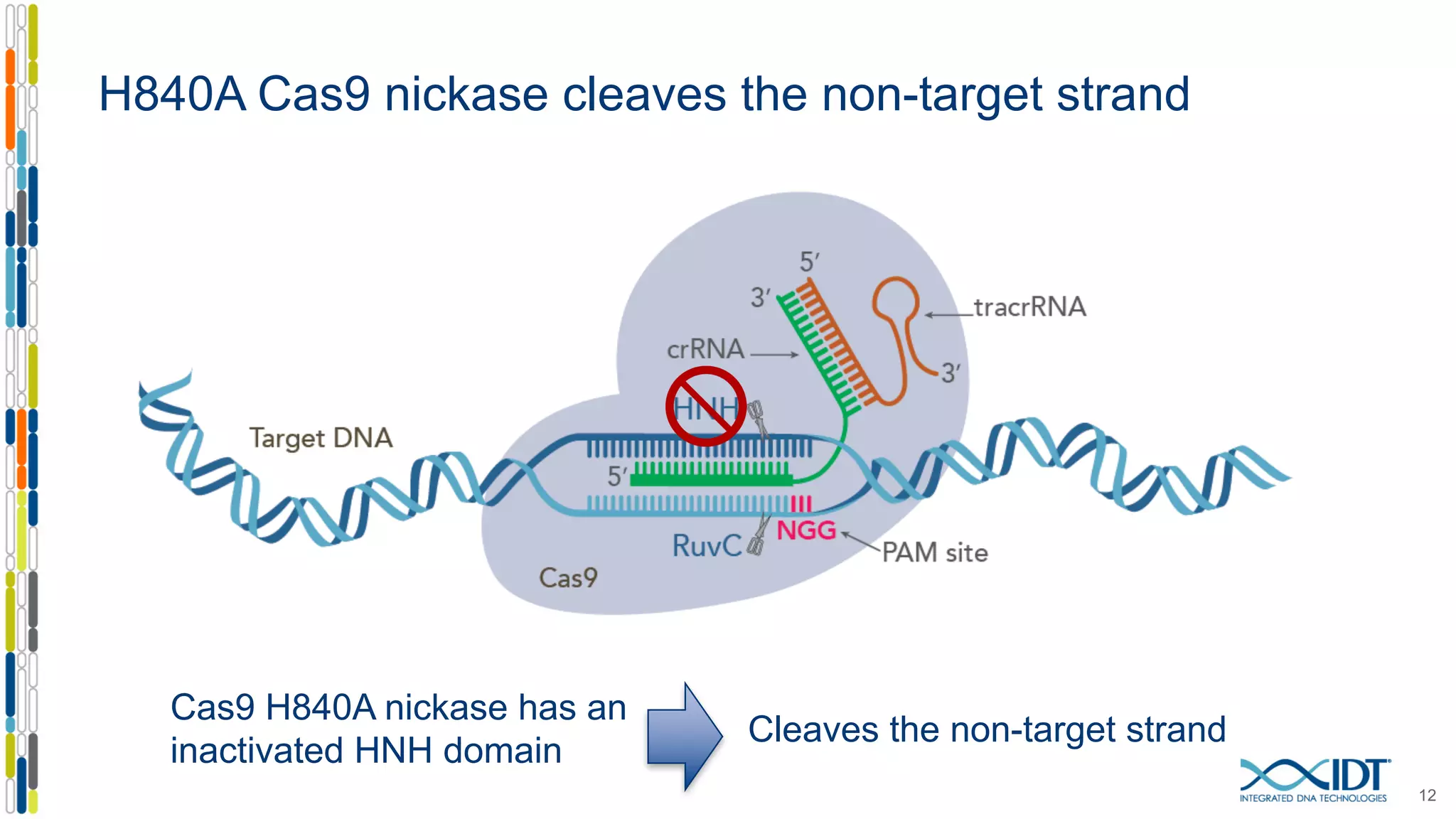
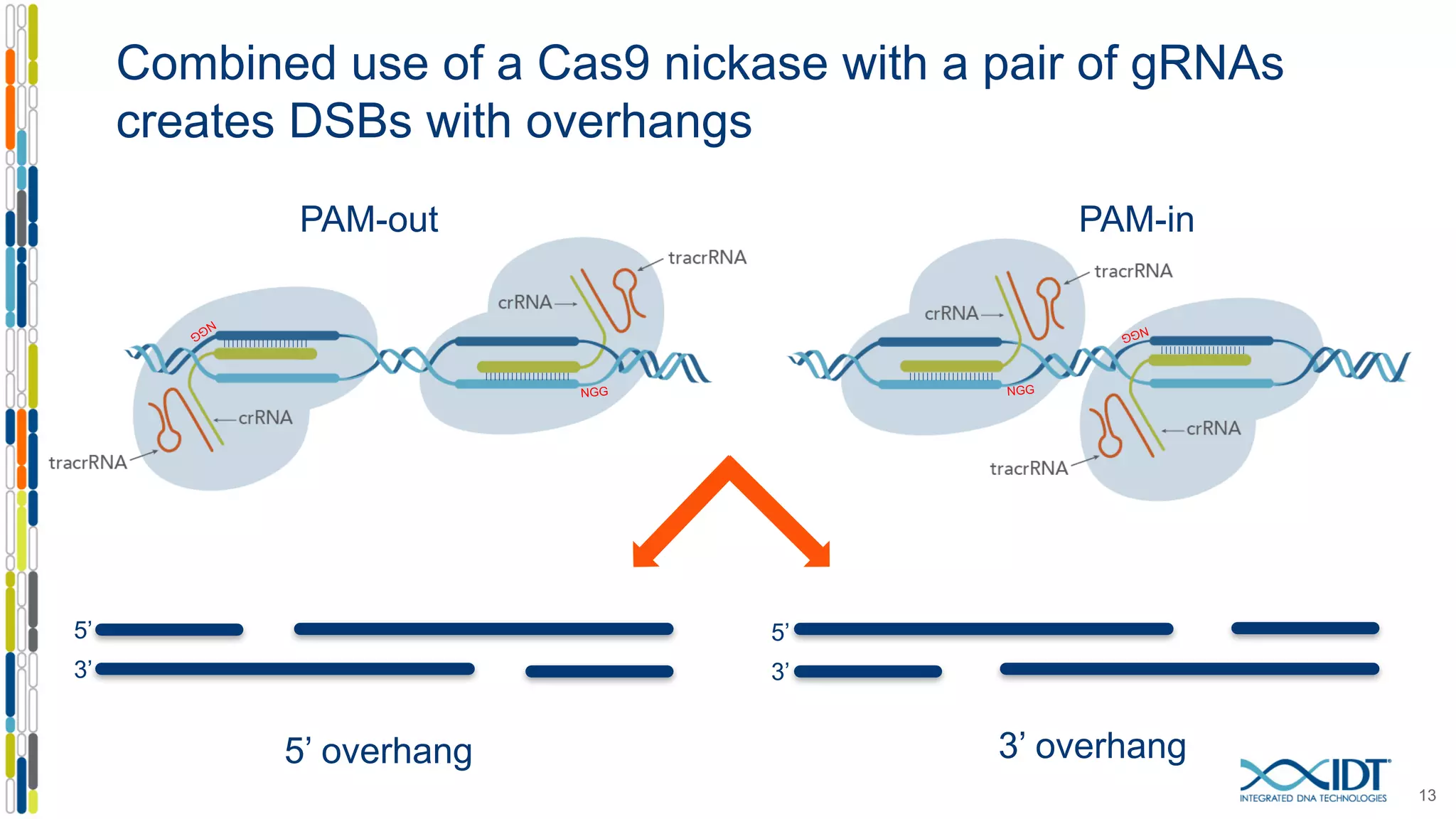
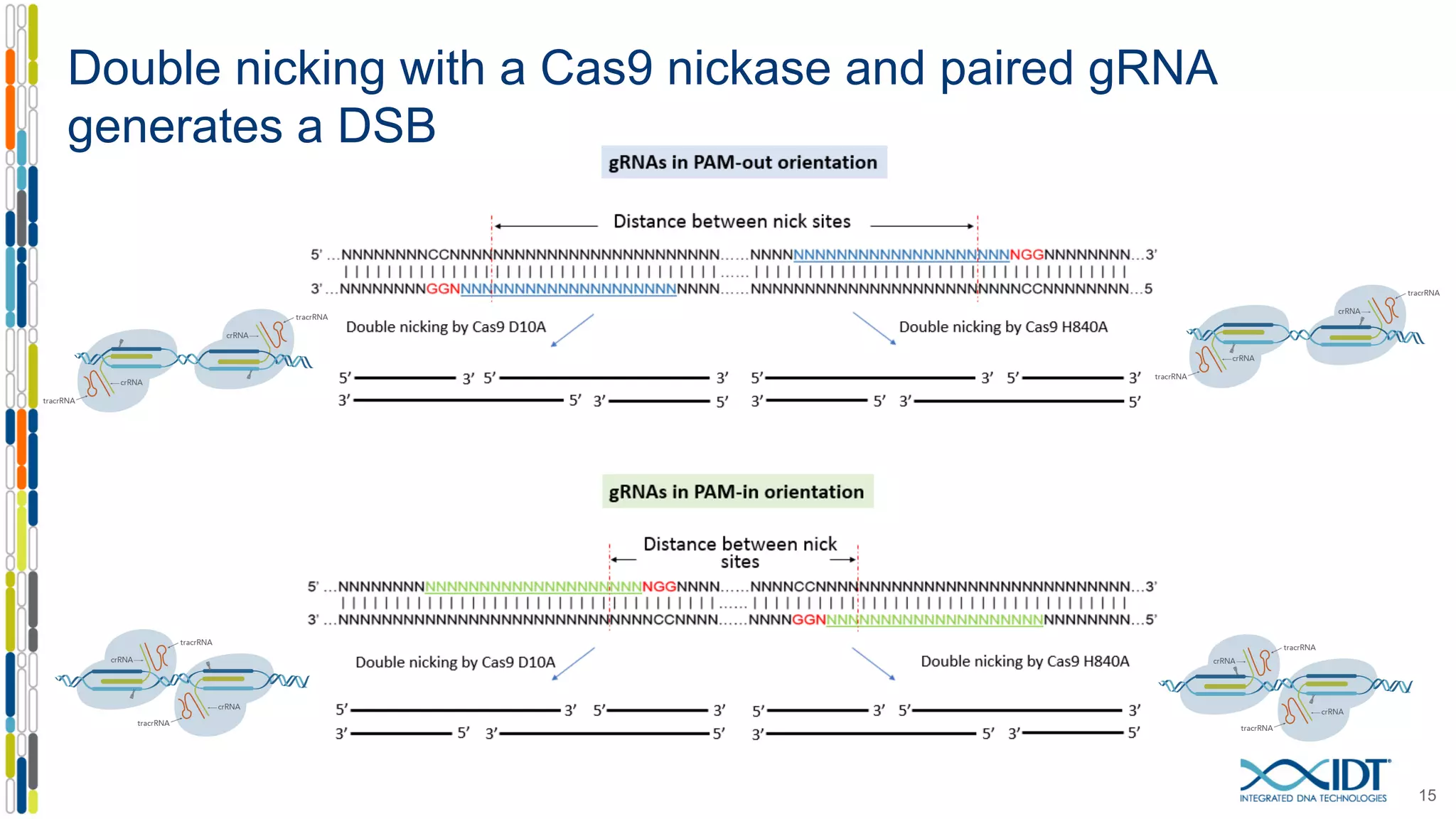
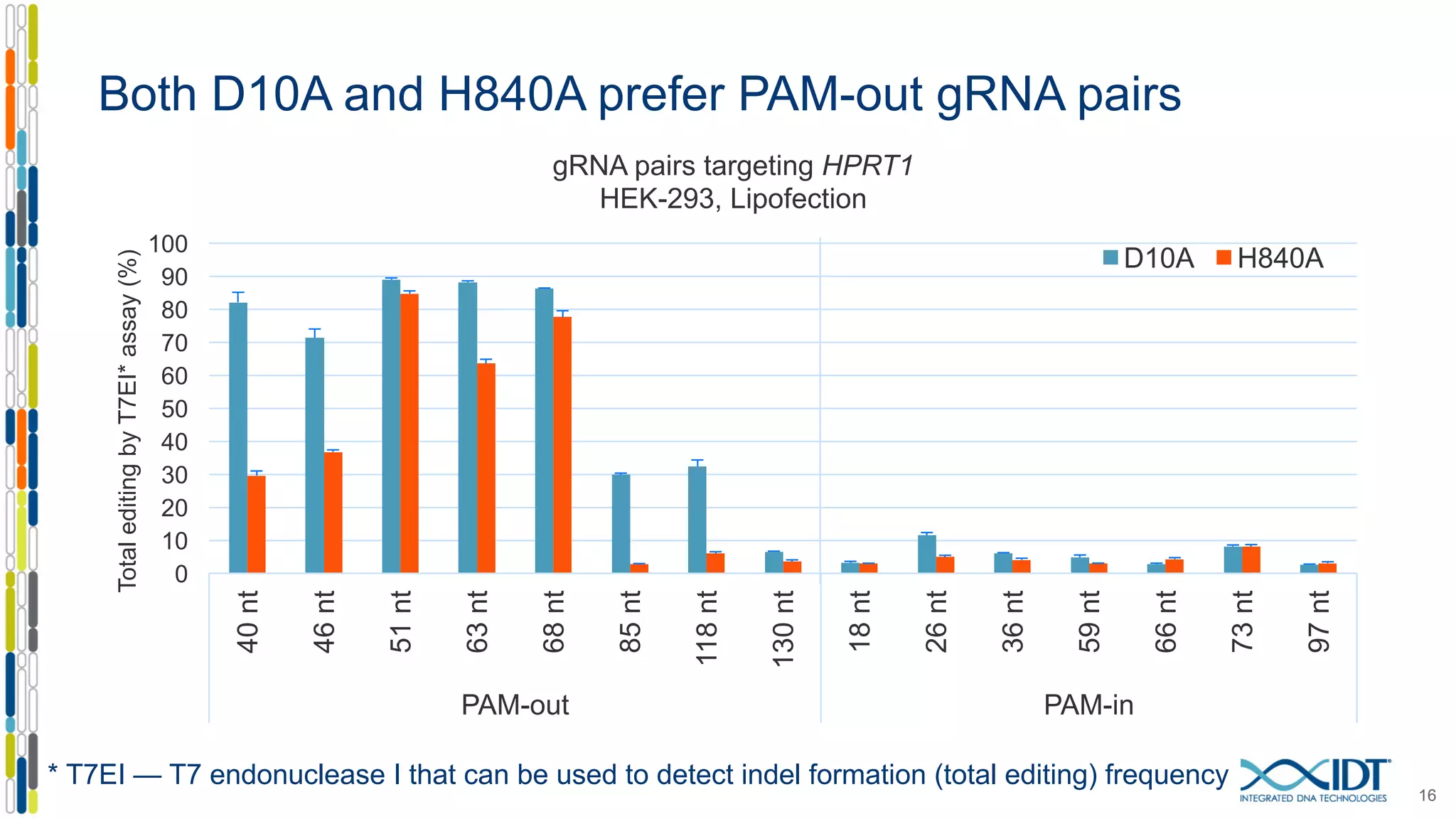
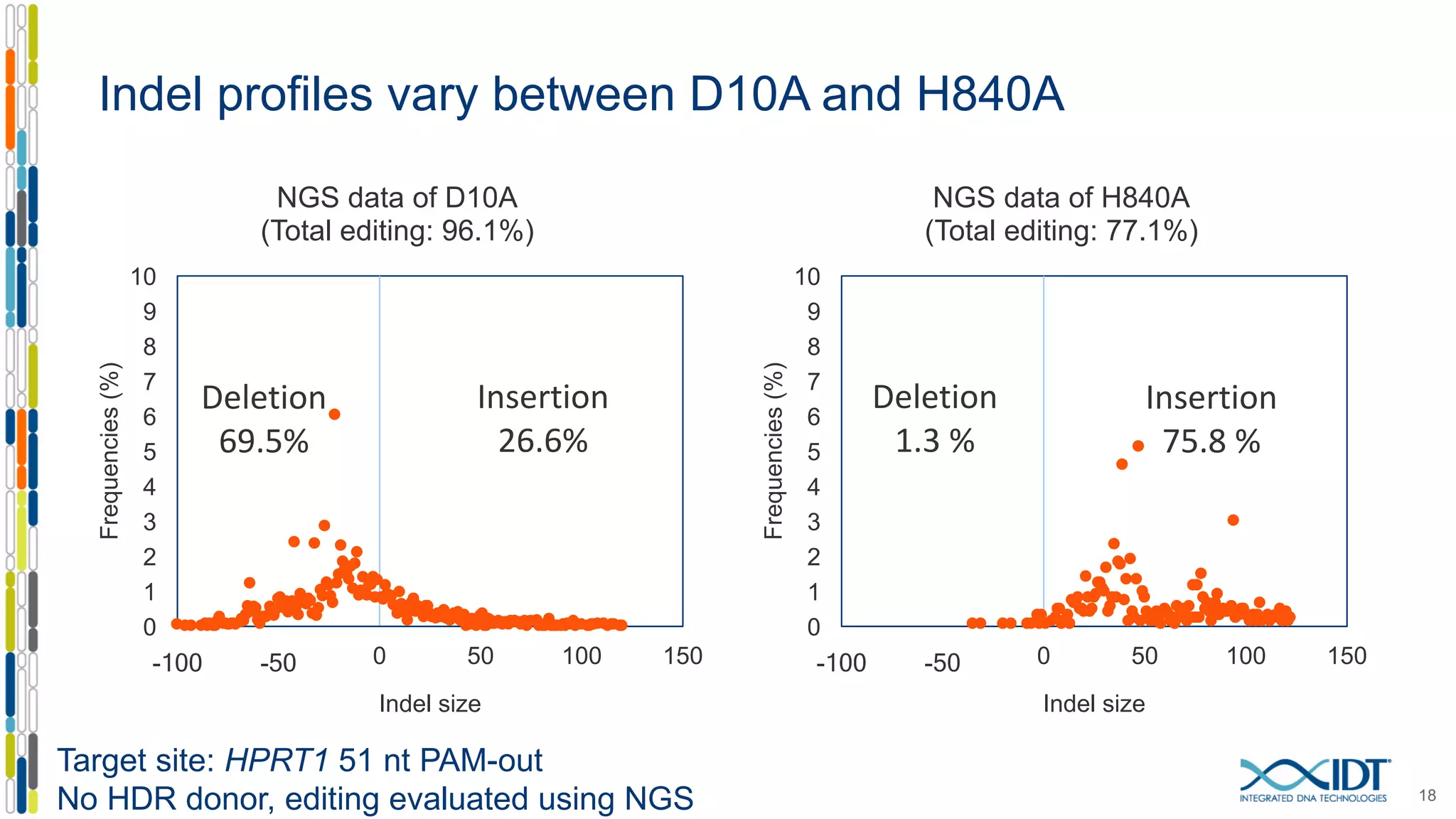
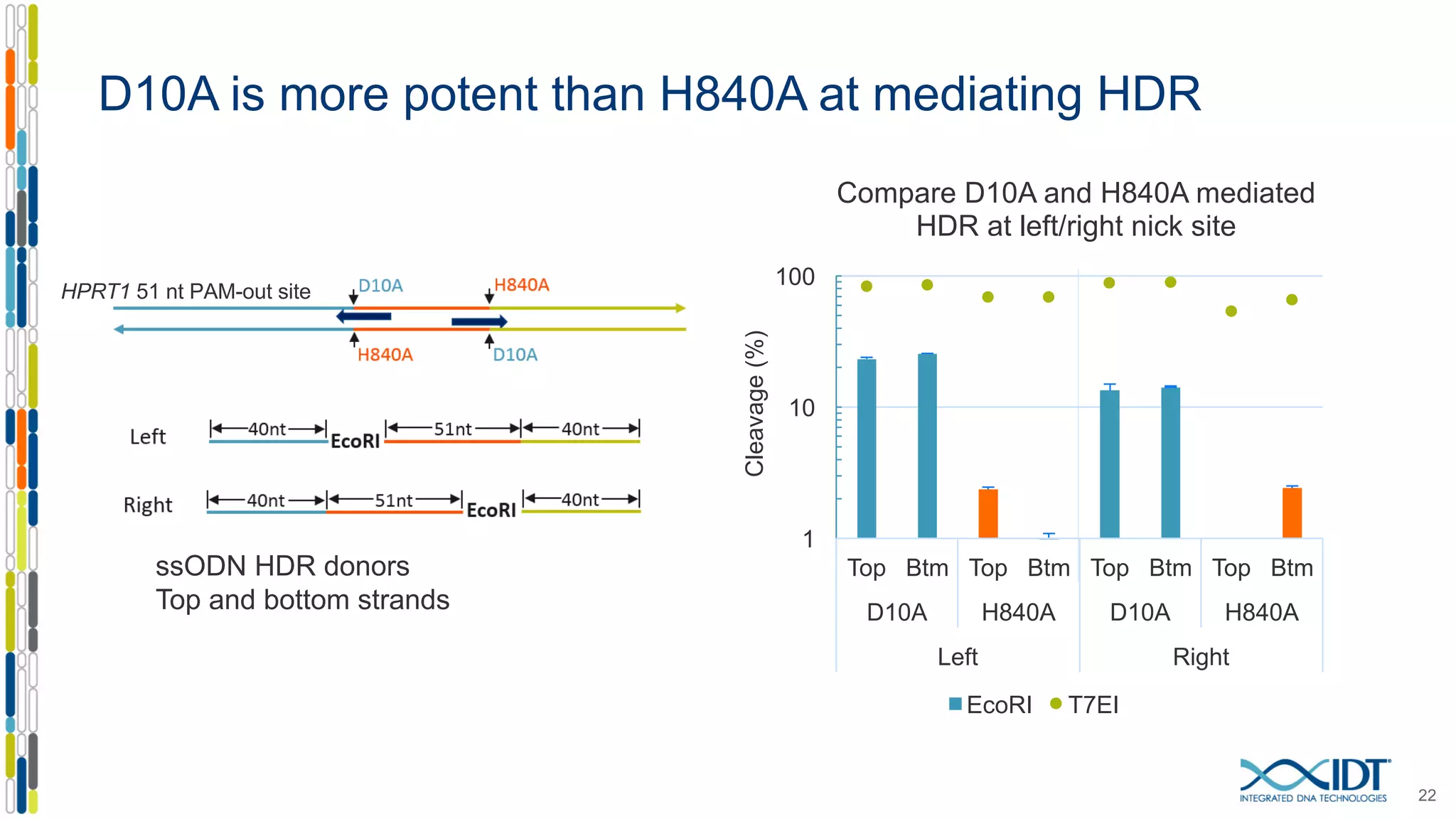
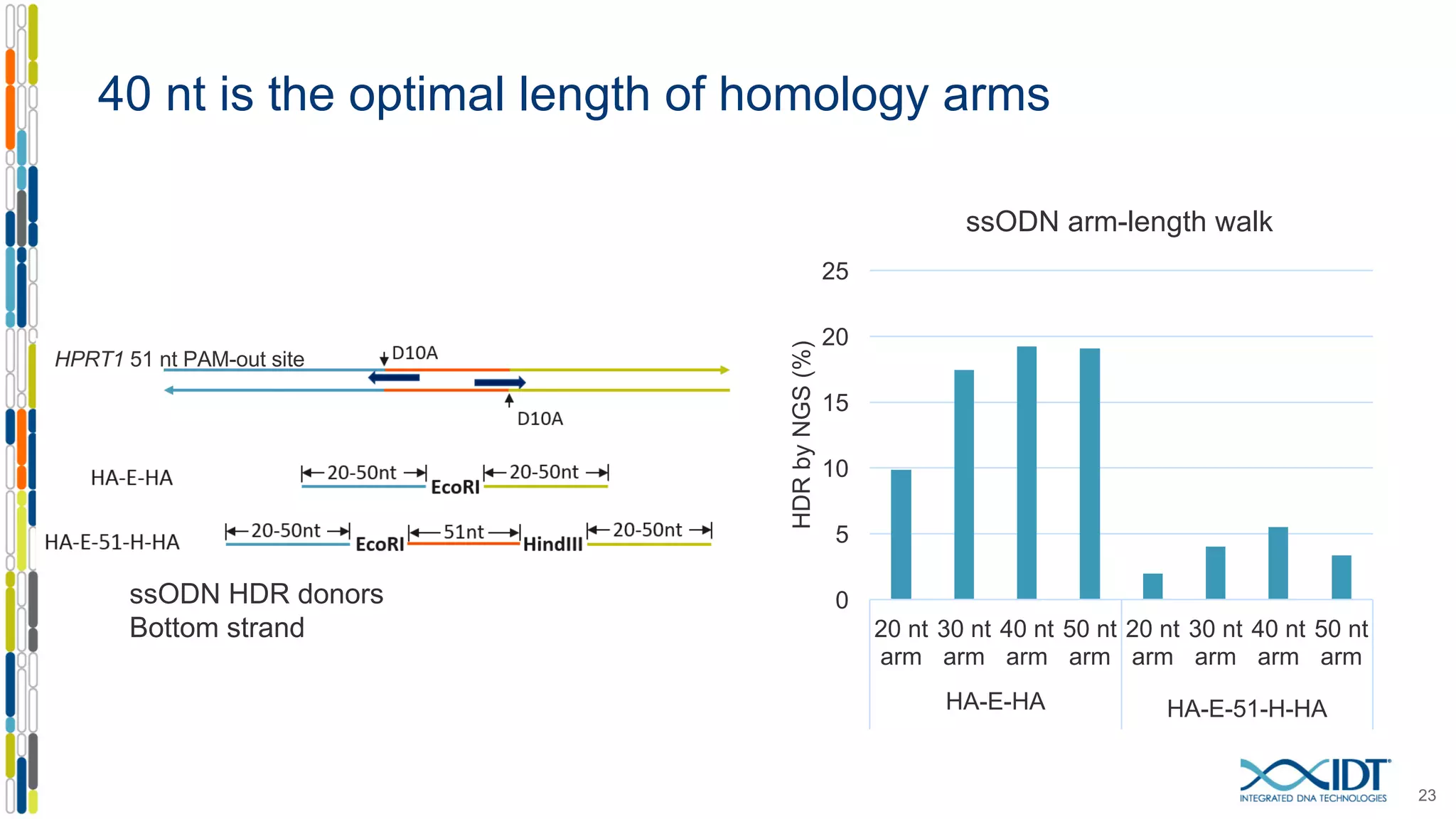
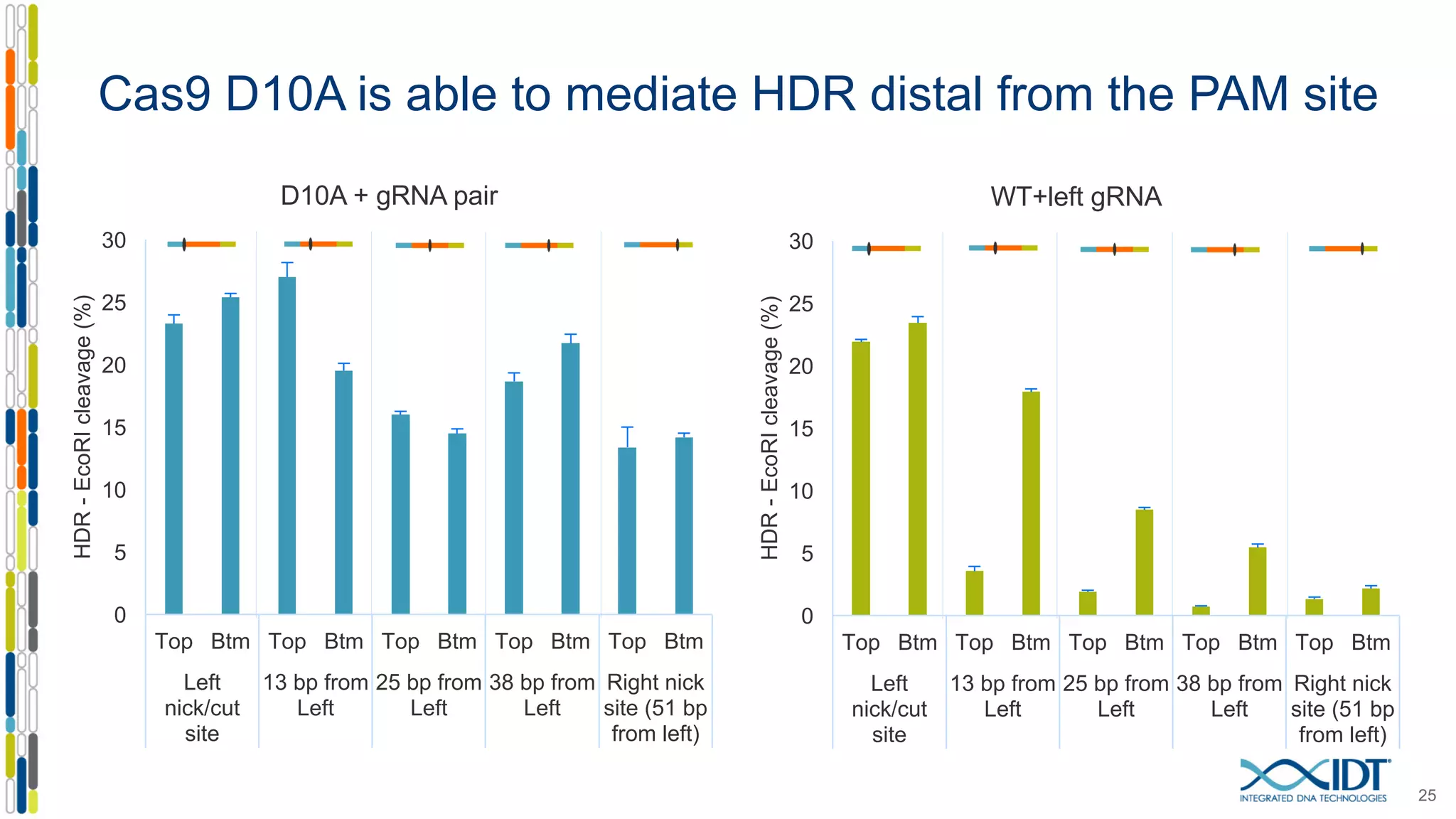
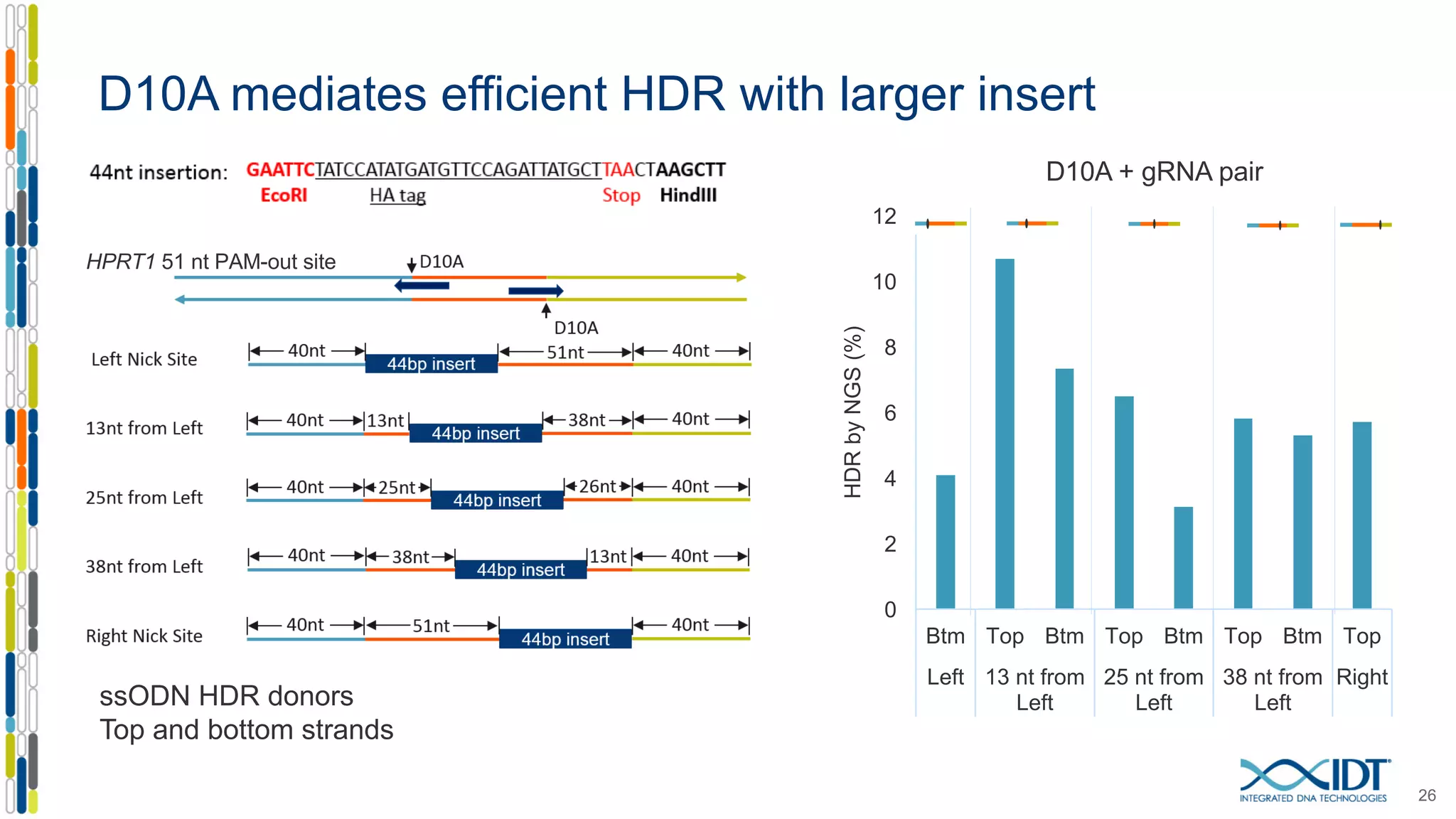
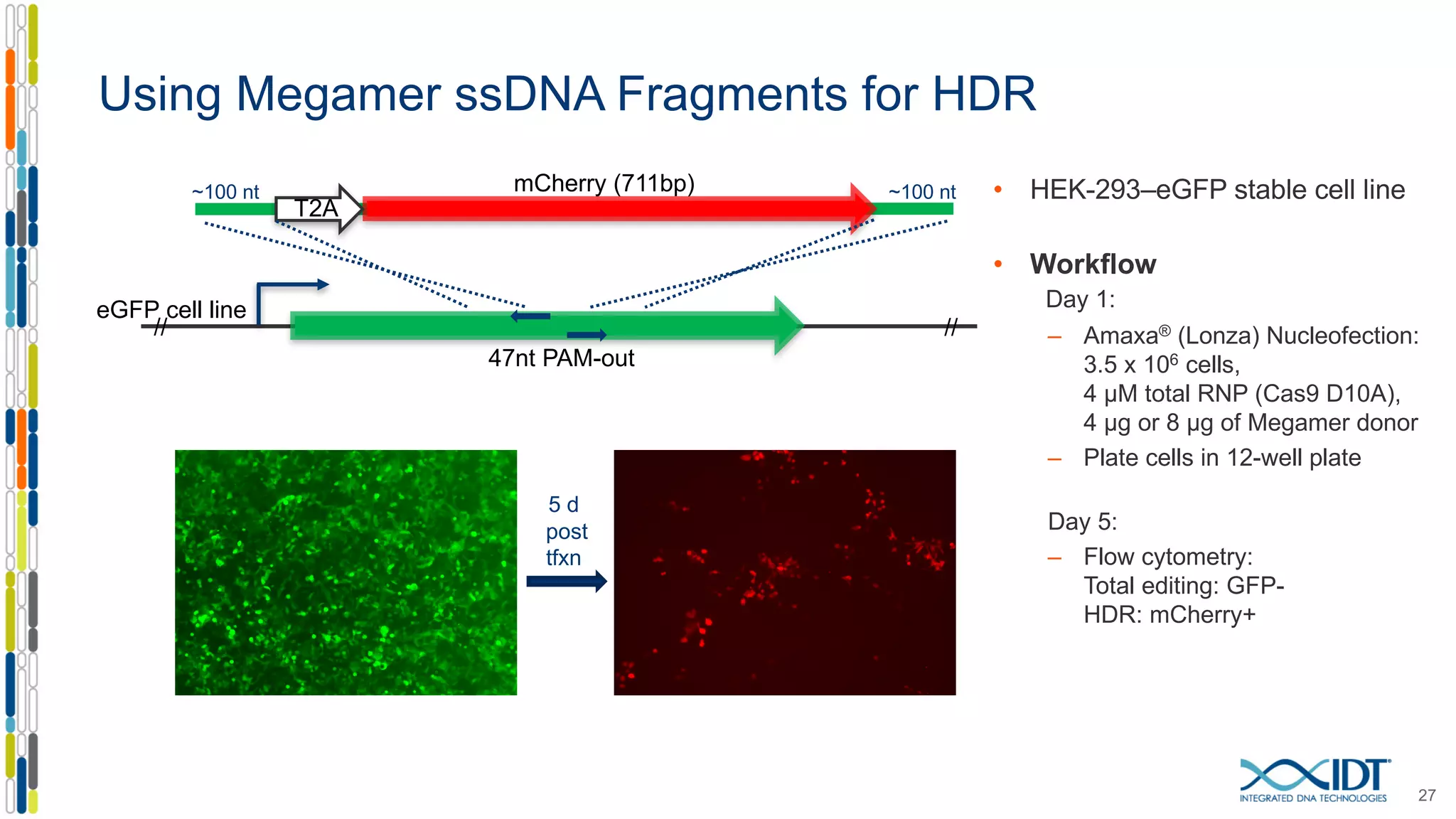
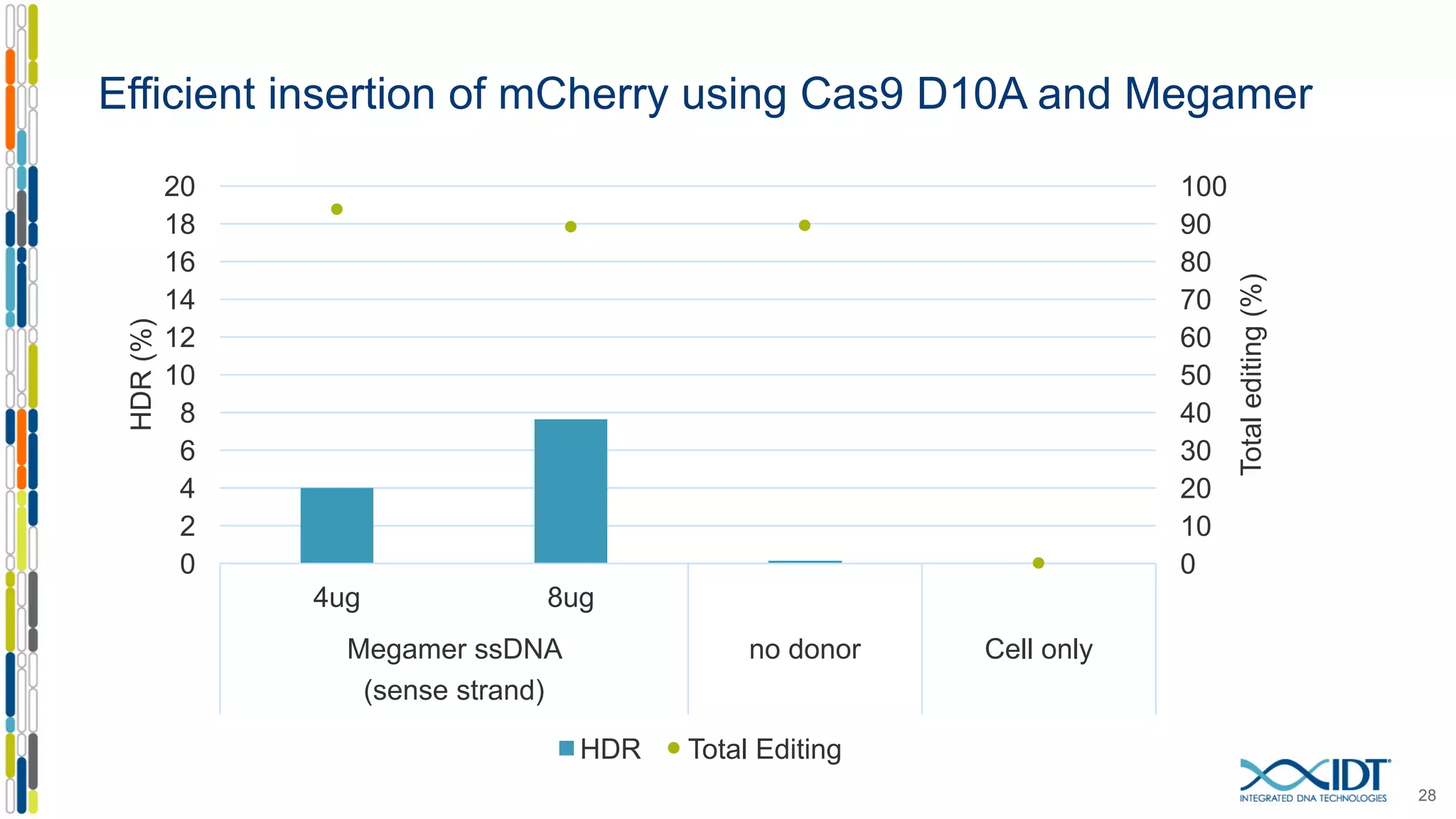
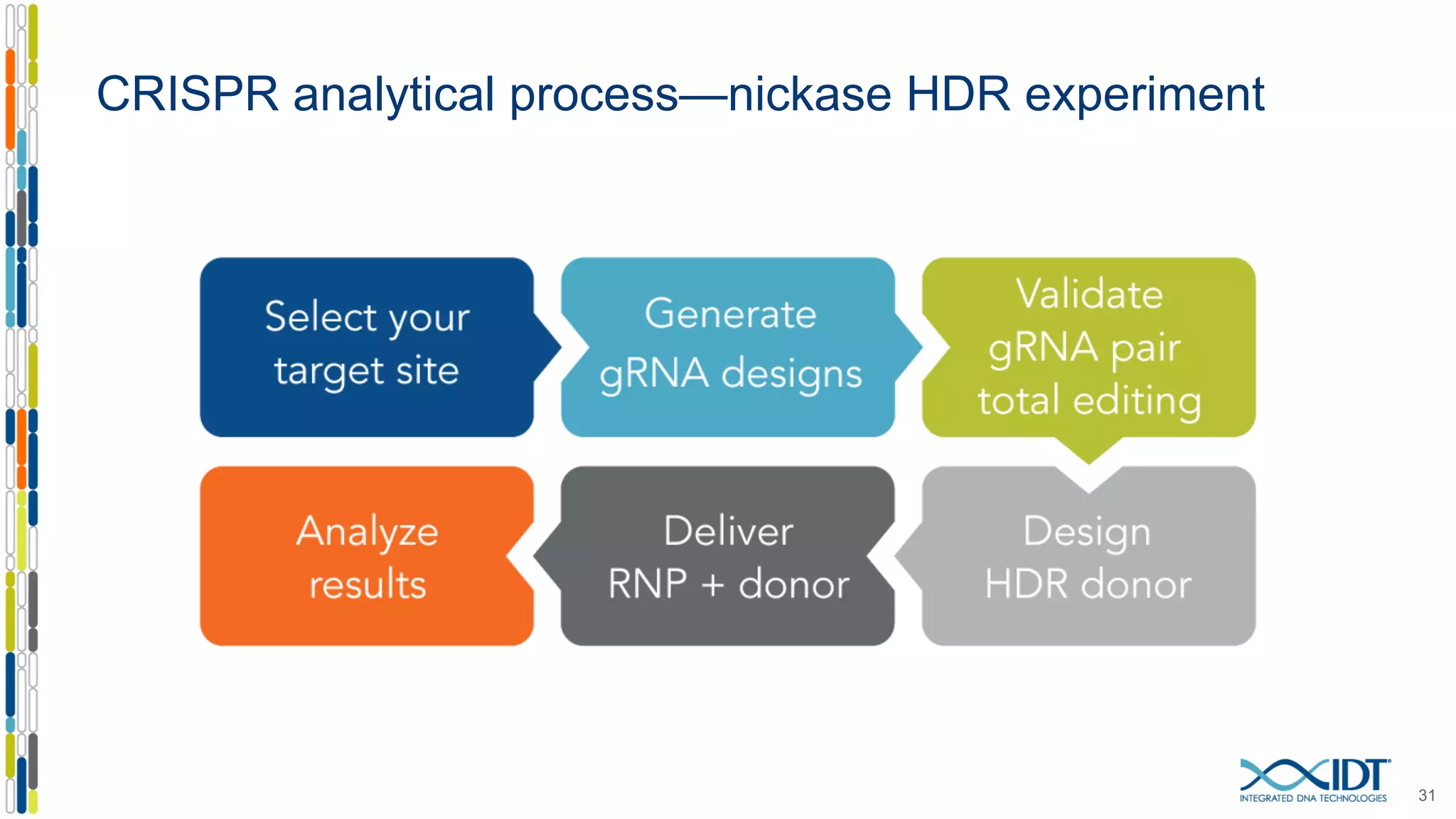
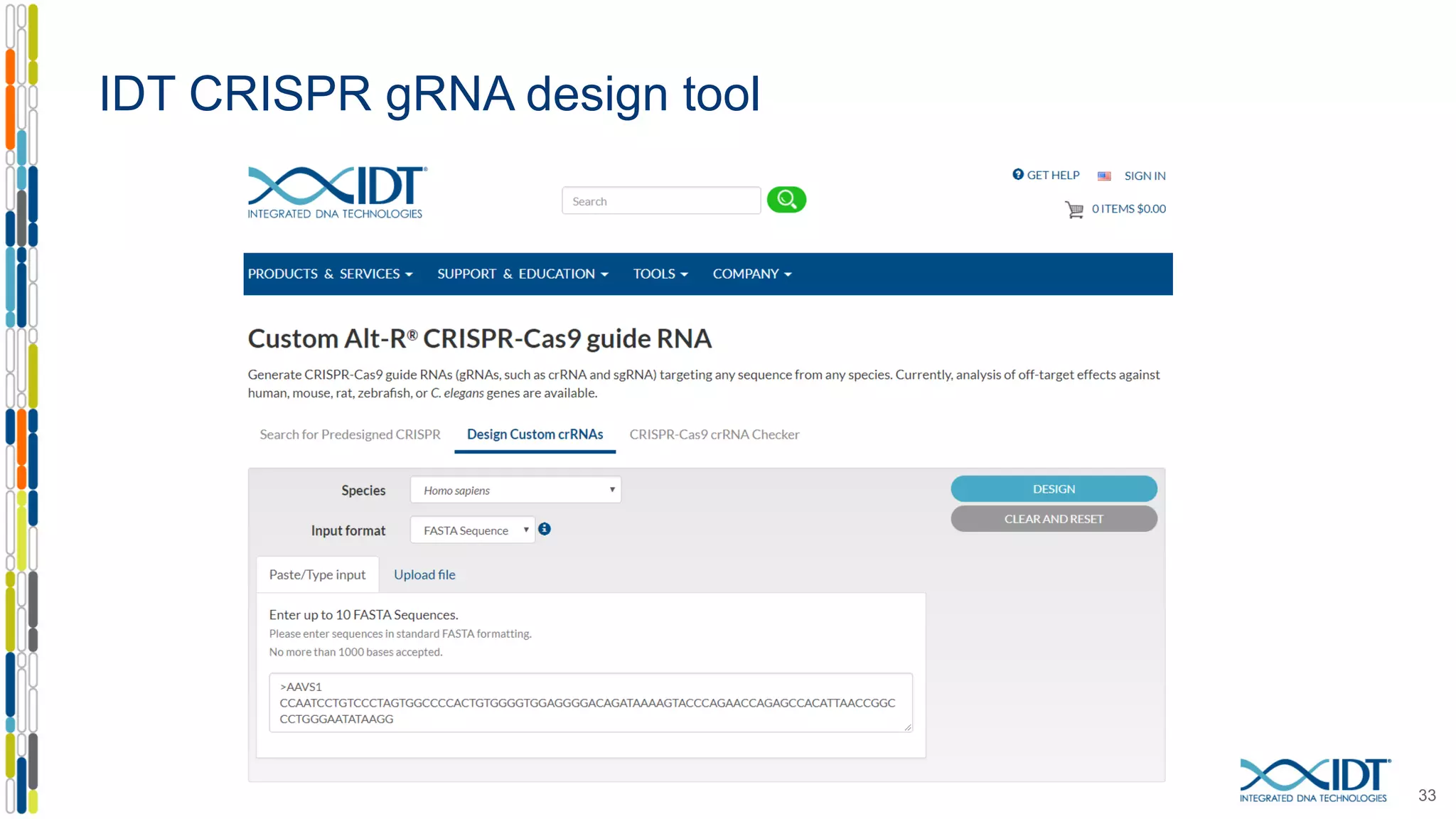
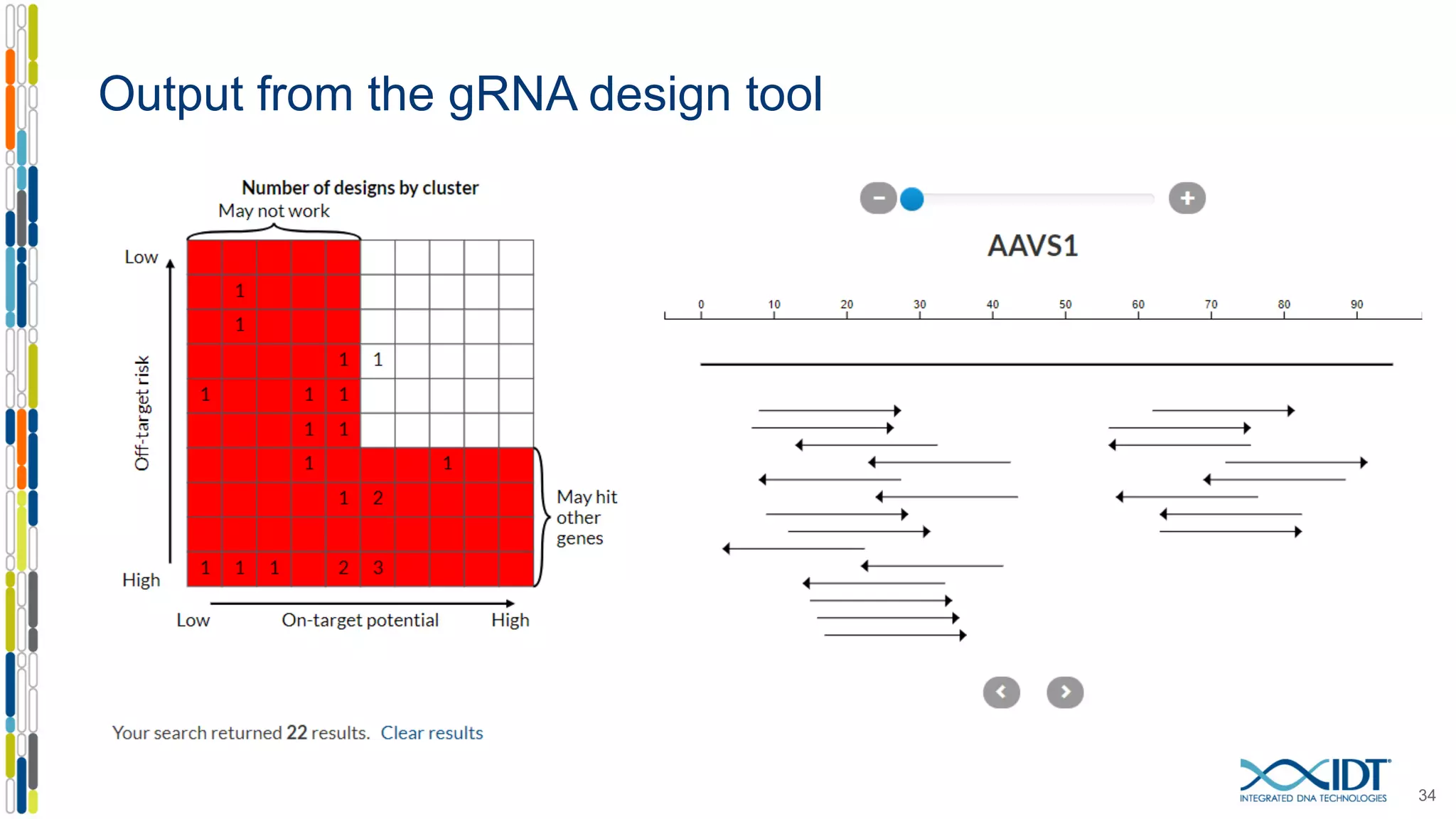
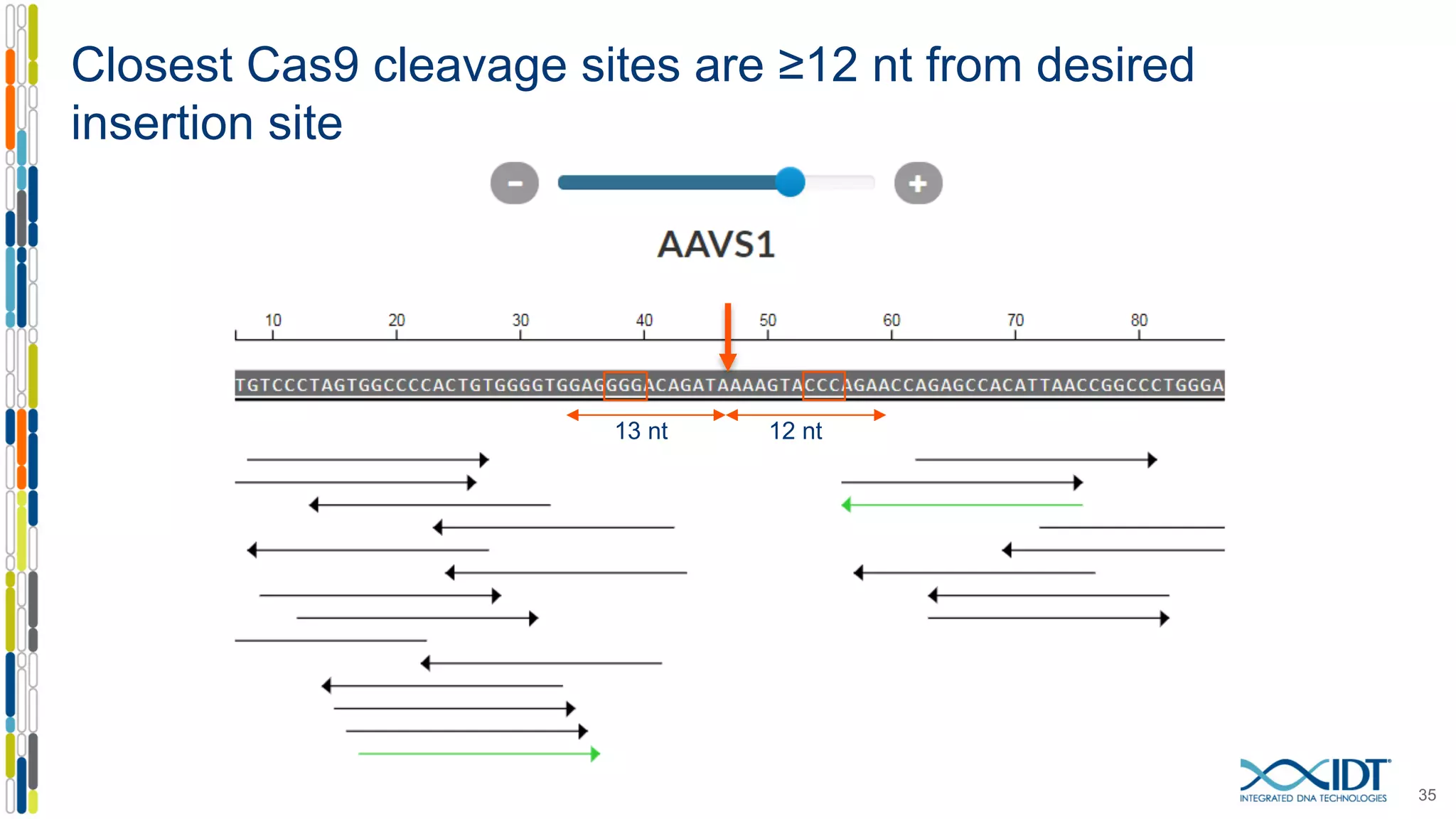
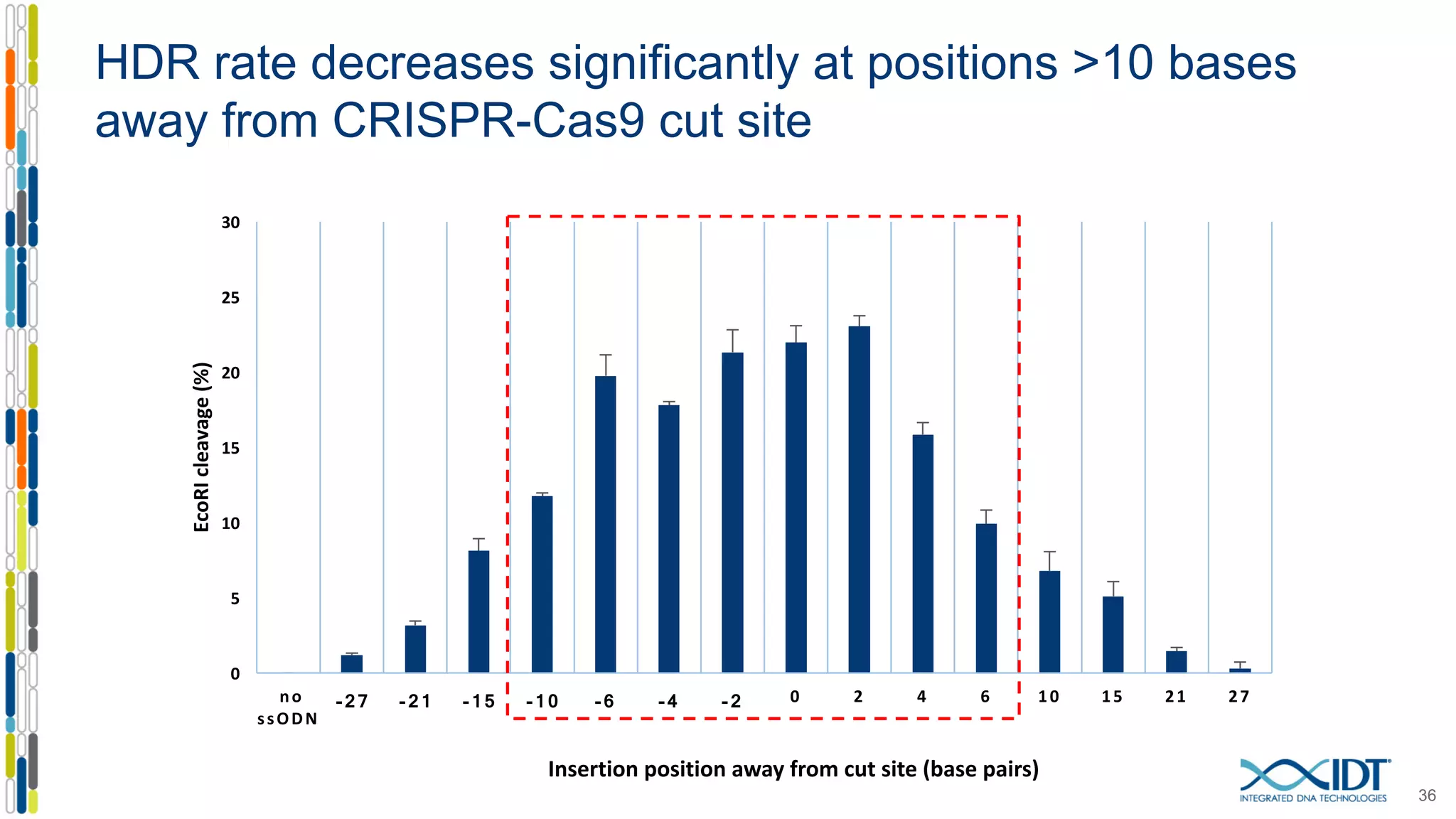
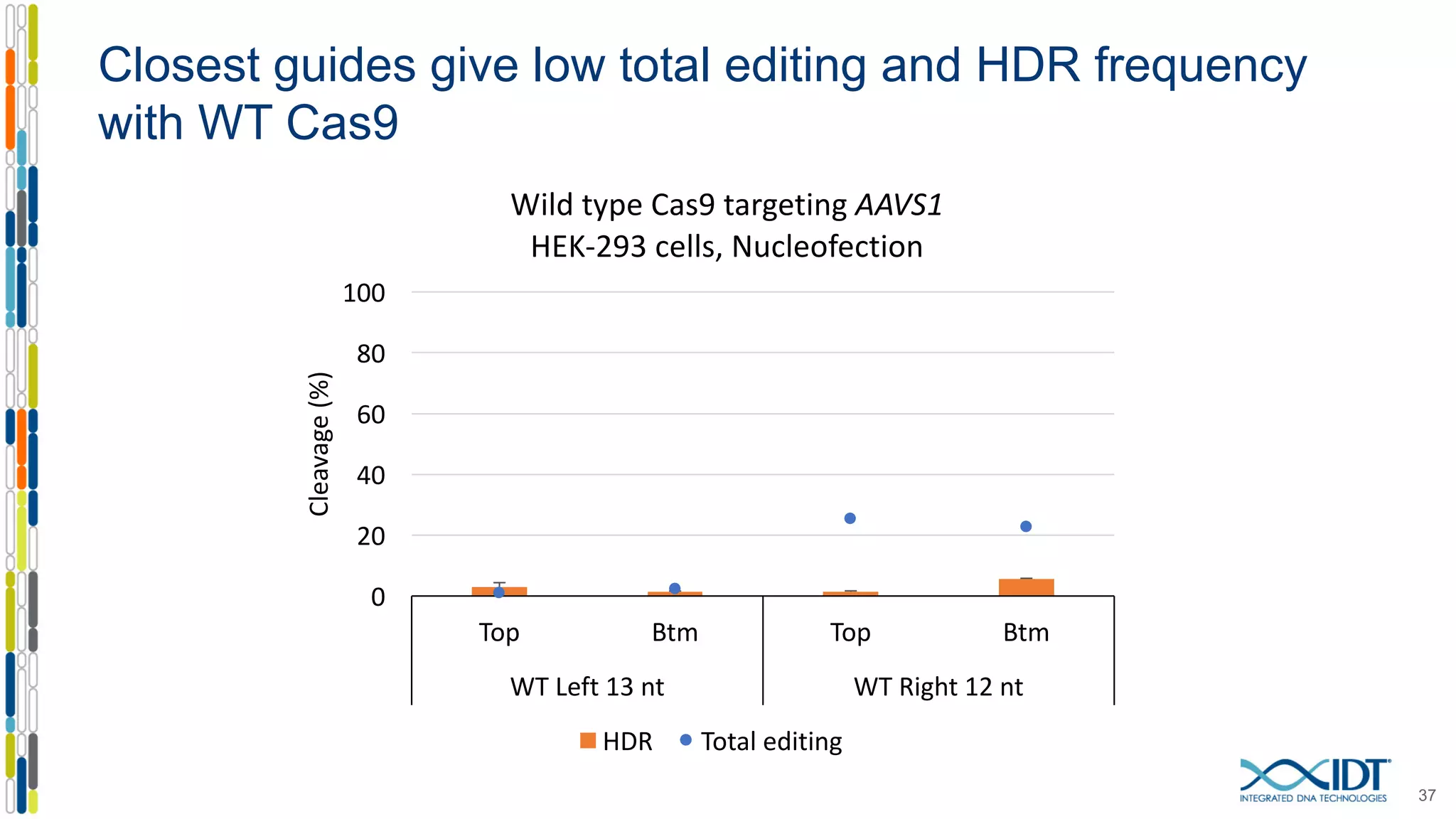
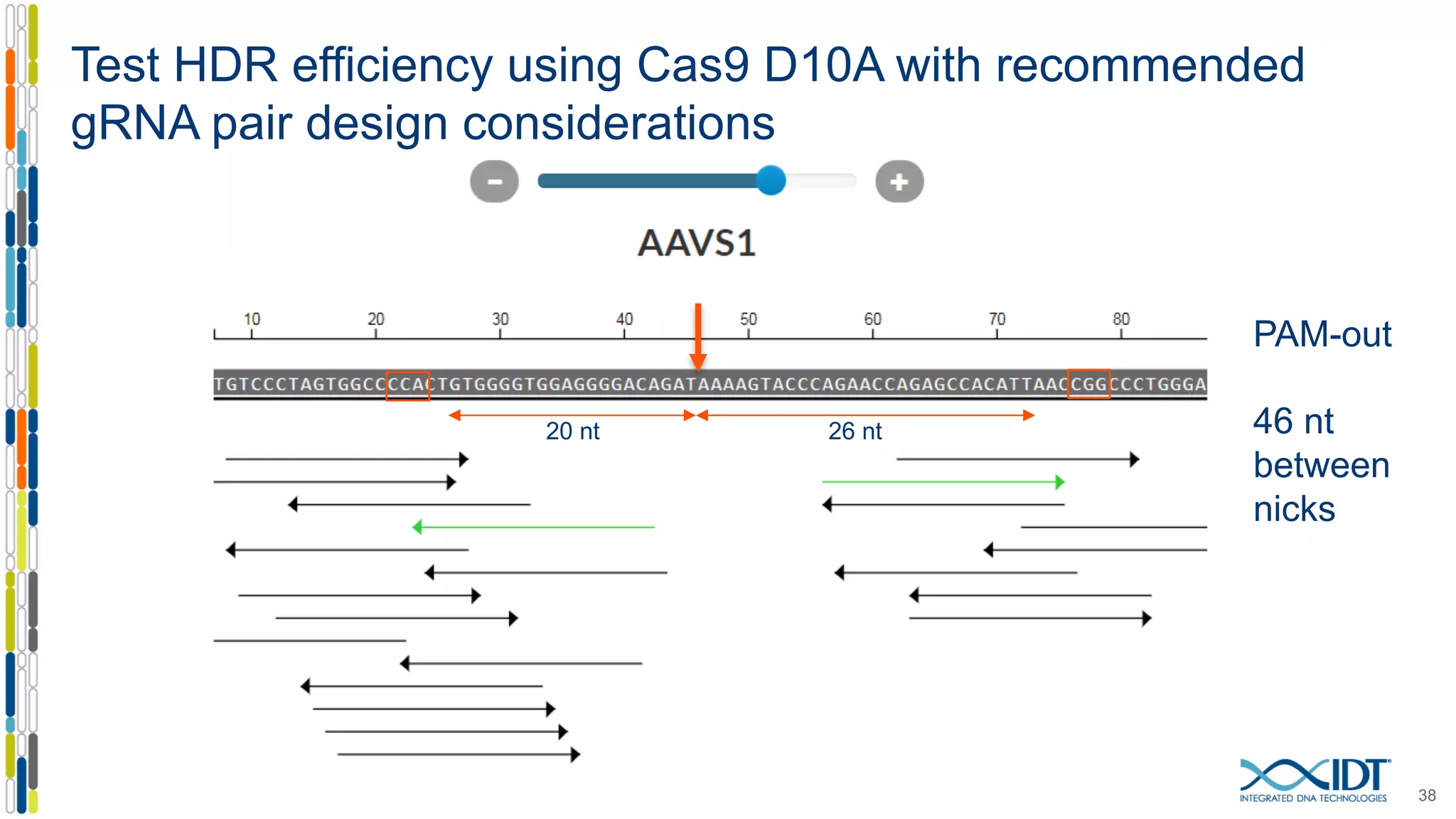
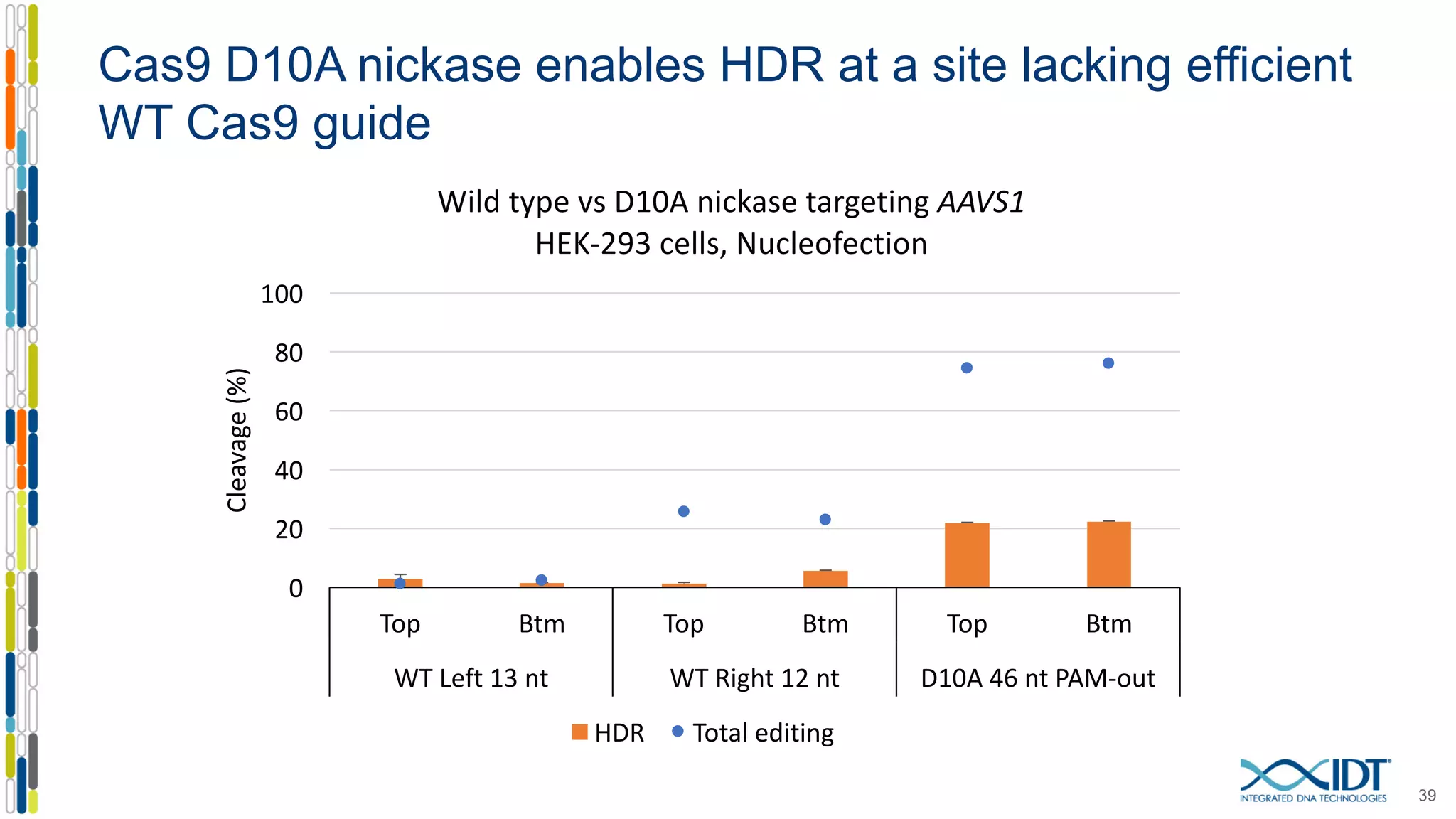
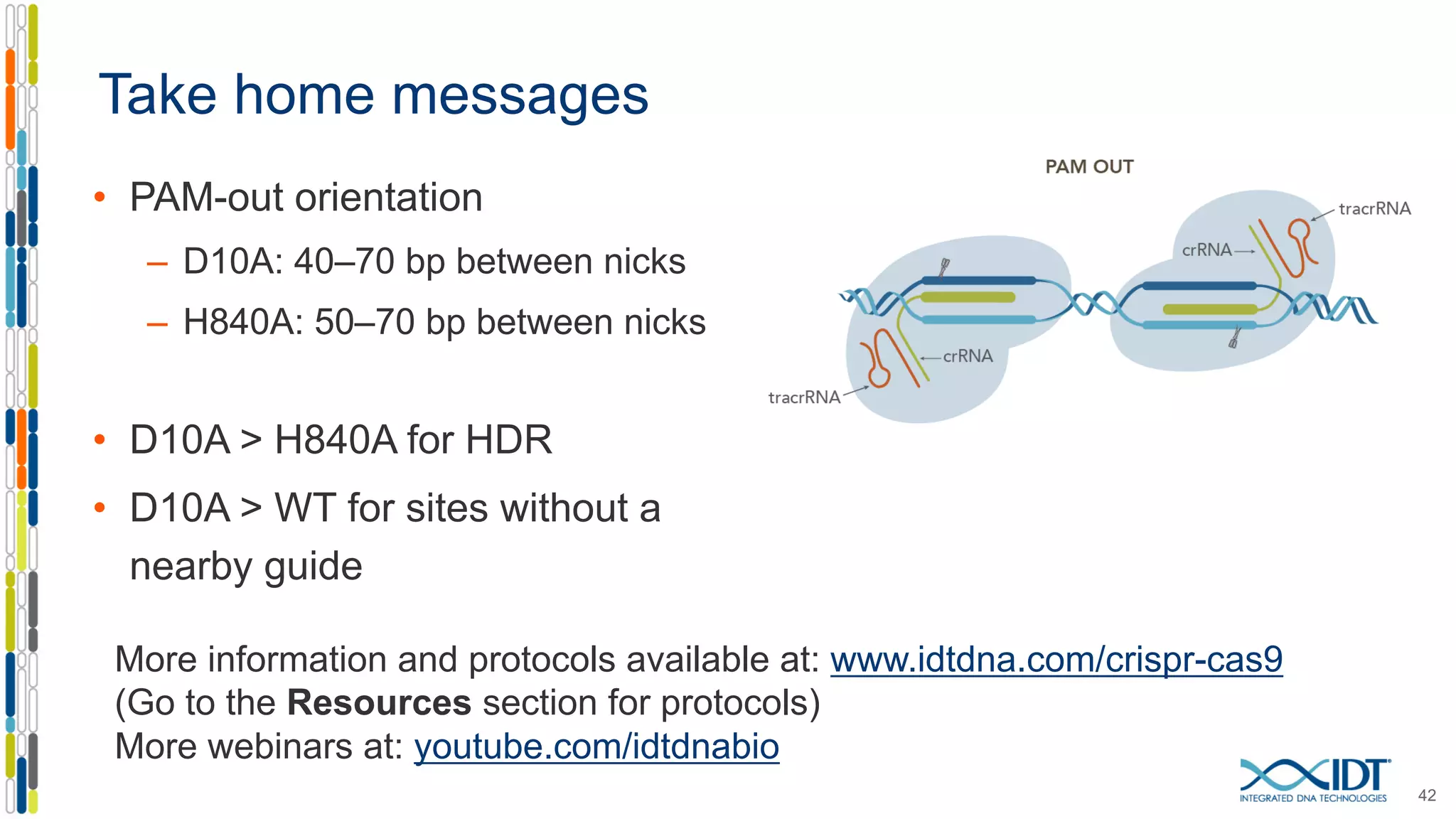
The document discusses the use of Alt-R Cas9 nickases (D10A and H840A) for genome editing, detailing techniques for designing gRNA pairs and donor templates for homology-directed repair (HDR). It emphasizes that D10A is more effective than H840A in mediating HDR and provides specific design guidelines for using these nickases to enhance editing efficiency. The authors recommend optimal distances between targeted nick sites and highlight additional considerations for successful HDR applications in different insertion contexts.