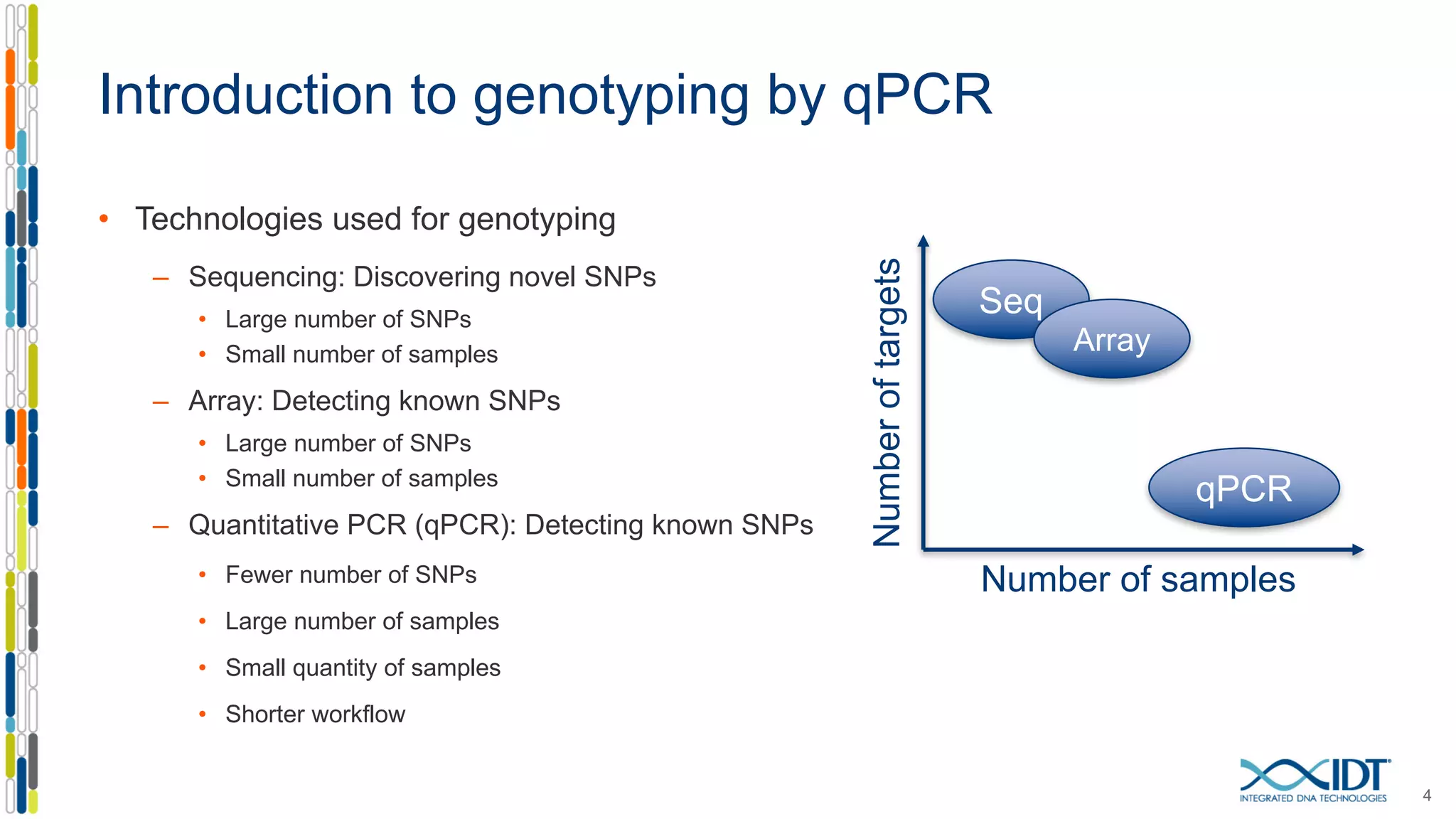
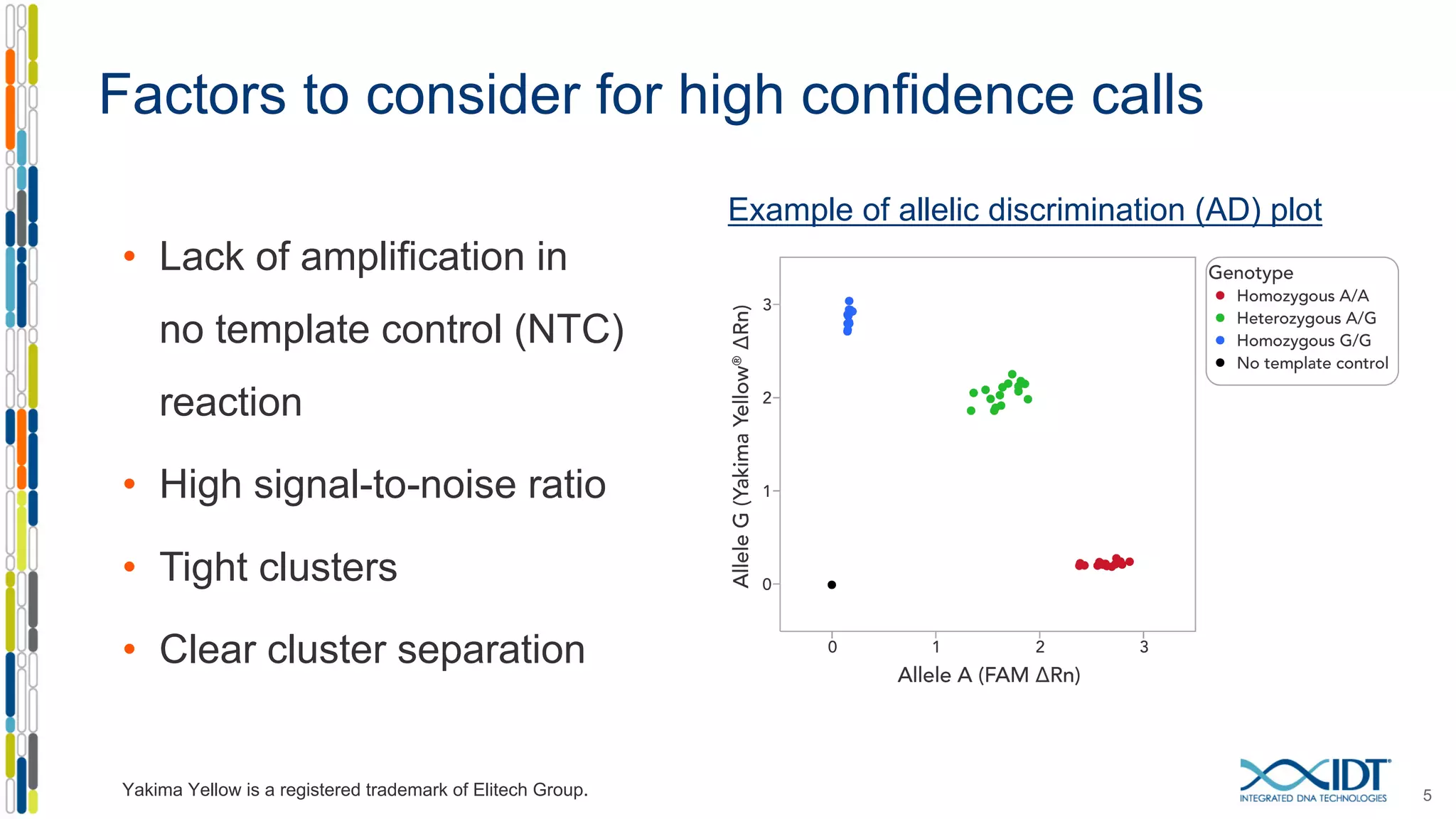
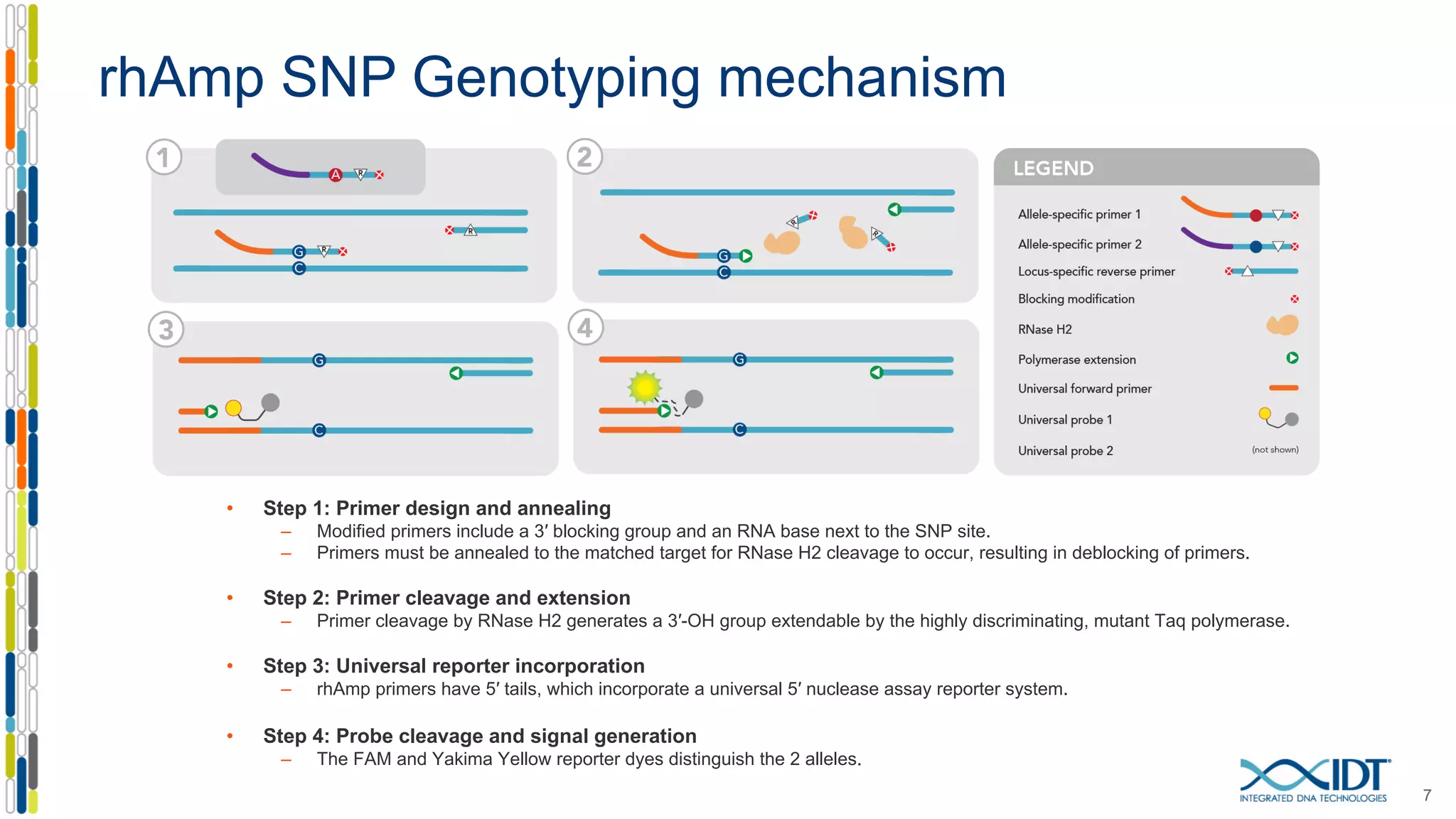
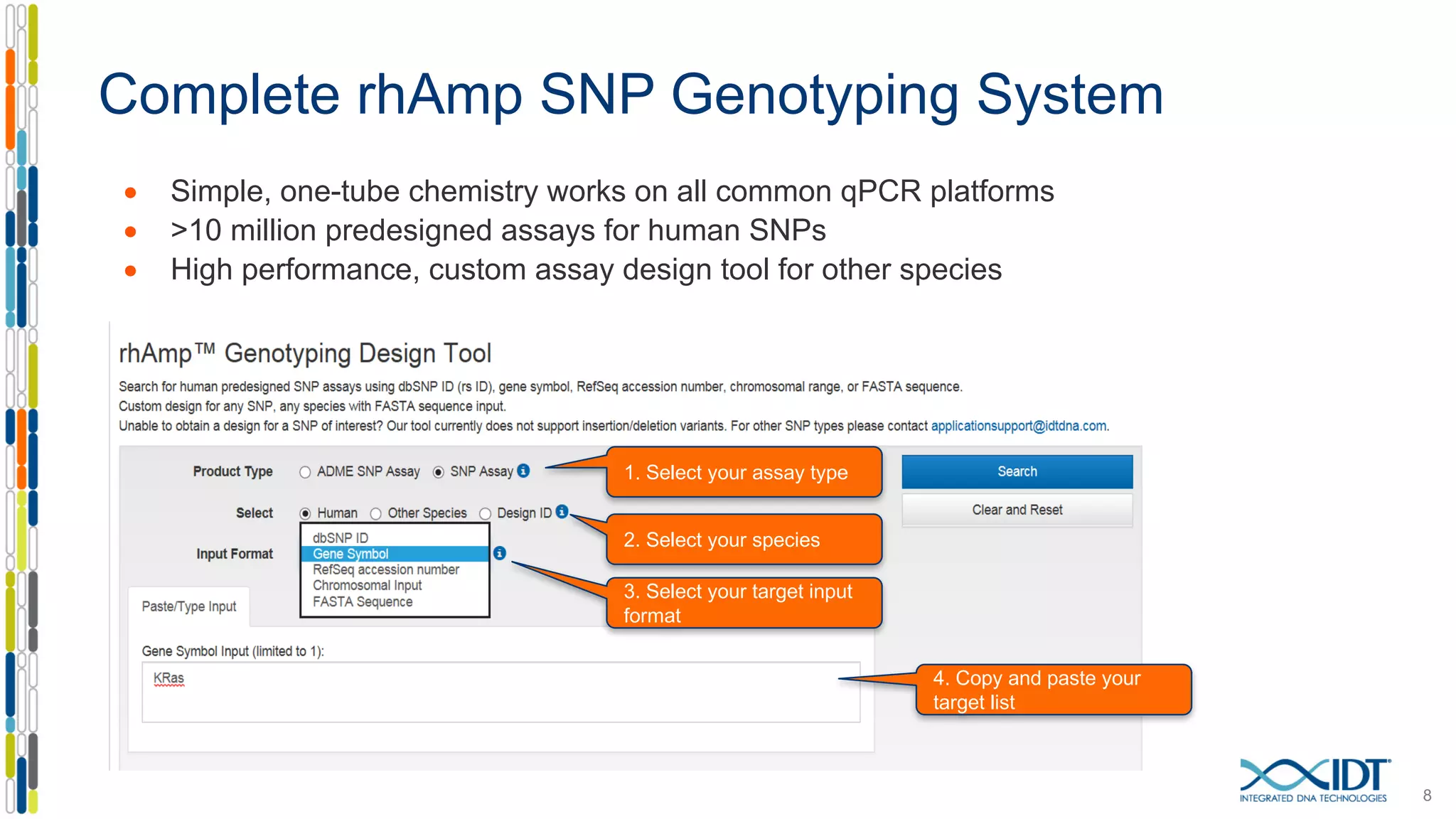
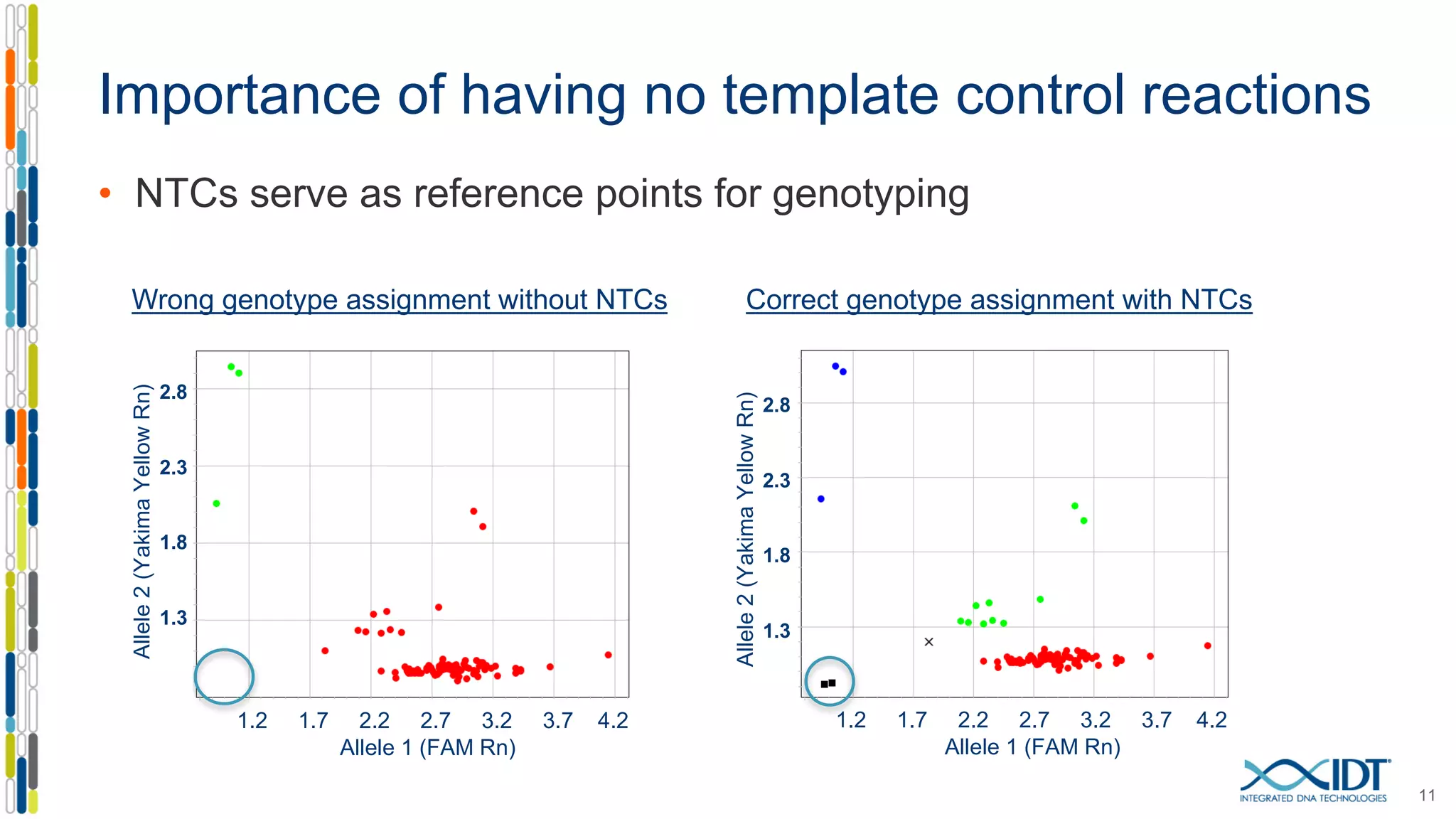
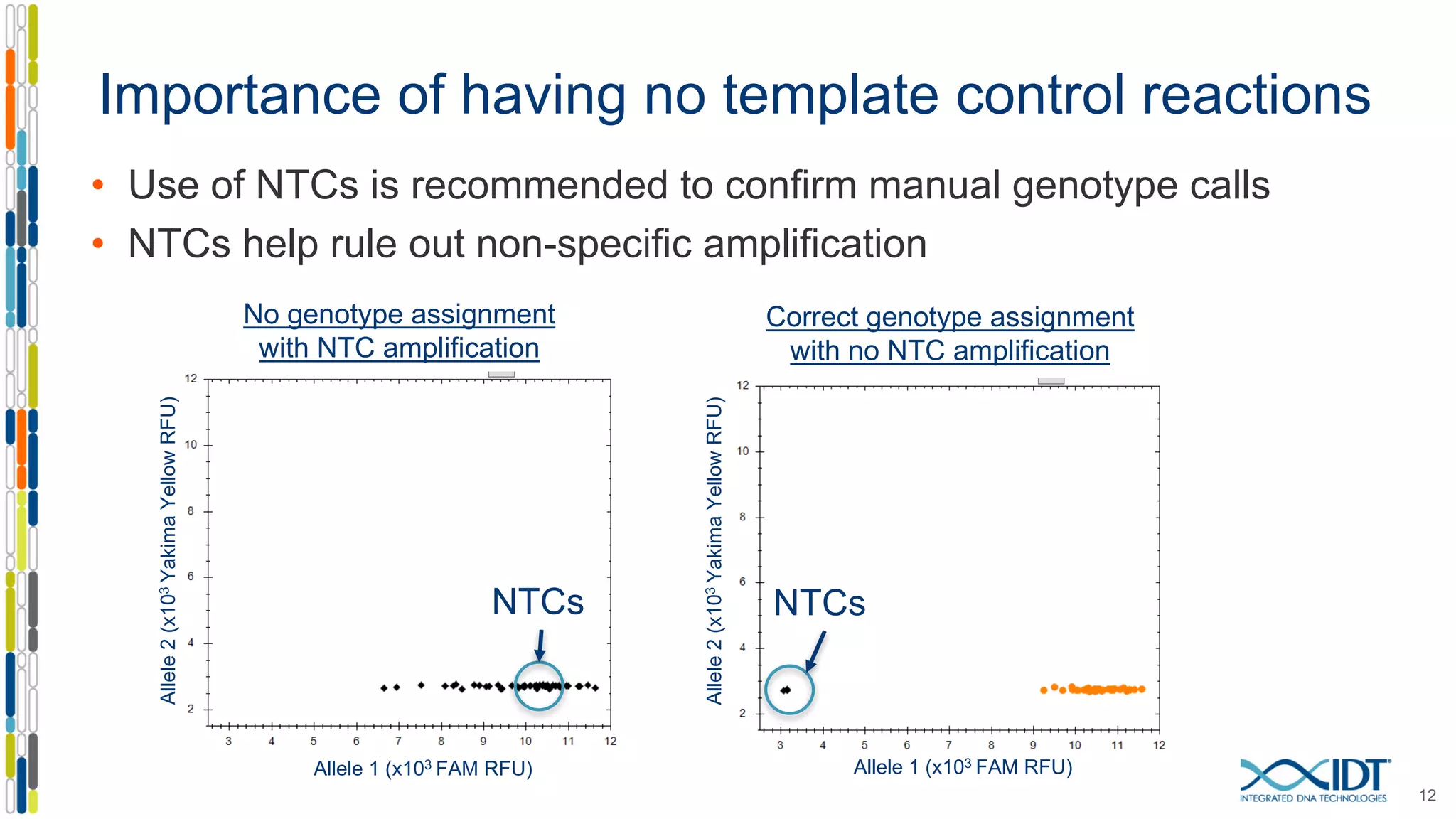
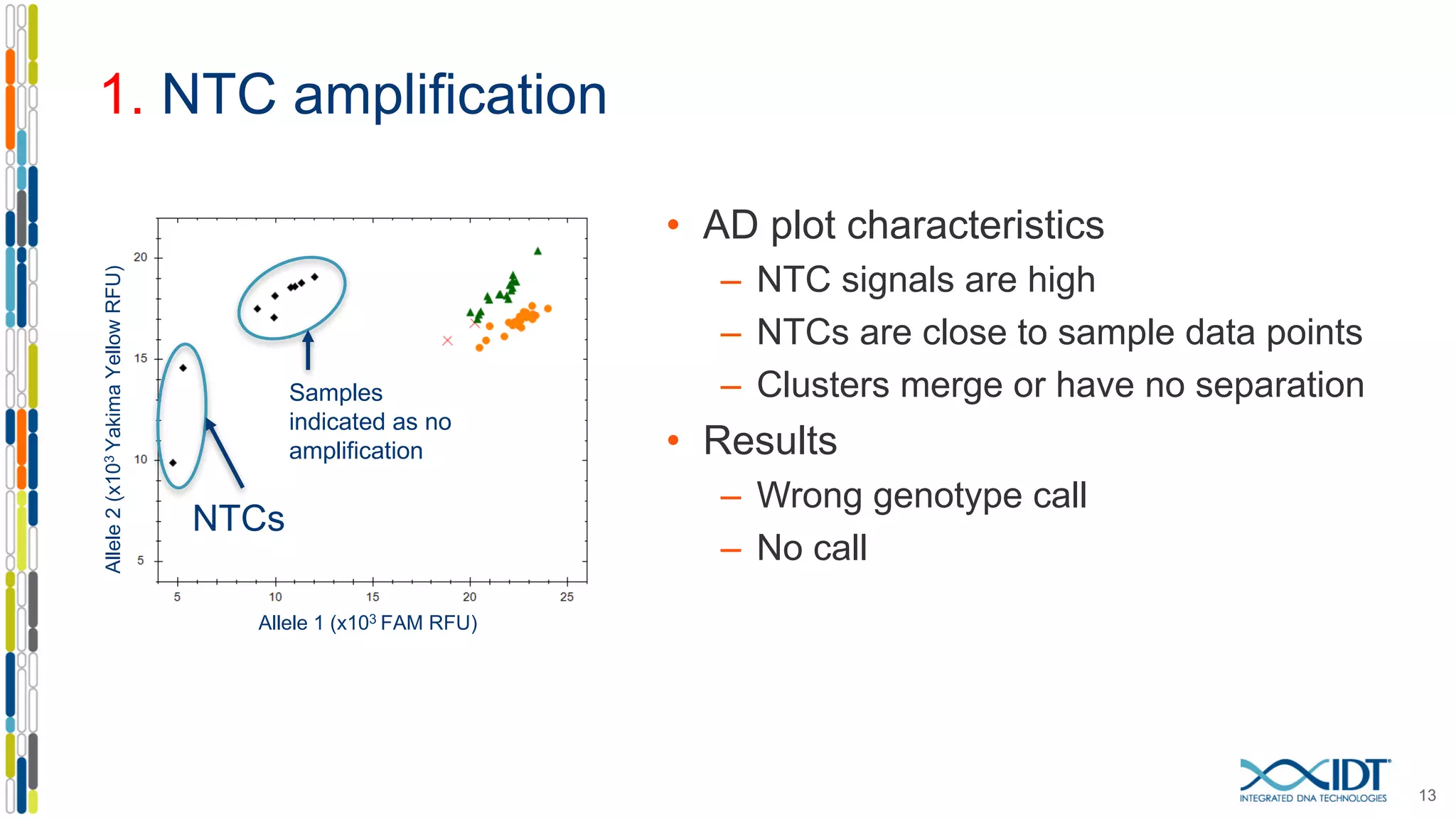
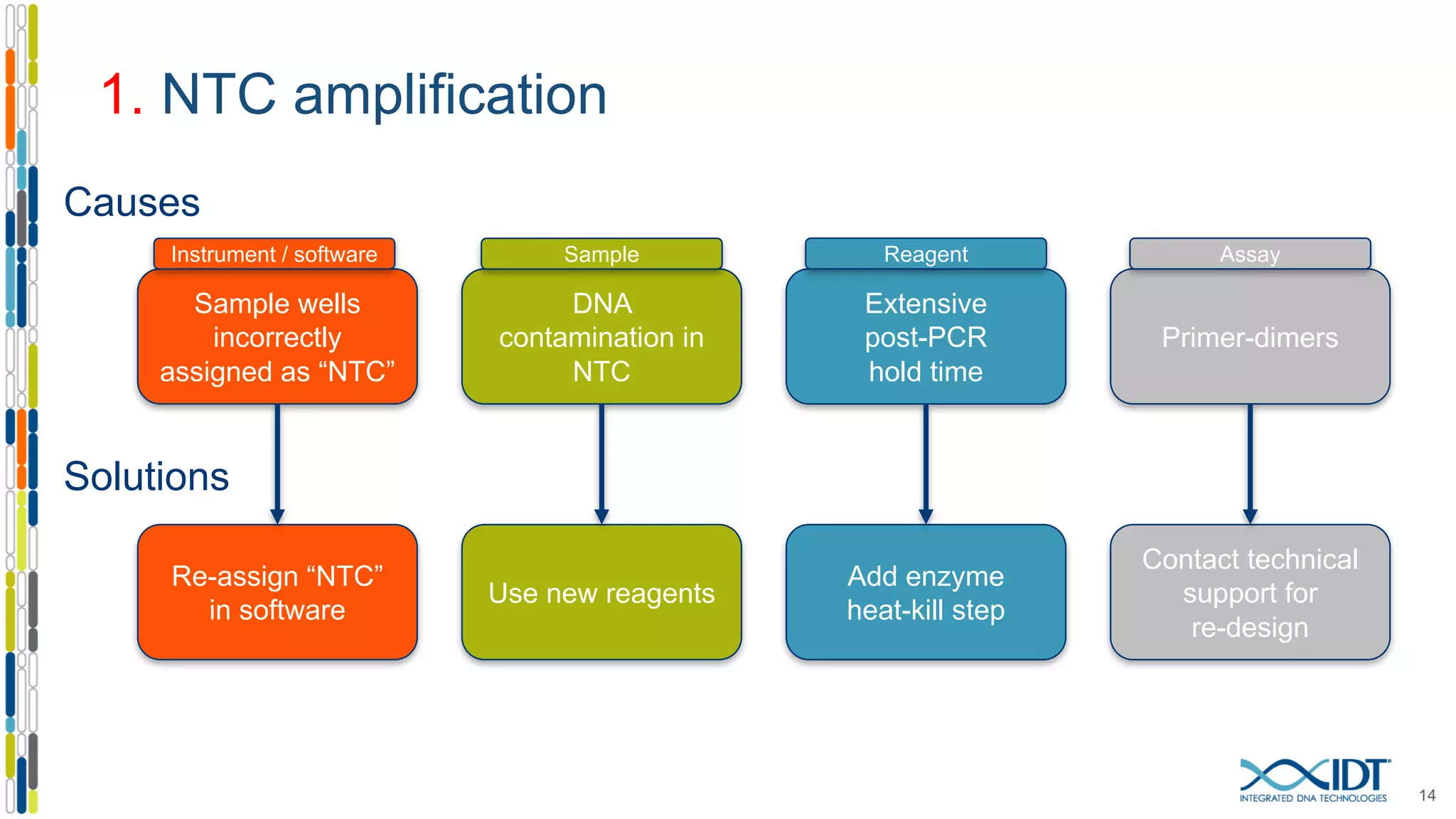
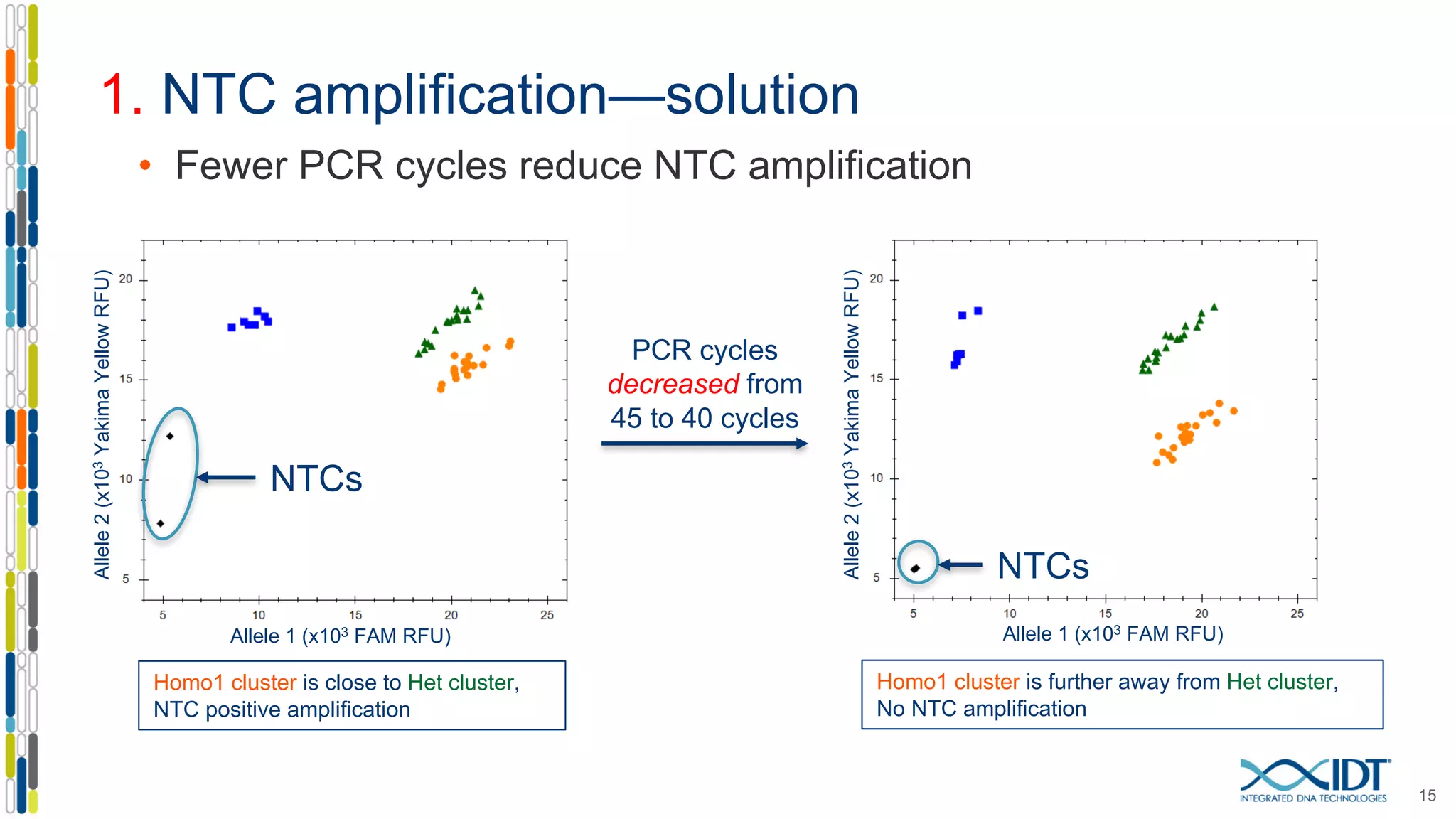
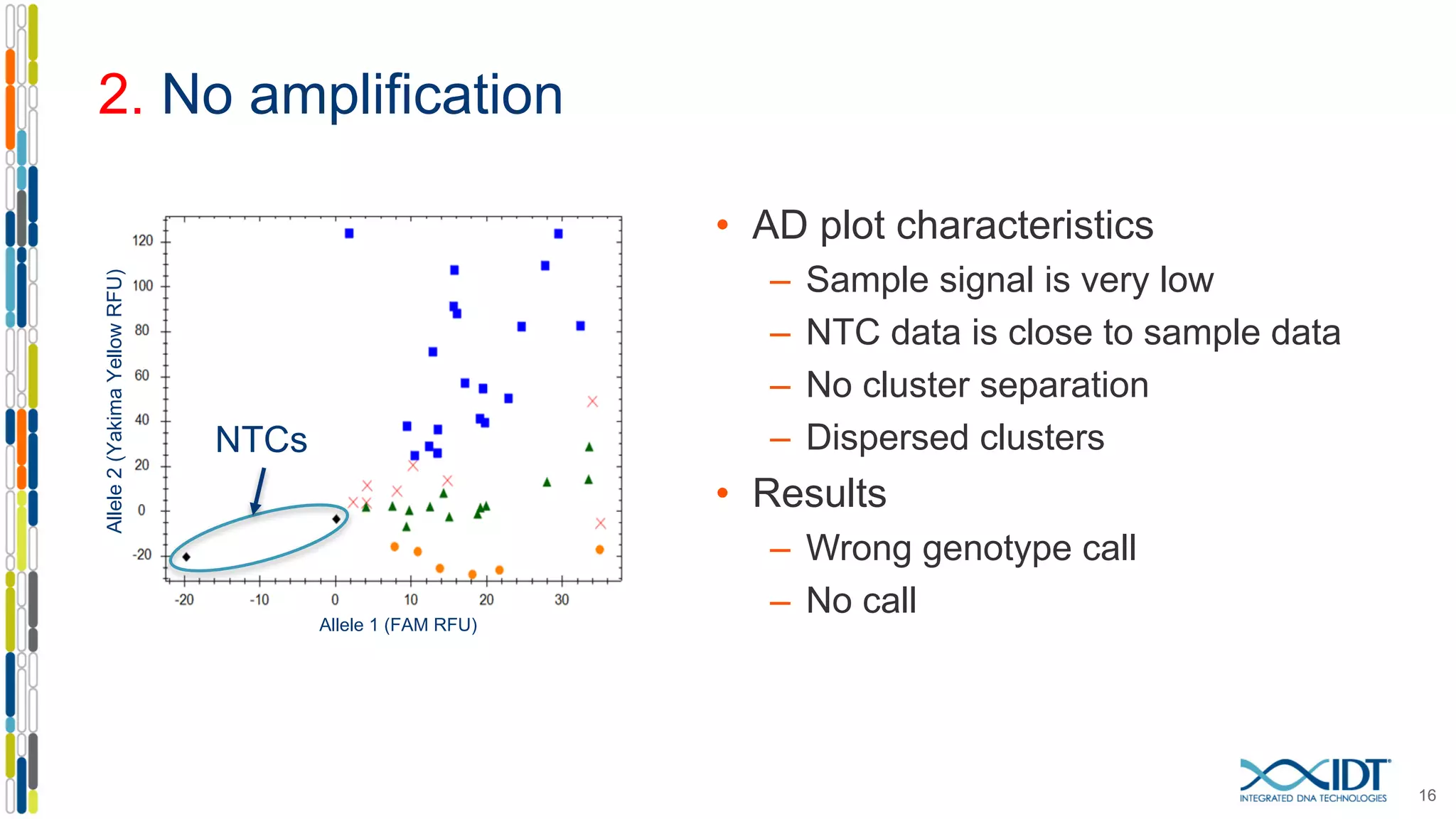
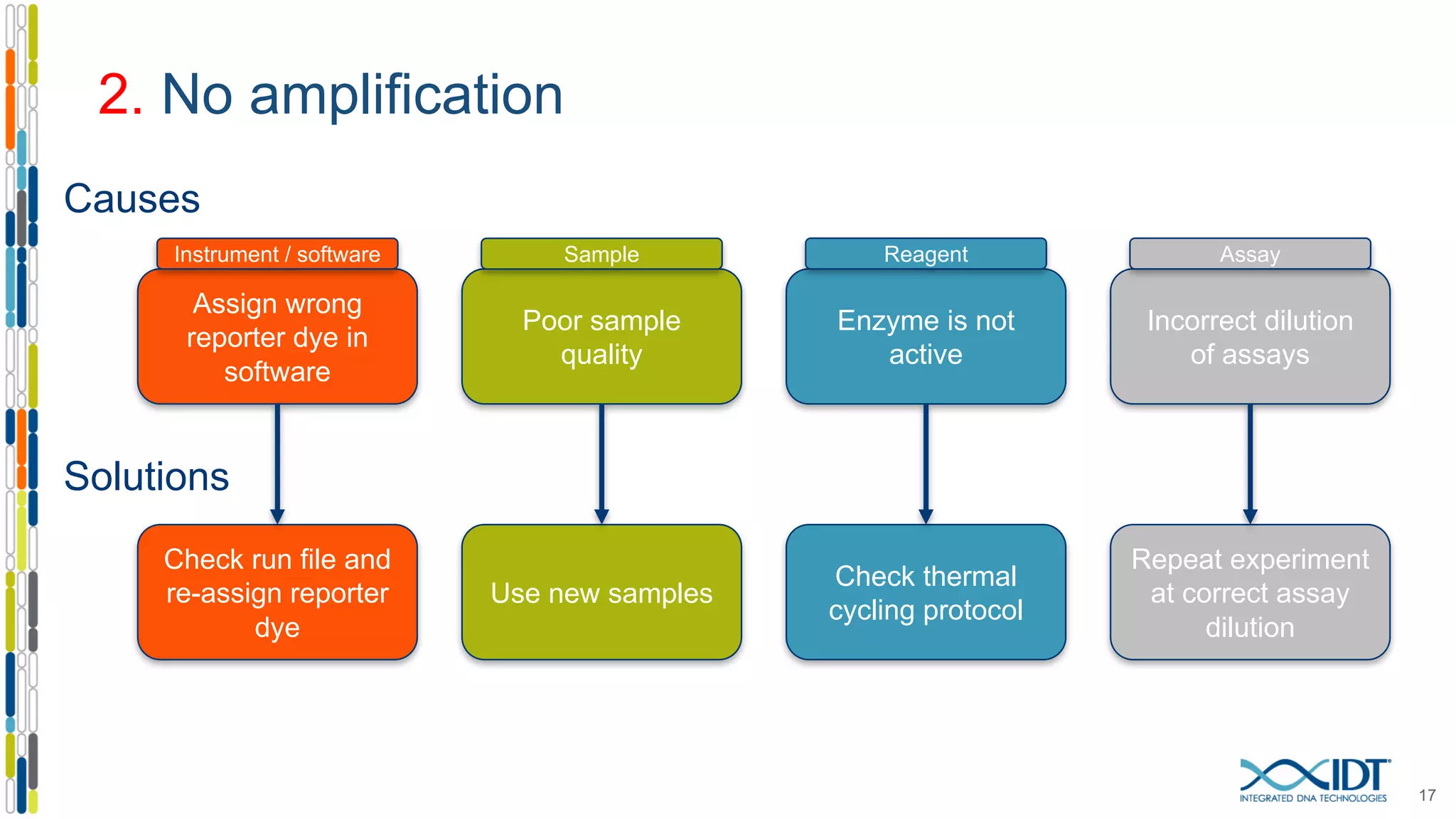
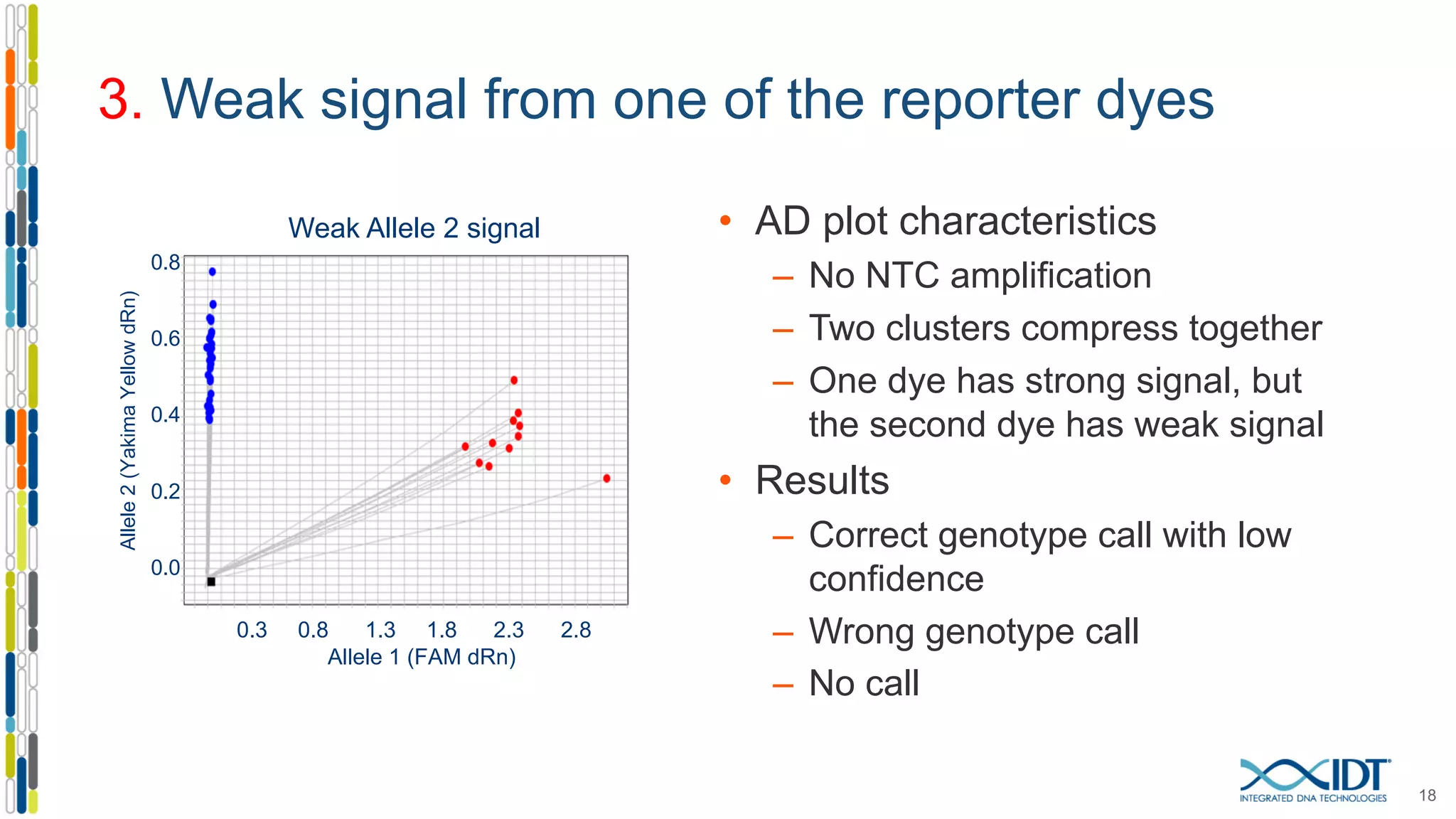
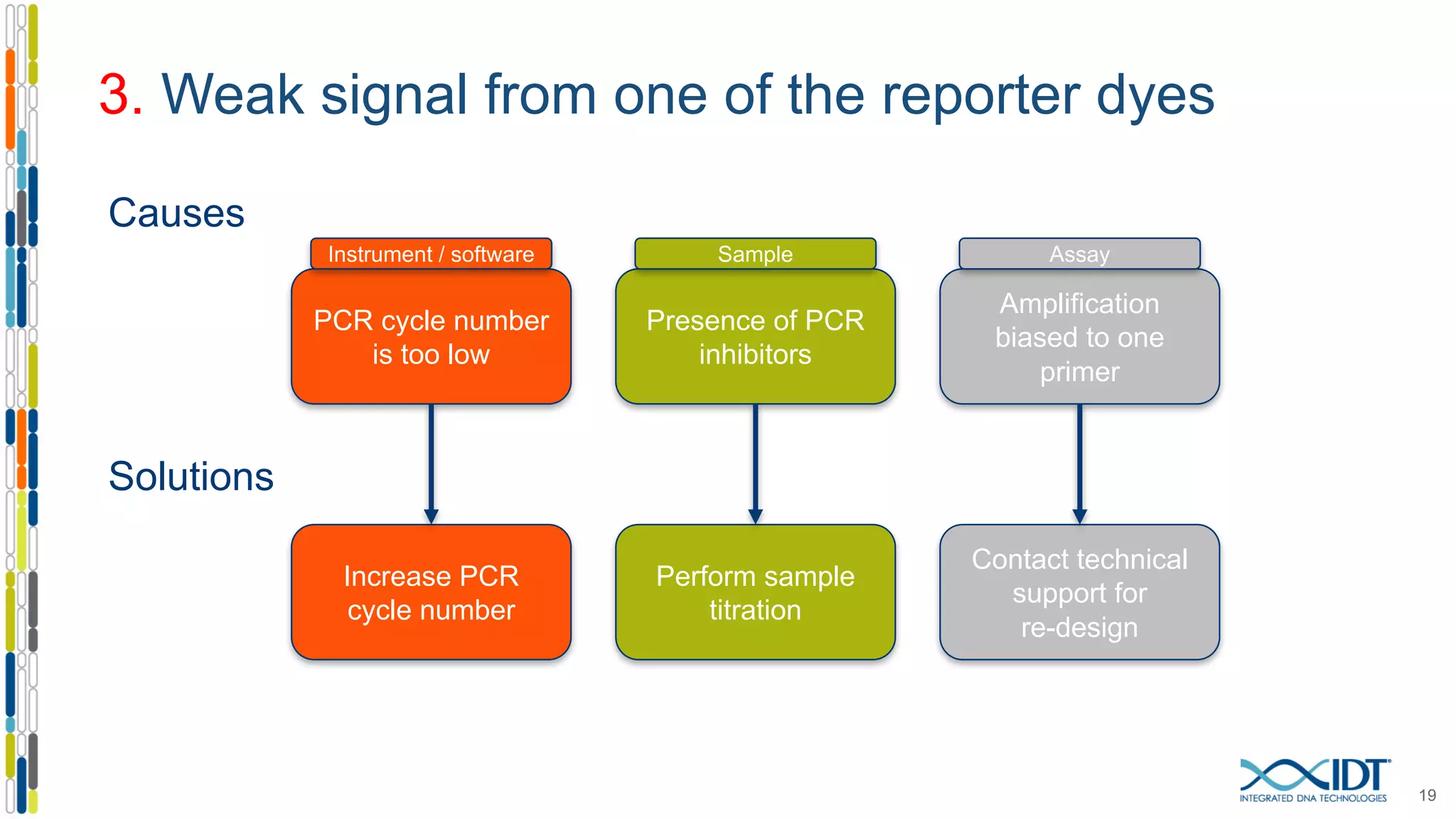
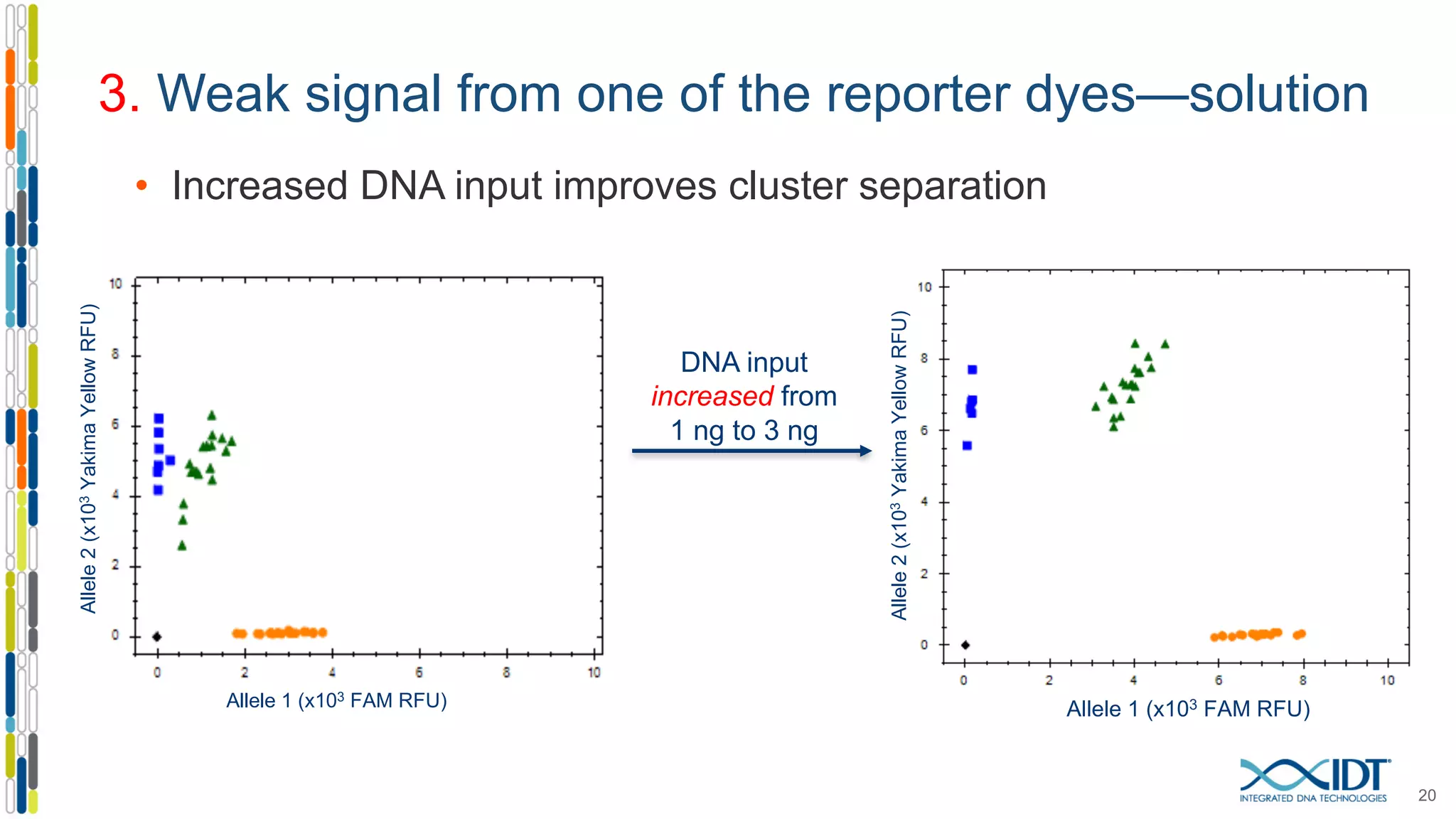
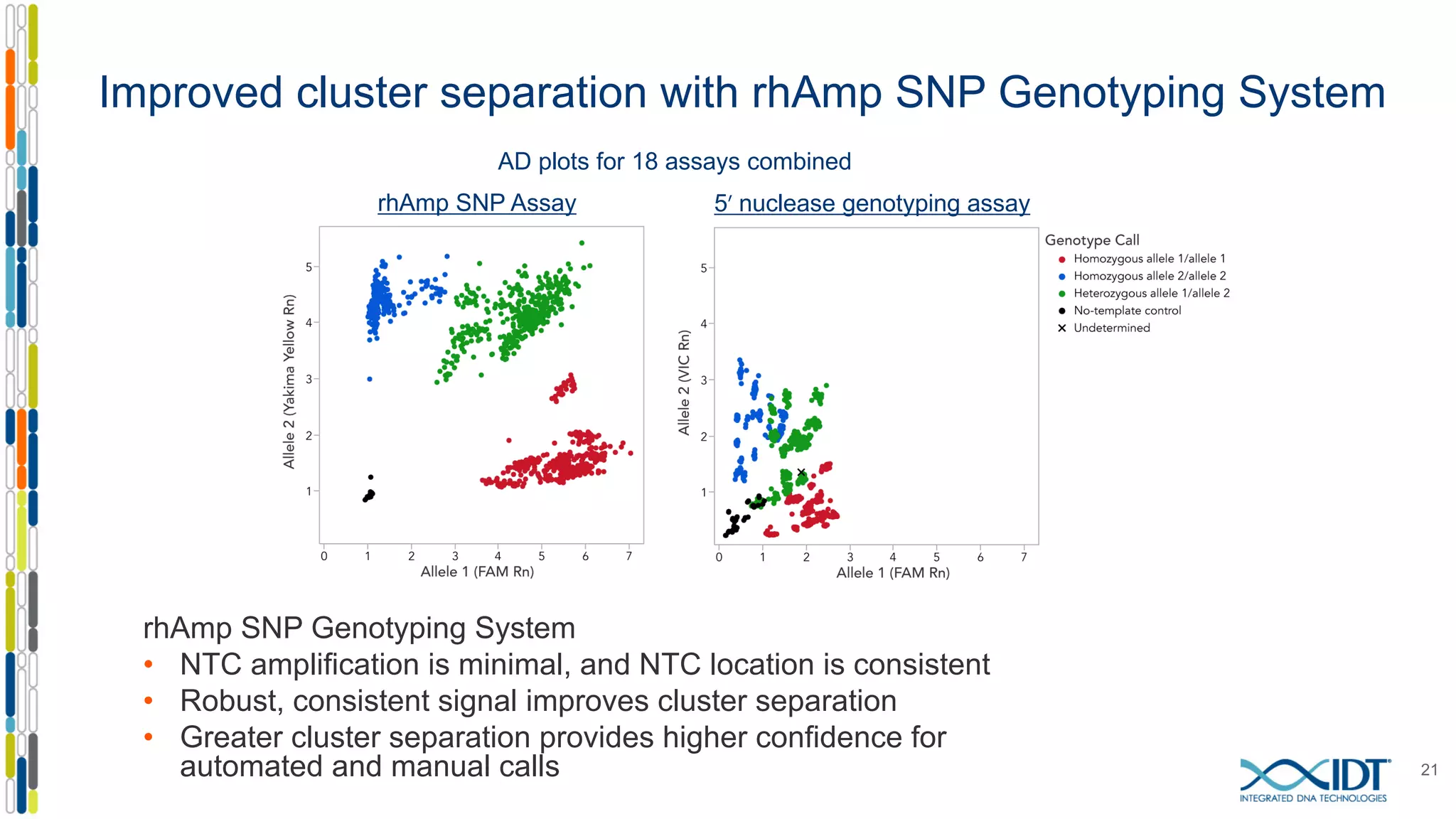
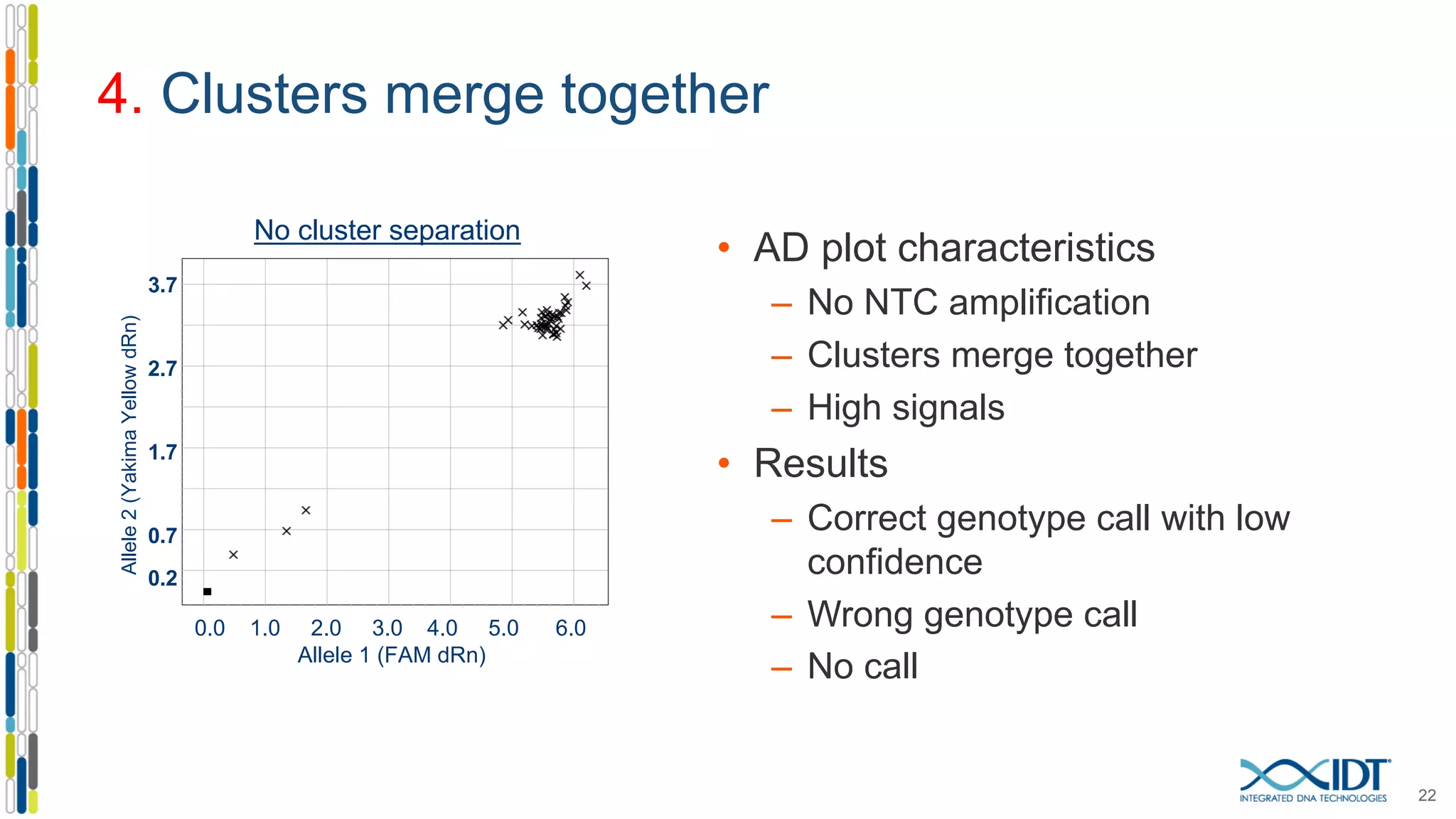
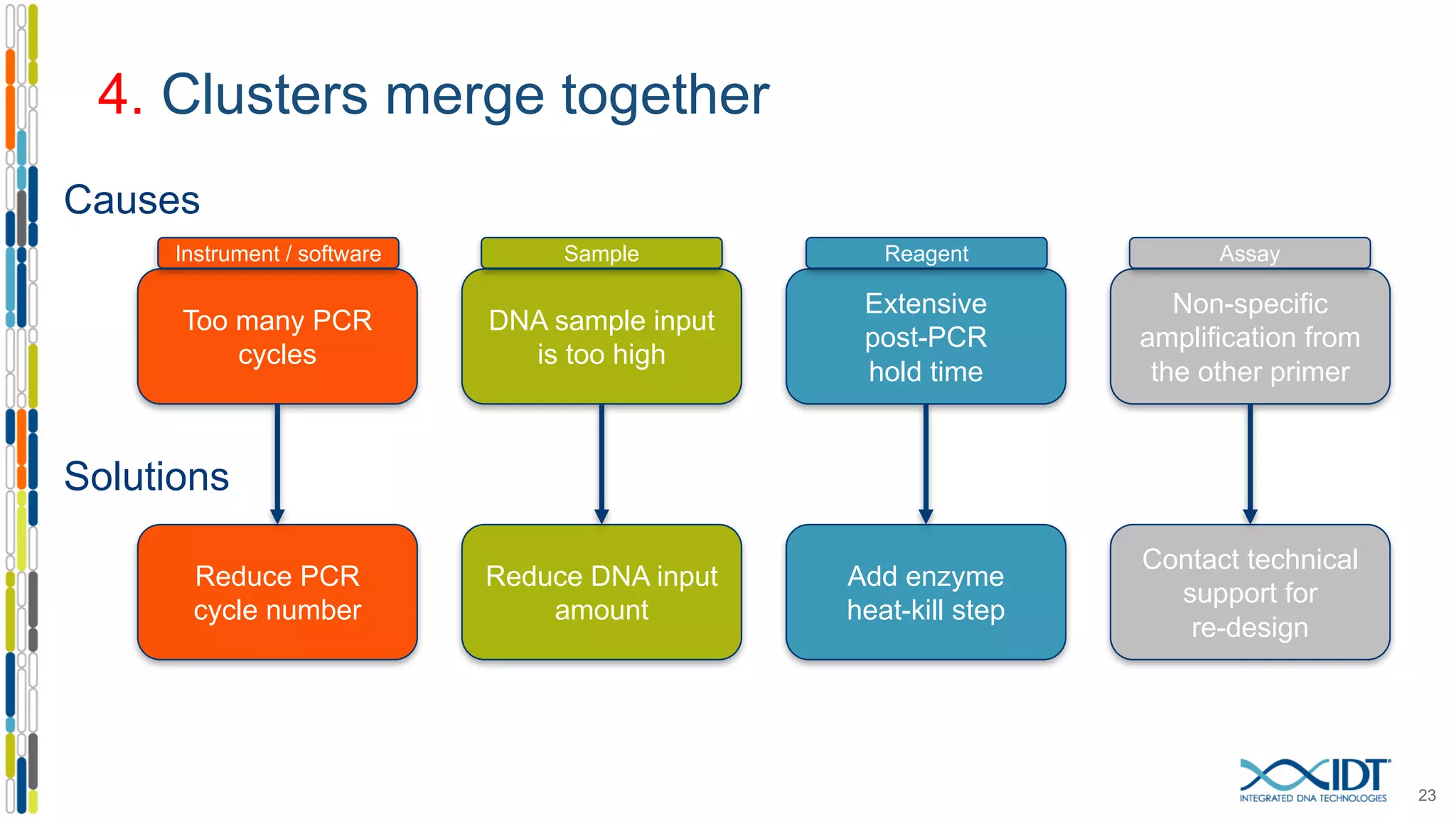
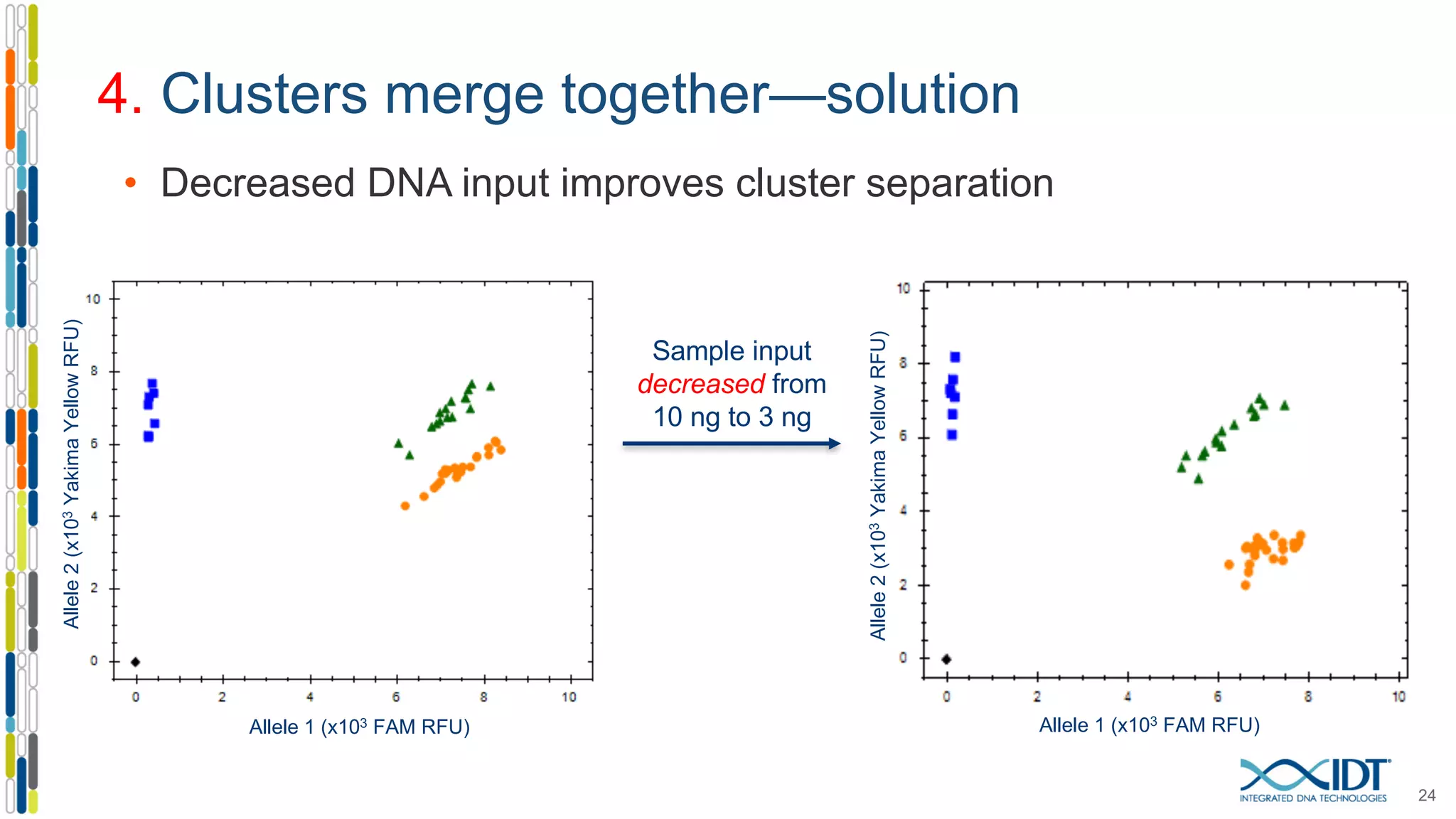
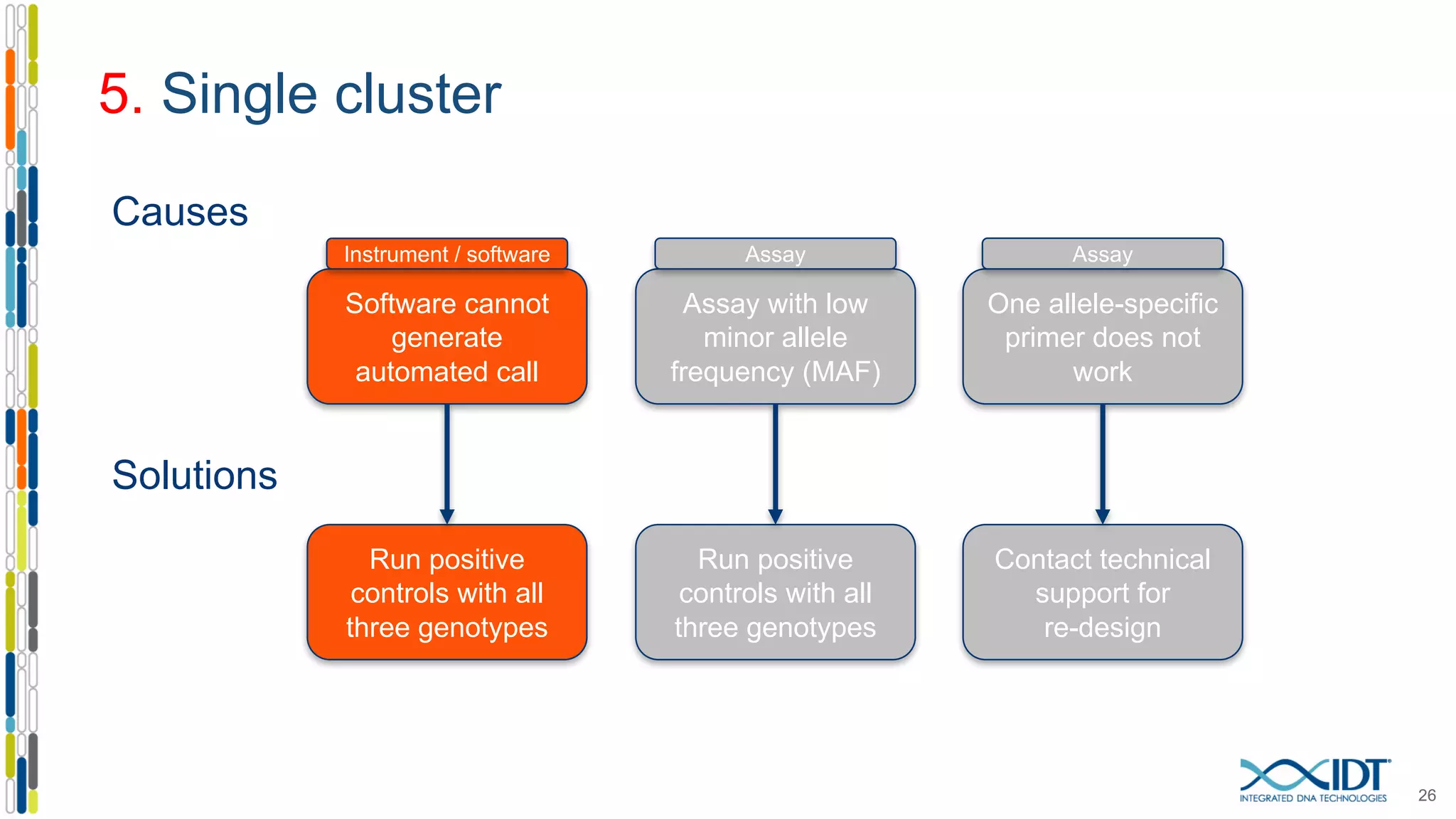
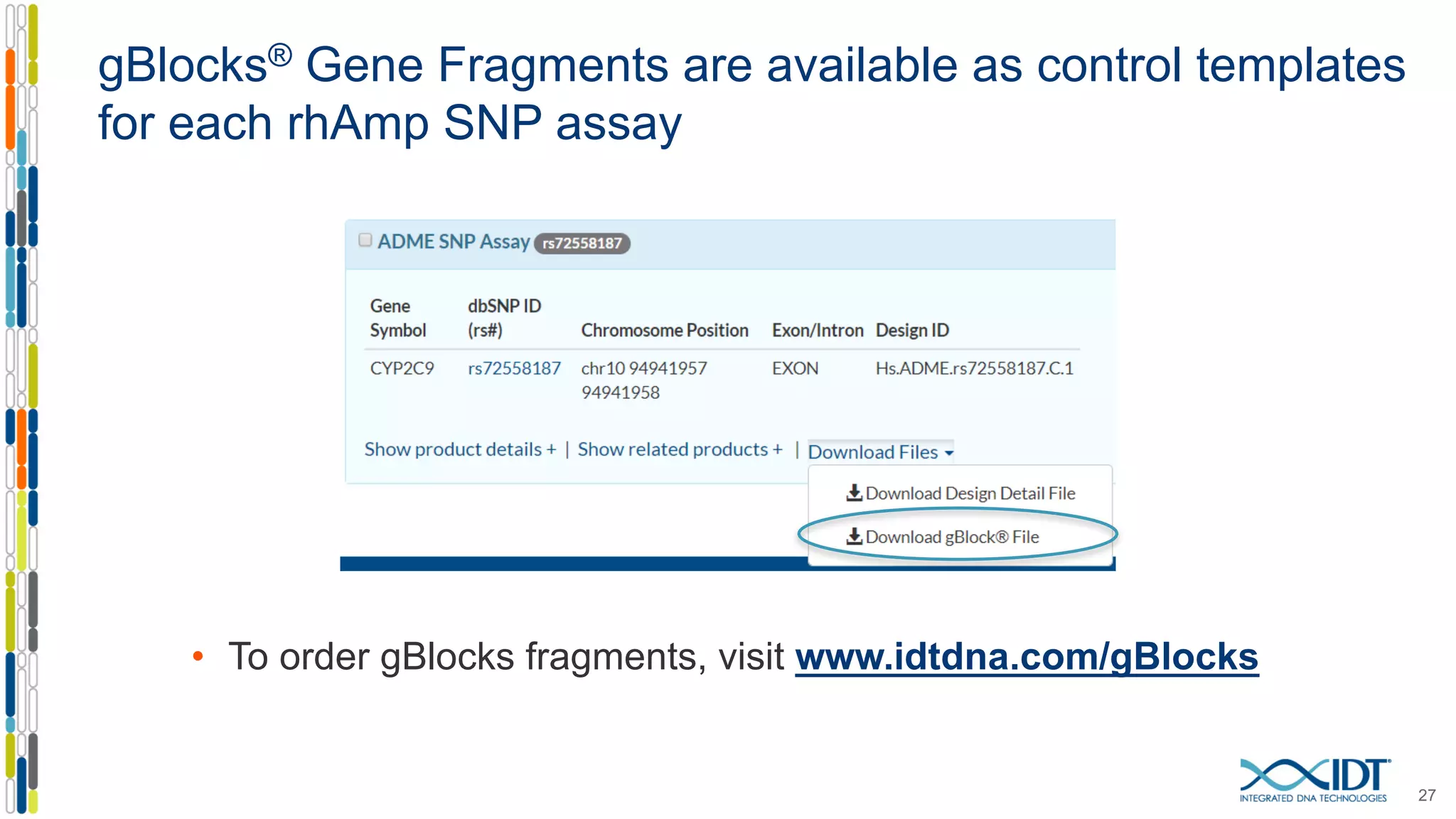
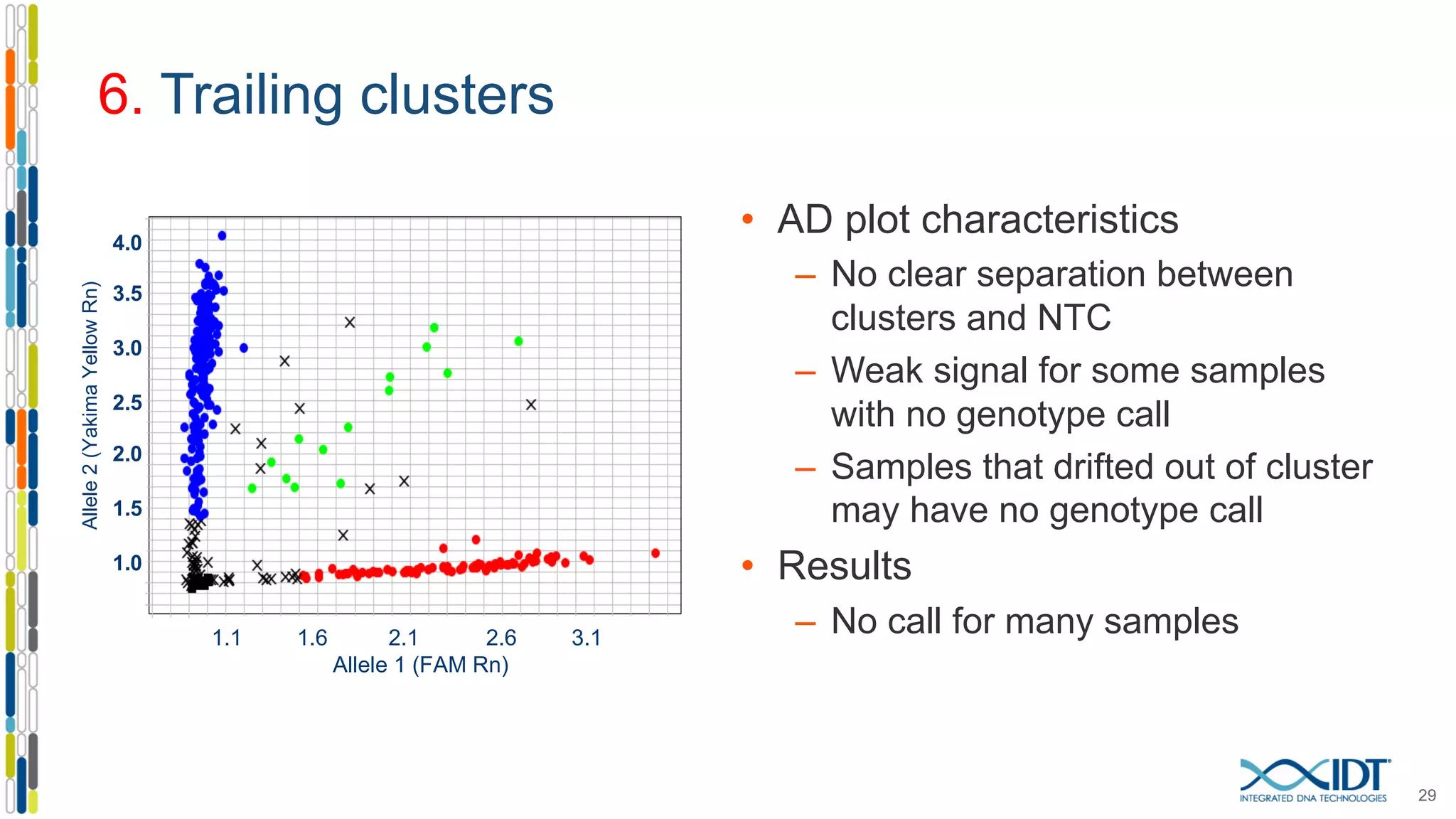
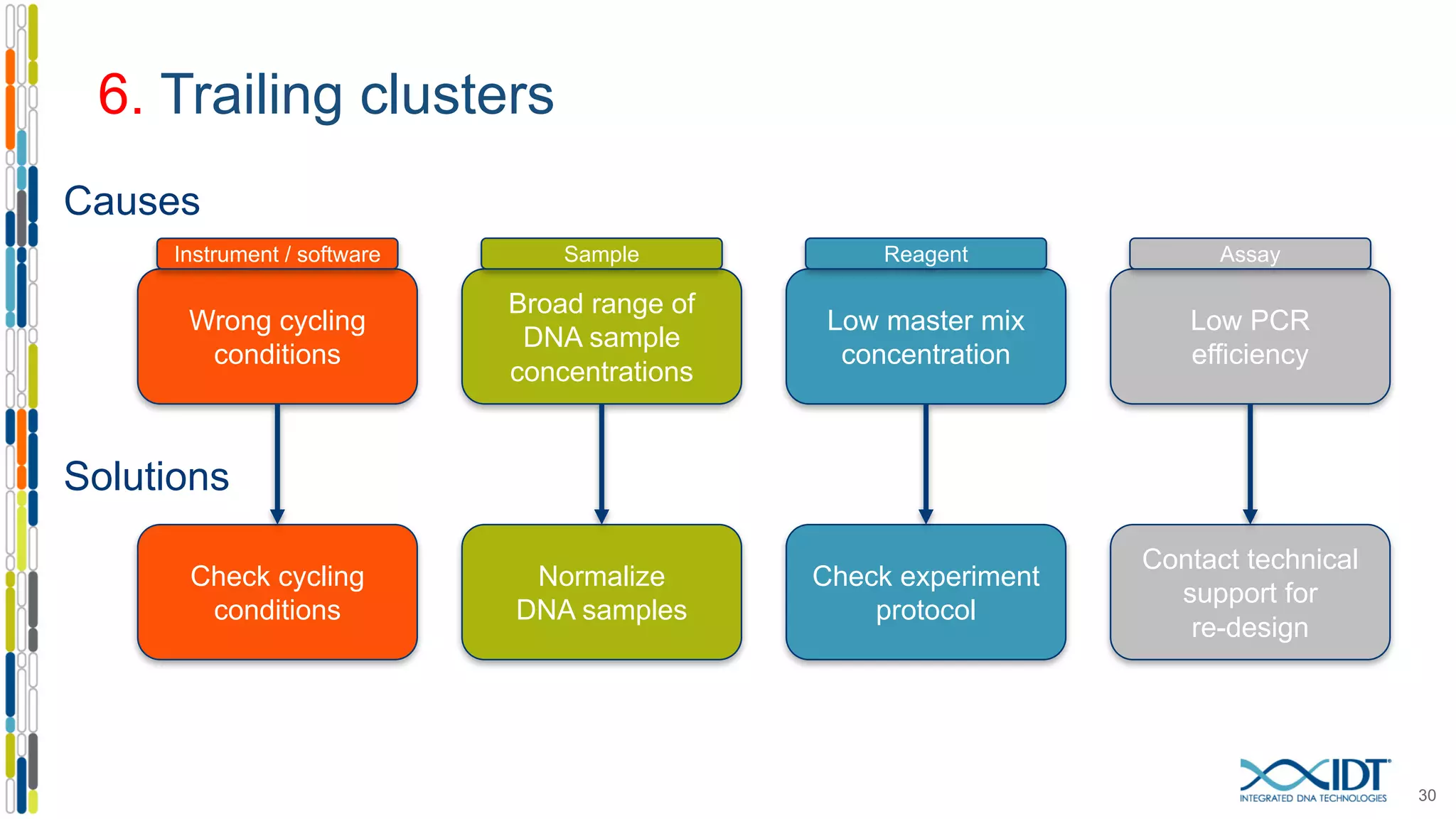
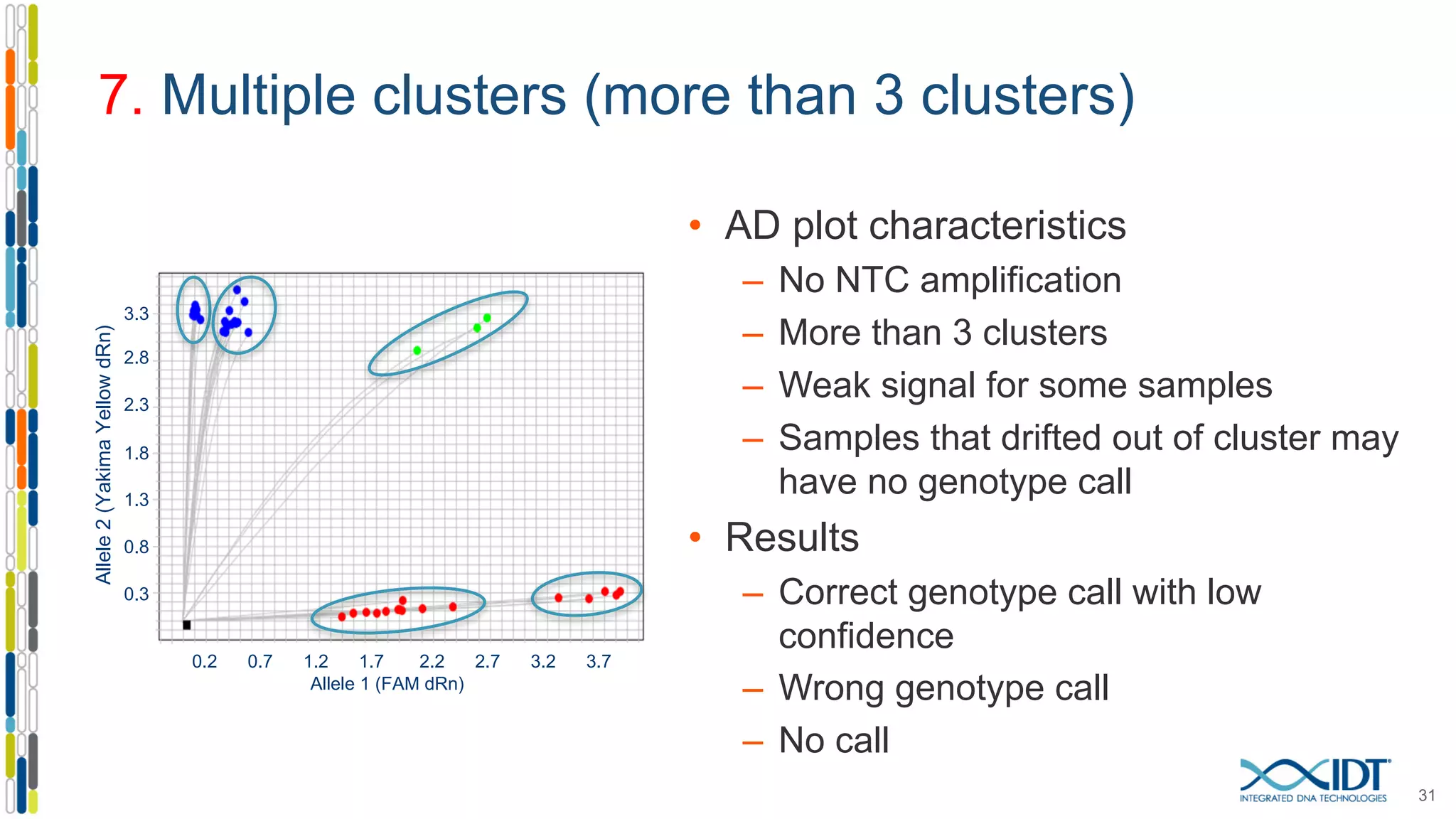
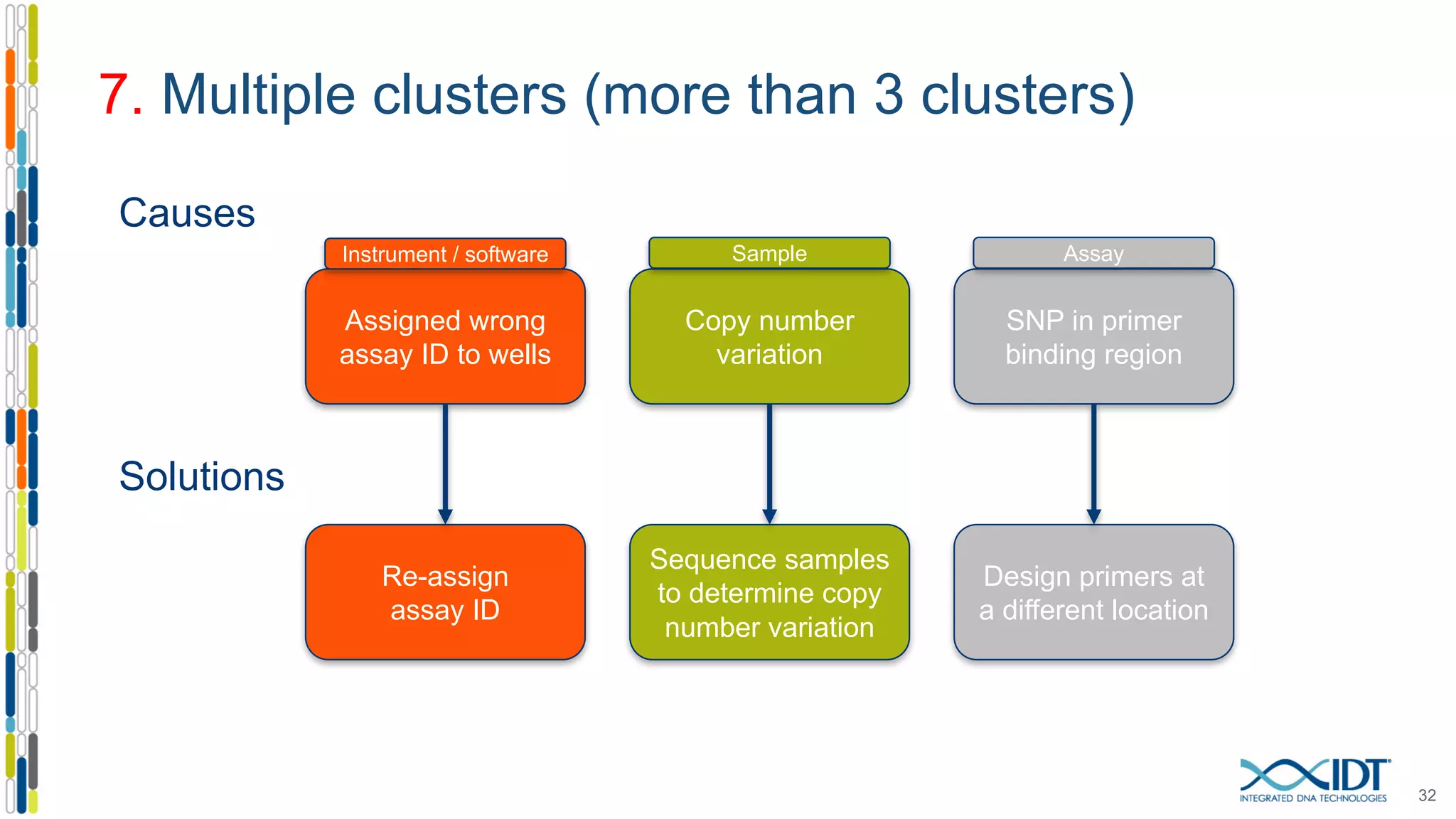
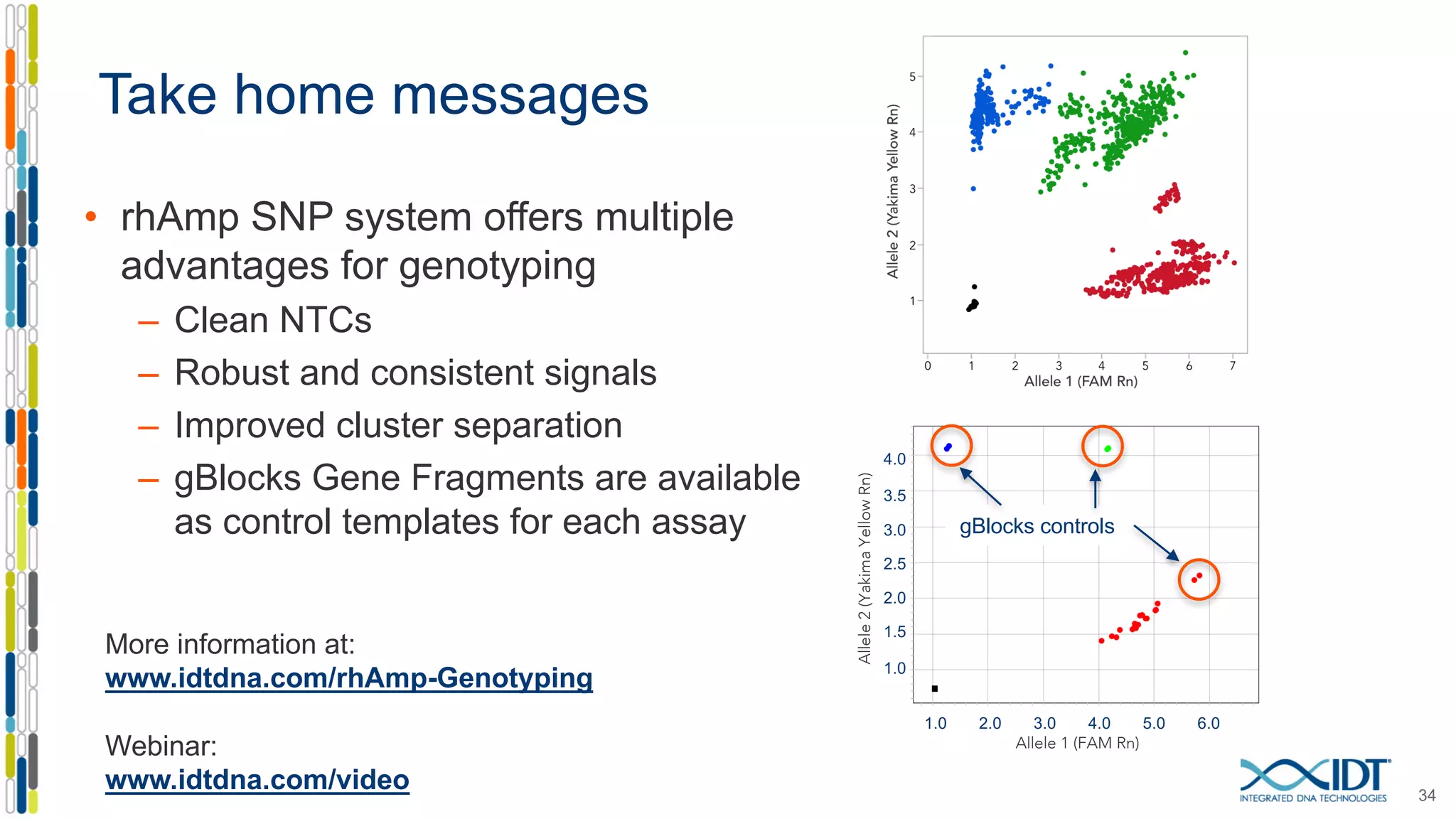
The document provides a comprehensive overview of SNP genotyping on qPCR platforms, specifically detailing the IDT RhAMP SNP genotyping system and its advantages. It also addresses common genotyping failures, emphasizing the importance of using no template control (NTC) reactions to ensure accurate results, and suggests solutions for common troubleshooting issues. The RhAMP system is highlighted for its robust performance, improved cluster separation, and availability of pre-designed assays.