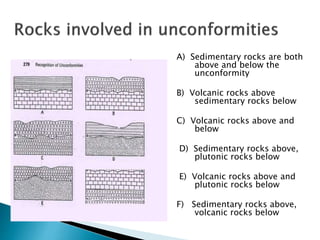
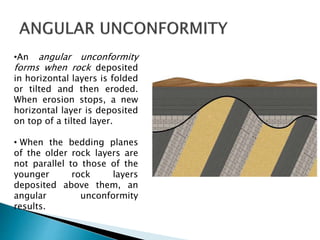
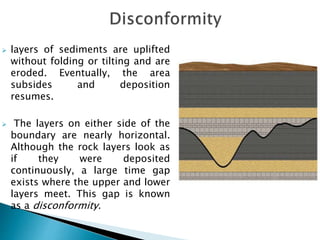
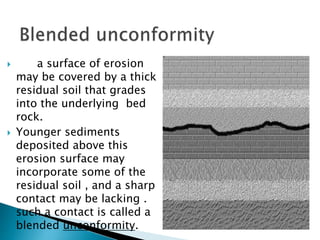
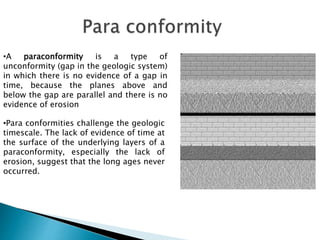
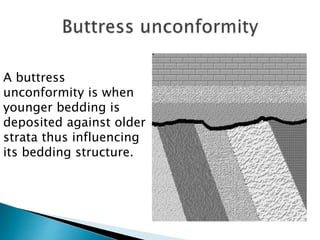
Unconformities represent gaps or missing time in the geologic record due to non-deposition or erosion. There are several types of unconformities that can form, such as angular unconformities, disconformities, and nonconformities. Unconformities are important as they provide information about periods of geologic activity, like folding or erosion of the land, and help place boundaries on geologic timescales. They can be identified in the field based on features like a lack of parallel bedding above and below the contact, presence of erosion surfaces, and fossils of widely different ages across the boundary.