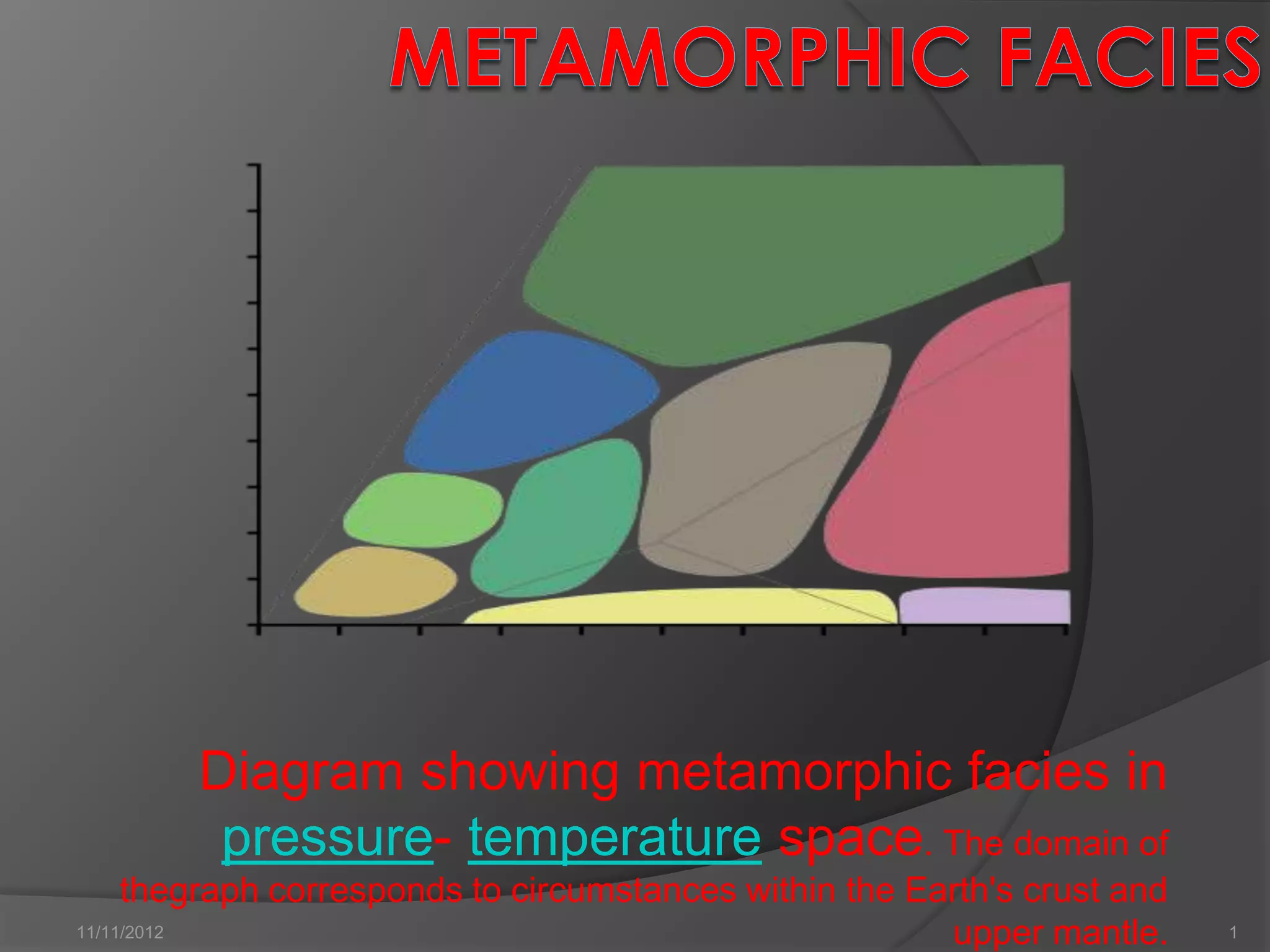
The document describes the different metamorphic facies defined by their mineral assemblages under varying pressure and temperature conditions within the Earth's crust and upper mantle. It outlines the key facies including zeolite, prehnite-pumpellyite, greenschist, amphibolite, granulite, blueschist, eclogite, albite-epidote hornfels, hornblende hornfels, pyroxene hornfels, and sanidinite facies. Each facies is characterized by index minerals and typical mineral assemblages that reflect the prevailing metamorphic conditions.